【学习记录】简单线程池的实现
此文记录学习线程池并创建一个简单实现的过程
所有代码已经过编译,编译环境ubuntu12.04LTS GCC 4.6.3
————————————2014.4.4—————————————
先看下资料
文章《linux c线程池简单实现_kankan231》中代码质量还不错,调理比较清晰并且备注较好,但是没有头文件= =...决定将这个文章作为主要资料看,把代码打印了出来方便上课看。
另一篇文章《一个Linux下C线程池的实现_XscKernel》写的也很不错,其中的头文件包含和运行时参数都比较完善,作为第二份资料参考。
————————————2014.4.17—————————————
前些日子在忙别的东西,没有顾上把线程池的内容整理上来,昨天把线程池debug基本完毕了,今天整理下把这篇写完。
写在前面的几行废话:
线程池的作用与原理
线程池的主要作用:当出现需要频繁创建和销毁线程,但主题任务时间很短的时候,我们就需要一个线程池了。这种情景常见于web服务器端。
那么线程池的工作原理就是提前创建一部分线程,并让它们在空闲时堵塞(堵塞时不占用cpu资源,仅占用极少的内存),当有任务出现时,唤醒线程并提取任务进行工作,工作完毕后,不销毁而是进入堵塞。
使用的POSIX函数
之后来看一下调用到的POSIX函数。
POSIX线程函数包含在头文件
<pthread.h>中,gcc对包含该头文件的代码进行编译时,后缀要加
-lpthread,否则会报函数未定义。
pthread_create函数
函数pthread_create是类Unix操作系统的创建线程的函数。
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread,
const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine) (void *),
void *arg
);
该函数含有四个参数。
第一个:存储线程的线程号;
第二个:用来设置线程的属性(常为NULL);
第三个:传递线程的入口函数;
第四个:传递给第三个参数函数的参数。
返回值:若线程创建成功,则返回0。若线程创建失败,则返回出错编号。
pthread_join函数
函数pthread_join用来等待一个线程的结束。
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
该函数的两个参数:
第一个:等待结束的线程号;
第二个:用户定义的指针,用来存储被等待线程的返回值(一般设NULL)。
返回值: 0代表成功。 失败,返回的则是错误号。
互斥锁函数
pthread_mutex_init函数:初始化互斥锁。
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr); //第二个参数常设为空
pthread_mutex_lock函数:对互斥锁加锁。
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
pthread_mutex_unlock函数:对互斥锁解锁。
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
pthread_mutex_destroy函数:销毁互斥锁。
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
第二个:用户定义的指针,用来存储被等待线程的返回值(一般设NULL)。
返回值: 0代表成功。 失败,返回的则是错误号。
条件变量函数
条件变量是利用线程间共享的全局变量进行同步的一种机制,主要包括两个动作:一个线程等待"条件变量的条件成立"而挂起;另一个线程使"条件成立"(给出条件成立信号)。为了防止竞争,条件变量的使用总是和一个互斥锁结合在一起。
pthread_cond_init函数:初始化条件变量。
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond, const pthread_condattr_t *cond_attr);//第二个变量常设为空
pthread_cond_wait函数:使该线程进入等待,直到收到pthread_cond_signal函数发送对应的条件变量。
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond);
pthread_cond_signal函数:发送条件变量给另外一个正在处于阻塞等待状态的线程(pthread_cond_wait导致该状态),使其脱离阻塞状态,继续执行
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
pthread_cond_destroy函数:销毁条件变量。
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
线程池的结构
任务队列结构体
/*任务队列元素*/
struct job
{
void * (*callback_function)(void *arg); //线程回调函数
void * arg; //回调函数参数
struct job * next;
};
线程池结构体
/*进程池结构体*/
struct threadpool
{
int thread_num; //线程池中开启的线程数
struct job *head; //指向job的头指针,任务队列的头
struct job *tail; //指向job的尾指针,任务队列的尾
pthread_t *pthreads; //线程池中所有线程的pthread_t存储空间头地址
pthread_mutex_t mutex; //互斥锁
pthread_cond_t queue_empty; //队列为空的条件变量
pthread_cond_t queue_not_empty; //队列非空的条件变量
pthread_cond_t queue_not_full; //队列非满的条件变量
int queue_max_num; //任务队列的最大长度
int queue_cur_num; //任务队列的当前长度
int queue_close; //任务队列是否关闭 0:开启;1:关闭
int pool_close; //线程池是否关闭 0:开启;1:关闭
};
线程池创建函数
struct threadpool * threadpool_init(int thread_num, int queue_max_num);
任务添加函数
任务添加函数
int
threadpool_add_job(struct threadpool * pool, void * (*callback_function)(void * arg), void * arg);
工作线程入口函数
void * threadpool_function(void * pool_arg);
线程池销毁函数
int threadpool_destroy(struct threadpool * pool);
线程池完整代码
好吧最后,贴上我的进程池代码
主要参考《 linux c线程池简单实现_kankan231》一文,有部分代码经过调整。整体代码经gcc编译,运行通过。
函数代码
/* * Author: [email protected] * * Created Time: 2014年04月13日 星期日 14时02分25秒 * * FileName: Threads_Pool.c * * Description: 编译时加后缀: -lpthread * */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <assert.h> /*任务队列元素*/ struct job { void * (*callback_function)(void *arg); //线程回调函数 void * arg; //回调函数参数 struct job * next; }; /*进程池结构体*/ struct threadpool { int thread_num; //线程池中开启的线程数 struct job *head; //指向job的头指针,任务队列的头 struct job *tail; //指向job的尾指针,任务队列的尾 pthread_t *pthreads; //线程池中所有线程的pthread_t存储空间头地址 pthread_mutex_t mutex; //互斥锁 pthread_cond_t queue_empty; //队列为空的条件变量 pthread_cond_t queue_not_empty; //队列非空的条件变量 pthread_cond_t queue_not_full; //队列非满的条件变量 int queue_max_num; //任务队列的最大长度 int queue_cur_num; //任务队列的当前长度 int queue_close; //任务队列是否关闭 0:开启;1:关闭 int pool_close; //线程池是否关闭 0:开启;1:关闭 }; struct threadpool * threadpool_init(int thread_num, int queue_max_num); int threadpool_add_job(struct threadpool * pool, void * (*callback_function)(void * arg), void * arg); int threadpool_destroy(struct threadpool * pool); void * threadpool_function(void * pool_arg); struct threadpool * threadpool_init(int thread_num, int queue_max_num) { struct threadpool * pool= NULL; do//循环的目的只是为了初始化时,若任意if初始化失败,直接跳过下面的初始化 { /*申请线程池空间*/ pool = malloc(sizeof(struct threadpool)); if(NULL == pool) { printf("Failed to malloc threadpool!