遗传算法原理与应用详解
一.进化论知识
作为遗传算法生物背景的介绍,下面内容了解即可:
种群(Population):生物的进化以群体的形式进行,这样的一个群体称为种群。
个体:组成种群的单个生物。
基因 ( Gene ) :一个遗传因子。
染色体 ( Chromosome ) :包含一组的基因。
生存竞争,适者生存:对环境适应度高的、牛B的个体参与繁殖的机会比较多,后代就会越来越多。适应度低的个体参与繁殖的机会比较少,后代就会越来越少。
遗传与变异:新个体会遗传父母双方各一部分的基因,同时有一定的概率发生基因变异。
简单说来就是:繁殖过程,会发生基因交叉( Crossover ) ,基因突变 ( Mutation ) ,适应度( Fitness )低的个体会被逐步淘汰,而适应度高的个体会越来越多。那么经过N代的自然选择后,保存下来的个体都是适应度很高的,其中很可能包含史上产生的适应度最高的那个个体。
二.遗传算法思想
借鉴生物进化论,遗传算法将要解决的问题模拟成一个生物进化的过程,通过复制、交叉、突变等操作产生下一代的解,并逐步淘汰掉适应度函数值低的解,增加适应度函数值高的解。这样进化N代后就很有可能会进化出适应度函数值很高的个体。
举个例子,使用遗传算法解决“0-1背包问题”的思路:0-1背包的解可以编码为一串0-1字符串(0:不取,1:取) ;首先,随机产生M个0-1字符串,然后评价这些0-1字符串作为0-1背包问题的解的优劣;然后,随机选择一些字符串通过交叉、突变等操作产生下一代的M个字符串,而且较优的解被选中的概率要比较高。这样经过G代的进化后就可能会产生出0-1背包问题的一个“近似最优解”。
编码:需要将问题的解编码成字符串的形式才能使用遗传算法。最简单的一种编码方式是二进制编码,即将问题的解编码成二进制位数组的形式。例如,问题的解是整数,那么可以将其编码成二进制位数组的形式。将0-1字符串作为0-1背包问题的解就属于二进制编码。
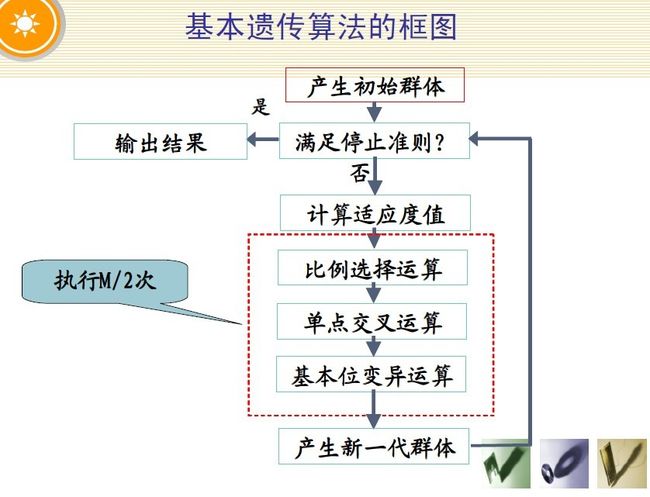
遗传算法有3个最基本的操作:选择,交叉,变异。
选择:选择一些染色体来产生下一代。一种常用的选择策略是 “比例选择”,也就是个体被选中的概率与其适应度函数值成正比。假设群体的个体总数是M,那么那么一个体Xi被选中的概率为f(Xi)/( f(X1) + f(X2) + …….. + f(Xn) ) 。比例选择实现算法就是所谓的“轮盘赌算法”( Roulette Wheel Selection ) ,轮盘赌算法的一个简单的实现如下:
轮盘赌算法
/*
* 按设定的概率,随机选中一个个体
* P[i]表示第i个个体被选中的概率
*/
int RWS()
{
m = 0;
r =Random(0,1); //r为0至1的随机数
for(i=1;i<=N; i++)
{
/* 产生的随机数在m~m+P[i]间则认为选中了i
* 因此i被选中的概率是P[i]
*/
m = m + P[i];
if(r<=m) return i;
}
}
交叉(Crossover):2条染色体交换部分基因,来构造下一代的2条新的染色体。例如:
交叉前:
00000|011100000000|10000
11100|000001111110|00101
交叉后:
00000|000001111110|10000
11100|011100000000|00101
染色体交叉是以一定的概率发生的,这个概率记为Pc 。
变异(Mutation):在繁殖过程,新产生的染色体中的基因会以一定的概率出错,称为变异。变异发生的概率记为Pm 。例如:
变异前:
000001110000000010000
变异后:
000001110000100010000
适应度函数 ( Fitness Function ):用于评价某个染色体的适应度,用f(x)表示。有时需要区分染色体的适应度函数与问题的目标函数。例如:0-1背包问题的目标函数是所取得物品价值,但将物品价值作为染色体的适应度函数可能并不一定适合。适应度函数与目标函数是正相关的,可对目标函数作一些变形来得到适应度函数。
三.基本遗传算法的代码
说明:求取x[1]^2-x[1]*x[2]+x[3]的最大值,工程下的gadata.txt里面每一行分别代表x[1]、x[2]和x[3]的范围,输出结果在工程下的galog.txt里面。初始种群规模、最大迭代次数、交叉概率、变异概率等详见代码。
/**************************************************************************/
/* This is a simple genetic algorithm implementation where the */
/* evaluation function takes positive values only and the */
/* fitness of an individual is the same as the value of the */
/* objective function */
/**************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
/* Change any of these parameters to match your needs */
#define POPSIZE 50 /* population size */
#define MAXGENS 1000 /* max. number of generations */
#define NVARS 3 /* no. of problem variables */ //gadata.txt中有3行数据,可以给定3组不同范围的数据
#define PXOVER 0.8 /* probability of crossover */
#define PMUTATION 0.15 /* probability of mutation */
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
int generation; /* current generation no. */
int cur_best; /* best individual */
FILE *galog; /* an output file */
struct genotype /* genotype (GT), a member of the population */
{
double gene[NVARS]; /* a string of variables */
double fitness; /* GT's fitness */
double upper[NVARS]; /* GT's variables upper bound */
double lower[NVARS]; /* GT's variables lower bound */
double rfitness; /* relative fitness */
double cfitness; /* cumulative fitness */
};
struct genotype population[POPSIZE+1]; /* population */
struct genotype newpopulation[POPSIZE+1]; /* new population; */
/* replaces the */
/* old generation */
/* Declaration of procedures used by this genetic algorithm */
void initialize(void);
double randval(double, double);
void evaluate(void);
void keep_the_best(void);
void elitist(void);
void select(void);
