ICTCLAS分词系统研究(四)--初次切分
经过原子分词后,源字符串成了一个个独立的最小语素单位。下面的初次切分,就是把原子之间所有可能的组合都先找出来。算法是用两个循环来实现,第一层遍历整个原子单位,第二层是当找到一个原子时,不断把后面相邻的原子和该原子组合到一起,访问词典库看它能否构成一个有意义有词组。
用数学方法可以做如下描述:
有一个原子序列:A(n)(0<=n<m)(其中m为原子序列A的长度)。当I=n时,判断AnAn+1..Ap是否为一个词组,其中n<p<m.
用伪码表示:
for(int I=0;I<m;I++){
String s=A[I];
for(int j=I+1;j<m;j++){
s+=A[j];
if(s是一个词组){
把s加入到初次切分的列表中;
记录该词组的词性;
记录该词组所在表中的坐标位置及其它信息;
}
else
break;
}
}
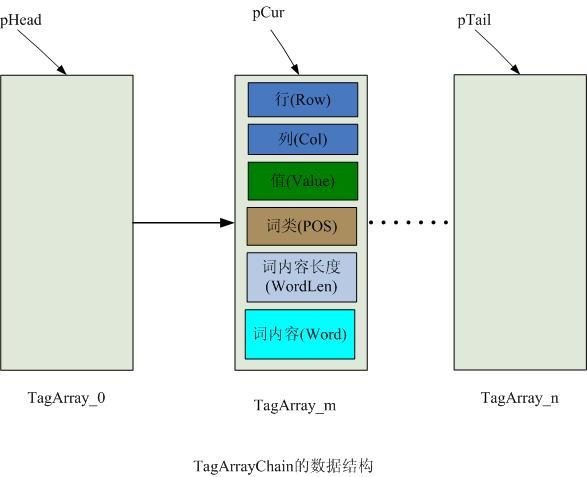
初次切分后的数据结构如下图一所示:
图一
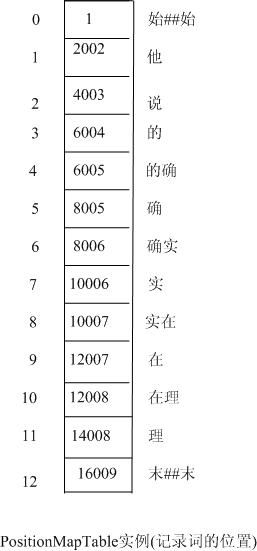
分词用例”他说的确实在理”经过初次切分后的结果如下图二所示:
图二
用二维表来表示图一中的链表结构如下图二所示:
图三
从上图三可以看出,在二维表中,初次切分后的词组,第一次字相同的在同一行,最后一个字相同的在同一列,原来的原子在对称轴上.
对上述过程进行处理的参考源代码如下:
bool CSegment::BiSegment(char *sSentence, double dSmoothingPara, CDictionary &dictCore, CDictionary &dictBinary, unsigned int nResultCount)
{
......
//在此处完成上图一的处理结果,生成一个链表结构
m_graphSeg.GenerateWordNet(sSentence,dictCore,true);//Generate words array
......
在生成图二所示的表结构之后,进一步生成二叉图表.
....
//Generate the biword link net
BiGraphGenerate(m_graphSeg.m_segGraph,aBiwordsNet,dSmoothingPara,dictBinary,dictCore);
....
对该函数进行深入分析:
bool CSegment::BiGraphGenerate(CDynamicArray &aWord, CDynamicArray &aBinaryWordNet,double dSmoothingPara,CDictionary &DictBinary,CDictionary &DictCore)
{
......
