Linux内核中的PID散列表实例
开发平台:基于虚拟机的Ubuntu 11.04
内核源码:linux-2.6.38.8.tar.bz2
目标平台:ARM体系结构
参考文献:《深入Linux内核架构》
关于散列表的概念可以参考博文《散列表的基本概念及其运算》。
1、PID散列表
PID散列表是在系统启动过程中通过pidhash_init函数(被start_kernel函数所调用)所创建的。
PID散列表实际上就是一个像struct hlist_head pid_hash[i]这样的数组,其中i的大小由alloc_large_system_hash函数所确定,最大取值为4096,最小值为16。
/* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/pid.c */
void __init pidhash_init(void)
{
int i, pidhash_size;
pid_hash = alloc_large_system_hash("PID", sizeof(*pid_hash), 0, 18,
HASH_EARLY | HASH_SMALL,
&pidhash_shift, NULL, 4096);
pidhash_size = 1 << pidhash_shift;
for (i = 0; i < pidhash_size; i++)
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&pid_hash[i]);
}
其中的alloc_large_system_hash函数能够根据机器物理内存的大小灵活地分配散列表的存储空间,以及改变pidhash_shift变量的默认值(默认值为4),从而确定pid_hash数组的大小(pidhash_size)。
最后,pidhash_init函数通过宏INIT_HLIST_HEAD把pid_hash数组的每个元素(struct hlist_head类型的变量)都初始化为空指针。
alloc_large_system_hash函数的实现比较复杂,没有时间也没有必要去分析它的每个语句,可以通过其中的打印语句来查看系统中的PID散列表到底有多大。
/* linux-2.6.38.8/mm/page_alloc.c */ printk(KERN_INFO "%s hash table entries: %ld (order: %d, %lu bytes)\n", tablename, (1UL << log2qty), ilog2(size) - PAGE_SHIFT, size);
例如,在基于虚拟机的Ubuntu 11.04中,当它的物理内存为512MB时,PID散列表的表项为2048个;当把物理内存修改为1GB时,PID散列表的表项提升到最大值4096个。
//512MB物理内存 $ dmesg | grep "PID hash table entries" [ 0.000000] PID hash table entries: 2048 (order: 1, 8192 bytes) //1GB物理内存 $ dmesg | grep "PID hash table entries" [ 0.000000] PID hash table entries: 4096 (order: 2, 16384 bytes)
2、散列函数
PID散列表的散列函数为pid_hashfn,定义在linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/pid.c文件中。
#define pid_hashfn(nr, ns) \
hash_long((unsigned long)nr + (unsigned long)ns, pidhash_shift)
/* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/hash.h */
#define hash_long(val, bits) hash_32(val, bits)
#define GOLDEN_RATIO_PRIME_32 0x9e370001UL
static inline u32 hash_32(u32 val, unsigned int bits)
{
/* On some cpus multiply is faster, on others gcc will do shifts */
u32 hash = val * GOLDEN_RATIO_PRIME_32;
/* High bits are more random, so use them. */
return hash >> (32 - bits);
}
散列函数pid_hashfn先使关键字(nr和ns的和)乘以0x9e370001UL,然后取乘积的低pidhash_shift位(即bit[0]到bit[pidhash_shift-1])。例如,对于拥有2048个表项的PID散列表,散列函数pid_hashfn的返回值(取乘积的低11位)最终都会落在0到2047之间。
3、处理冲突
PID散列表采用链地址法来处理冲突。
4、PID散列表的运算函数
在介绍PID散列表的运算函数之前,先介绍一下相关的结构体。
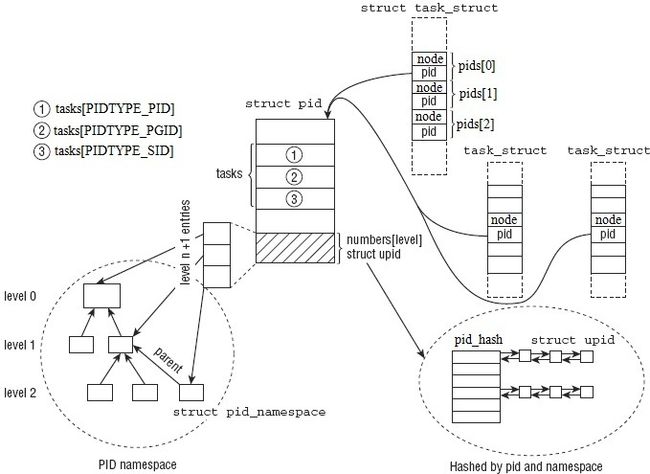
struct pid是内核对PID的内部表示,而struct upid则表示特定的命名空间中可见的信息。
/* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/pid.h */
enum pid_type
{
PIDTYPE_PID,
PIDTYPE_PGID,
PIDTYPE_SID,
PIDTYPE_MAX
};
struct upid {
/* Try to keep pid_chain in the same cacheline as nr for find_vpid */
int nr;
struct pid_namespace *ns;
struct hlist_node pid_chain;
};
struct pid
{
atomic_t count;
unsigned int level;
/* lists of tasks that use this pid */
struct hlist_head tasks[PIDTYPE_MAX];