void crossover(void);
void Xover(int,int);
void swap(double *, double *);
void mutate(void);
void report(void);
/***************************************************************/
/* Initialization function: Initializes the values of genes */
/* within the variables bounds. It also initializes (to zero) */
/* all fitness values for each member of the population. It */
/* reads upper and lower bounds of each variable from the */
/* input file `gadata.txt'. It randomly generates values */
/* between these bounds for each gene of each genotype in the */
/* population. The format of the input file `gadata.txt' is */
/* var1_lower_bound var1_upper bound */
/* var2_lower_bound var2_upper bound ... */
/***************************************************************/
void initialize(void)
{
FILE *infile;
int i, j;
double lbound, ubound;
if ((infile = fopen("gadata.txt","r"))==NULL)
{
fprintf(galog,"\nCannot open input file!\n");
exit(1);
}
/* initialize variables within the bounds */
for (i = 0; i < NVARS; i++)
{
fscanf(infile, "%lf",&lbound);
fscanf(infile, "%lf",&ubound);
for (j = 0; j < POPSIZE; j++)
{
population[j].fitness = 0;
population[j].rfitness = 0;
population[j].cfitness = 0;
population[j].lower[i] = lbound;
population[j].upper[i]= ubound;
population[j].gene[i] = randval(population[j].lower[i],population[j].upper[i]);
}
}
fclose(infile);
}
/***********************************************************/
/* Random value generator: Generates a value within bounds */
/***********************************************************/
double randval(double low, double high)
{
double val;
val = ((double)(rand()%1000)/1000.0)*(high - low) + low;
return(val);
}
/*************************************************************/
/* Evaluation function: This takes a user defined function. */
/* Each time this is changed, the code has to be recompiled. */
/* The current function is: x[1]^2-x[1]*x[2]+x[3] */
/*************************************************************/
void evaluate(void)
{
int mem;
int i;
double x[NVARS+1];
for (mem = 0; mem < POPSIZE; mem++)
{
for (i = 0; i < NVARS; i++)
x[i+1] = population[mem].gene[i];
population[mem].fitness = (x[1]*x[1]) - (x[1]*x[2]) + x[3]; //利用自定义函数求适应度
}
}
/***************************************************************/
/* Keep_the_best function: This function keeps track of the */
/* best member of the population. Note that the last entry in */
/* the array Population holds a copy of the best individual */
/***************************************************************/
void keep_the_best()
{
int mem;
int i;
cur_best = 0; /* stores the index of the best individual */
for (mem = 0; mem < POPSIZE; mem++)
{
if (population[mem].fitness > population[POPSIZE].fitness)
{
cur_best = mem;
population[POPSIZE].fitness = population[mem].fitness; //population[50]存放最好的fitness
}
}
/* once the best member in the population is found, copy the genes */
for (i = 0; i < NVARS; i++)
population[POPSIZE].gene[i] = population[cur_best].gene[i]; //population[50]存放最好的gene
}
/****************************************************************/
/* Elitist function: The best member of the previous generation */
/* is stored as the last in the array. If the best member of */
/* the current generation is worse then the best member of the */
/* previous generation, the latter one would replace the worst */
/* member of the current population */
/****************************************************************/