//获取链表的长度
m_nWordCount=aWord.GetTail(&pTail);//Get tail element and return the words count
if(m_npWordPosMapTable)
{//free buffer
delete [] m_npWordPosMapTable;
m_npWordPosMapTable=0;
}
//分配一个数组,存贮图二中每个结点的词的位置,如下图四所示
if(m_nWordCount>0)//Word count is greater than 0
m_npWordPosMapTable=new int[m_nWordCount];//Record the position of possible words
//把指针指向当前链表的开头,并计算每个词的位置,然后把它放到数组中
pCur=aWord.GetHead();
while(pCur!=NULL)//Set the position map of words
{
m_npWordPosMapTable[nWordIndex++]=pCur->row*MAX_SENTENCE_LEN+pCur->col;
pCur=pCur->next;
}
//遍历所有的结点,并计算相临两个词之间的平滑值
pCur=aWord.GetHead();
while(pCur!=NULL)//
{
if(pCur->nPOS>=0)//It's not an unknown words
dCurFreqency=pCur->value;
else//Unknown words
dCurFreqency=DictCore.GetFrequency(pCur->sWord,2);
//取得和当前结点列值(col)相同的下个结点
aWord.GetElement(pCur->col,-1,pCur,&pNextWords);
while(pNextWords&&pNextWords->row==pCur->col)//Next words
{
//前后两个词用@分隔符连接起来
strcpy(sTwoWords,pCur->sWord);
strcat(sTwoWords,WORD_SEGMENTER);
strcat(sTwoWords,pNextWords->sWord);
//计算两个连接词的边长
nTwoWordsFreq=DictBinary.GetFrequency(sTwoWords,3);
//Two linked Words frequency
dTemp=(double)1/MAX_FREQUENCE;
//计算平滑值
dValue=-log(dSmoothingPara*(1+dCurFreqency)/(MAX_FREQUENCE+80000)+(1-dSmoothingPara)*((1-dTemp)*nTwoWordsFreq/(1+dCurFreqency)+dTemp));
//-log{a*P(Ci-1)+(1-a)P(Ci|Ci-1)} Note 0<a<1
if(pCur->nPOS<0)//Unknown words: P(Wi|Ci);while known words:1
dValue+=pCur->value;
//Get the position index of current word in the position map table
nCurWordIndex=BinarySearch(pCur->row*MAX_SENTENCE_LEN+pCur->col,m_npWordPosMapTable,m_nWordCount);
nNextWordIndex=BinarySearch(pNextWords->row*MAX_SENTENCE_LEN+pNextWords->col,m_npWordPosMapTable,m_nWordCount);
//把当前结点在位置表中的位置和下个结点在位置表中的位置及平滑值/词性插入到二叉链表中
aBinaryWordNet.SetElement(nCurWordIndex,nNextWordIndex,dValue,pCur->nPOS);
pNextWords=pNextWords->next;//Get next word
}
pCur=pCur->next;
}
return true;
}
图四
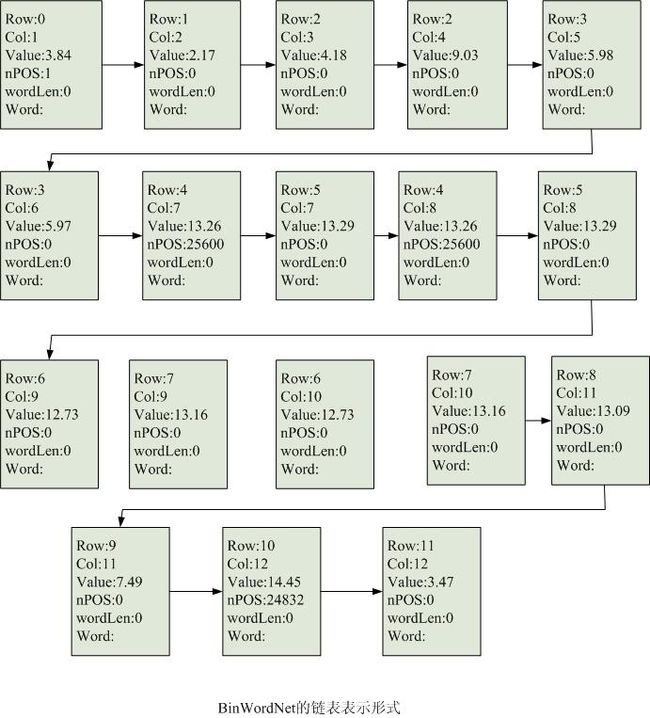
最终生成的键表结果如下图五所示:
图五
对应的二维图表表示形式如下图六所示:
图六
其中小数值代表了相临两个词之间的耦合成度,即构成更大长度词的可能性的机率,值越小说明两个词独立成词的可能性越大。