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct upid numbers[1];
};
在struct upid中,nr表示ID(这里ID的类型有三种,定义在pid_type枚举中)的数值,ns是指向该ID所属命名空间的指针,所有的upid实例都通过pid_chain成员链接到pid_hash散列表中。
在struct pid中,count表示一个引用计数器,level表示该进程的命名空间在命名空间层次结构中的深度,而numbers是一个struct upid实例的数组,每个数组项(形式上只有一个数组项,但实际上可以根据需要进行扩展)都对应着一个命名空间。Tasks是共享此struct pid实例的所有进程的链表表头,其中的进程通过它的pids[type]成员来构建链接。在Linux内核中,通过attach_pid函数来建立它们之间的链接。
/* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/pid.h */
struct pid_link
{
struct hlist_node node;
struct pid *pid;
};
/* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/sched.h */
struct task_struct {
...
struct pid_link pids[PIDTYPE_MAX];
...
}
/* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/pid.c */
void attach_pid(struct task_struct *task, enum pid_type type,
struct pid *pid)
{
struct pid_link *link;
link = &task->pids[type];
link->pid = pid;
hlist_add_head_rcu(&link->node, &pid->tasks[type]);
}
以上所述各种结构体的关系如下图所示(图片修改自《professional linux kernel architecture》):
在Linux内核中,使用过散列函数pid_hashfn的只有alloc_pid和find_pid_ns两个函数而已。
(1)、插入运算
alloc_pid函数用于创建struct pid结构体实例。
/* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/pid.c */
struct pid *alloc_pid(struct pid_namespace *ns)
{
struct pid *pid;
enum pid_type type;
int i, nr;
struct pid_namespace *tmp;
struct upid *upid;
pid = kmem_cache_alloc(ns->pid_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pid)
goto out;
tmp = ns;
for (i = ns->level; i >= 0; i--) {
nr = alloc_pidmap(tmp);
if (nr < 0)
goto out_free;
pid->numbers[i].nr = nr;
pid->numbers[i].ns = tmp;
tmp = tmp->parent;
}
get_pid_ns(ns);
pid->level = ns->level;
atomic_set(&pid->count, 1);
for (type = 0; type < PIDTYPE_MAX; ++type)
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&pid->tasks[type]);
upid = pid->numbers + ns->level;
spin_lock_irq(&pidmap_lock);
for ( ; upid >= pid->numbers; --upid)
hlist_add_head_rcu(&upid->pid_chain,
&pid_hash[pid_hashfn(upid->nr, upid->ns)]);
spin_unlock_irq(&pidmap_lock);
out:
return pid;
out_free:
while (++i <= ns->level)
free_pidmap(pid->numbers + i);
kmem_cache_free(ns->pid_cachep, pid);
pid = NULL;
goto out;
}
起始于建立进程的命名空间,一直到初始的全局命名空间,内核会为其中的每个命名空间分别创建一个局部PID,并把它们(用struct upid表示)都添加到pid_hash散列表中。
(2)、查找运算
find_pid_ns函数根据PID和命名空间指针来查找相应的struct pid实例。
/* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/pid.c */
struct pid *find_pid_ns(int nr, struct pid_namespace *ns)
{
struct hlist_node *elem;
struct upid *pnr;
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(pnr, elem,
&pid_hash[pid_hashfn(nr, ns)], pid_chain)
if (pnr->nr == nr && pnr->ns == ns)
return container_of(pnr, struct pid,
numbers[ns->level]);
return NULL;
}
其中,首先使用散列函数pid_hashfn确定所查找结点在散列表pid_hash中的表头,然后遍历表头所指向的链表,当nr和ns都匹配时,即找到了所需的struct upid结点,最后根据struct upid结点通过container_of宏获得包含它的struct pid实例。