void elitist()
{
int i;
double best, worst; /* best and worst fitness values */
int best_mem, worst_mem; /* indexes of the best and worst member */
best = population[0].fitness;
worst = population[0].fitness;
for (i = 0; i < POPSIZE - 1; ++i)
{
if(population[i].fitness > population[i+1].fitness)
{
if (population[i].fitness >= best)
{
best = population[i].fitness;
best_mem = i;
}
if (population[i+1].fitness <= worst)
{
worst = population[i+1].fitness;
worst_mem = i + 1;
}
}
else
{
if (population[i].fitness <= worst)
{
worst = population[i].fitness;
worst_mem = i;
}
if (population[i+1].fitness >= best)
{
best = population[i+1].fitness;
best_mem = i + 1;
}
}
}
/* if best individual from the new population is better than */
/* the best individual from the previous population, then */
/* copy the best from the new population; else replace the */
/* worst individual from the current population with the */
/* best one from the previous generation */
if (best >= population[POPSIZE].fitness)
{
for (i = 0; i < NVARS; i++)
population[POPSIZE].gene[i] = population[best_mem].gene[i];
population[POPSIZE].fitness = population[best_mem].fitness;
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < NVARS; i++)
population[worst_mem].gene[i] = population[POPSIZE].gene[i];
population[worst_mem].fitness = population[POPSIZE].fitness;
}
}
/**************************************************************/
/* Selection function: Standard proportional selection for */
/* maximization problems incorporating elitist model - makes */
/* sure that the best member survives */
/**************************************************************/
void select(void)
{
int mem, i,j;
double sum = 0;
double p;
/* find total fitness of the population */
for (mem = 0; mem < POPSIZE; mem++)
{
sum += population[mem].fitness;
}
/* calculate relative fitness */
for (mem = 0; mem < POPSIZE; mem++)
{
population[mem].rfitness = population[mem].fitness/sum; //计算相对fitness
}
/* calculate cumulative fitness */
population[0].cfitness = population[0].rfitness;
for (mem = 1; mem < POPSIZE; mem++)
{
population[mem].cfitness = population[mem-1].cfitness + population[mem].rfitness; //计算累计fitness
}
/* finally select survivors using cumulative fitness. */
for (i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
{
p = rand()%1000/1000.0;
if (p < population[0].cfitness)
newpopulation[i] = population[0];
else
{
for (j = 0; j < POPSIZE;j++)
if (p >= population[j].cfitness && p<population[j+1].cfitness)
newpopulation[i] = population[j+1];
}
}
/* once a new population is created, copy it back */
for (i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
population[i] = newpopulation[i];
}
/***************************************************************/
/* Crossover selection: selects two parents that take part in */
/* the crossover. Implements a single point crossover */
/***************************************************************/
void crossover(void)
{
int mem, one;
int first = 0; /* count of the number of members chosen */
double x;
for (mem = 0; mem < POPSIZE; ++mem)
{
x = rand()%1000/1000.0;
if (x < PXOVER)
{
++first;
if (first % 2 == 0)
Xover(one, mem);
else
one = mem;
}
}
}
/**************************************************************/
/* Crossover: performs crossover of the two selected parents. */
/**************************************************************/
void Xover(int one, int two)
{
int i;
int point; /* crossover point */
/* select crossover point */
if(NVARS > 1)
{
if(NVARS == 2)
point = 1;
else
point = (rand() % (NVARS - 1)) + 1;
for (i = 0; i < point; i++)
swap(&population[one].gene[i], &population[two].gene[i]);
}
}
/*************************************************************/
/* Swap: A swap procedure that helps in swapping 2 variables */
/*************************************************************/
void swap(double *x, double *y)
{
double temp;
temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
/**************************************************************/
/* Mutation: Random uniform mutation. A variable selected for */
/* mutation is replaced by a random value between lower and */
/* upper bounds of this variable */
/**************************************************************/
void mutate(void)
{
int i, j;
double lbound, hbound;
double x;
for (i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
for (j = 0; j < NVARS; j++)
{
x = rand()%1000/1000.0;
if (x < PMUTATION)
{
/* find the bounds on the variable to be mutated */
lbound = population[i].lower[j];
hbound = population[i].upper[j];
population[i].gene[j] = randval(lbound, hbound);
}
}
}
/***************************************************************/
/* Report function: Reports progress of the simulation. Data */
/* dumped into the output file are separated by commas */
/***************************************************************/
void report(void)
{
int i;
double best_val; /* best population fitness */
double avg; /* avg population fitness */
double stddev; /* std. deviation of population fitness */ //偏离、越轨
double sum_square; /* sum of square for std. calc */
double square_sum; /* square of sum for std. calc */
double sum; /* total population fitness */
sum = 0.0;
sum_square = 0.0;
for (i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
{
sum += population[i].fitness; //fitness之和
sum_square += population[i].fitness * population[i].fitness; //fitness的平方和
}
avg = sum/(double)POPSIZE;
square_sum = avg * avg * POPSIZE;
stddev = sqrt((sum_square - square_sum)/(POPSIZE - 1));
best_val = population[POPSIZE].fitness; //最大的fitness
fprintf(galog, "\n%5d, %6.3f, %6.3f, %6.3f \n\n", generation,
best_val, avg, stddev);
}
/**************************************************************/
/* Main function: Each generation involves selecting the best */
/* members, performing crossover & mutation and then */
/* evaluating the resulting population, until the terminating */
/* condition is satisfied */
/**************************************************************/
void main(void)
{
int i;
if ((galog = fopen("galog.txt","w"))==NULL)
{
exit(1);
}
generation = 0;
fprintf(galog, "\n generation best average standard \n");
fprintf(galog, " number value fitness deviation \n");
//前期三步曲
initialize();
evaluate();
keep_the_best();
//迭代筛选
while(generation<MAXGENS)
{
generation++;
select();
crossover();
mutate();
report(); //输出
evaluate(); //更新适应度
elitist();
}
fprintf(galog,"\n\n Simulation completed\n");
fprintf(galog,"\n Best member: \n");
for (i = 0; i < NVARS; i++)
{
fprintf (galog,"\n var(%d) = %3.3f",i,population[POPSIZE].gene[i]);
}
fprintf(galog,"\n\n Best fitness = %3.3f",population[POPSIZE].fitness);
fclose(galog);
printf("Success\n");
}
/***************************************************************/
四.基本遗传算法优化
精英主义选择:是基本遗传算法的一种优化。为了防止进化过程中产生的最优解被交叉和变异所破坏,可以将每一代中的最优解原封不动的复制到下一代中。
插入操作:可在3个基本操作的基础上增加一个插入操作。插入操作将染色体中的某个随机的片段移位到另一个随机的位置。