\n"); break; } /*初始化线程池参数*/ pool->thread_num = thread_num; pool->queue_max_num = queue_max_num; pool->queue_cur_num = 0; pool->head = NULL; pool->tail = NULL; /*初始化条件变量*/ if( pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->mutex), NULL) ) { printf("Failed to init mutex!\n"); break; } if( pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_empty), NULL) ) { printf("Failed to init queue_empty!\n"); break; } if( pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_not_empty), NULL) ) { printf("Failed to init queue_not_empty!\n"); break; } if( pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_not_full), NULL) ) { printf("Failed to init queue_not_full!\n"); break; } /*开辟存储所有线程的pthread_t的空间*/ pool->pthreads = malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * thread_num); if(NULL == pool->pthreads) { printf("Failed to malloc pthreads!\n"); break; } /*初始化任务队列信号量为开启,线程池信号量为开启*/ pool->queue_close = 0; pool->pool_close = 0; /*初始化所有线程*/ int i; for(i = 0; i < pool->thread_num; i++) { pthread_create(&(pool->pthreads[i]), NULL, threadpool_function, (void *)pool); } return pool; }while(0); return NULL; } /*将任务添加到任务队列中的函数*/ int threadpool_add_job(struct threadpool *pool, void * (*callback_function)(void * arg), void * arg) { assert(NULL != pool); assert(NULL != callback_function); assert(NULL != arg); pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex));//对线程加锁 //如果任务队列已满,将进程阻塞直到任务队列非满 while((pool->queue_cur_num == pool->queue_max_num) && !(pool->queue_close || pool->pool_close)) { pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_not_full),&(pool->mutex)); } if(pool->queue_close || pool->pool_close)//任务队列关闭或线程池关闭,则退出 { pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex)); return -1; } //开辟一个新任务空间pjob存储当前任务 struct job * pjob = (struct job *)malloc(sizeof(struct job)); if(NULL == pjob) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex)); return -1; } //将任务存储到新的任务空间pjob pjob->callback_function = callback_function; pjob->arg = arg; pjob->next = NULL; //将任务插到任务队列 if(NULL == pool->head) { pool->head = pool->tail = pjob; pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_empty)); //队列为空时,当有任务到来,则通知线程池中的线程:队列非空 } else { pool->tail->next = pjob; pool->tail = pjob; } pool->queue_cur_num++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex)); return 0; } /*线程工作入口函数*/ void * threadpool_function(void * pool_arg) { struct threadpool * pool = (struct threadpool *)pool_arg; //获取线程池地址 struct job *pjob = NULL; //初始化为NULL,后面会用到 while(1)//循环从任务队列中提取任务 { pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex)); //任务队列为空时,线程等待队列非空 while((pool->queue_cur_num == 0) && !pool->pool_close) { pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_not_empty),&(pool->mutex)); } //如果线程池被关闭,线程退出 if(pool->pool_close) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex)); pthread_exit(NULL); } //取出一个任务,任务队列长度-1 pool->queue_cur_num--; pjob = pool->head; //若取出任务后任务队列长度为空,将head = tail = NULL if(pool->queue_cur_num == 0) { pool->head = pool->tail = NULL; } //若不为空,头结点指向队列中的下一个任务 else { pool->head = pjob->next; } //threadpool_destory函数执行时,只有队列非空才可以执行销毁线程函数 if(pool->queue_cur_num == 0) { pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_empty)); } //如果队列非满,通知threadpool_add_job函数添加新任务 if(pool->queue_cur_num == pool->queue_max_num - 1) { pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_full)); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex)); //线程真正要做的:调用回调函数,进入工作 (*(pjob->callback_function))(pjob->arg); free(pjob);//执行完毕,销毁该任务 pjob = NULL; } } /*销毁线程池函数*/ int threadpool_destroy(struct threadpool * pool) { assert(pool != NULL); pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex)); if(pool->queue_close || pool->pool_close)//线程池已经退出了,则直接返回 { pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex)); return -1; } /*关闭任务队列*/ pool->queue_close = 1; while(pool->queue_cur_num != 0) { //等待队列为空 pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_empty),&(pool->mutex)); } /*关闭线程池*/ pool->pool_close = 1; pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex)); pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_empty));//唤醒所有正在阻塞的线程 pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_full));//唤醒添加任务的threadpool_add_job函数 int i; for(i = 0; i < pool->thread_num; i++) { pthread_join(pool->pthreads[i], NULL);//等待线程池的所有线程执行完毕 } pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->mutex)); pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->queue_empty)); pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->queue_not_empty)); pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->queue_not_full)); free(pool->pthreads); pool->pthreads = NULL; struct job *tmp; while(pool->head != NULL) { tmp = pool->head; pool->head = tmp->next; free(tmp); } free(pool); pool = NULL; return 0; }
work函数和main函数代码
void * work(void * arg)
{
char *work_str = (char *)arg;
printf("threadpool %ld callback function: %s.\n",pthread_self(),work_str);
sleep(1);
}
int main(void)
{
struct threadpool * pool = threadpool_init(10,20);
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "1");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "2");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "3");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "4");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "5");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "6");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "7");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "8");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "9");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "10");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "11");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "12");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "13");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "14");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "15");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "16");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "17");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "18");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "19");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "20");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "21");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "22");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "23");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "24");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "25");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "26");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "27");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "28");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "29");
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, "30");
//可以添加更多任务,如果你想的话
sleep(4);
threadpool_destroy(pool);
return 0;
}
遇到的问题
当把work()及main()函数中threadpool_add_job()传递的最后一个参数改为int时,int main(void)
{
struct threadpool * pool = threadpool_init(10,20);
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 40; i++)
{
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, &i);
}
//可以添加更多任务,如果你想的话
sleep(4);
threadpool_destroy(pool);
return 0;
}
打印数字出现异常:【21,25,25,25,25,27,29,30,......,40,40,40,40,40,...,40】。
原因:存储的i变量的数据是变化的(1-40);当线程提取任务时,i的数值已经发生了变化。
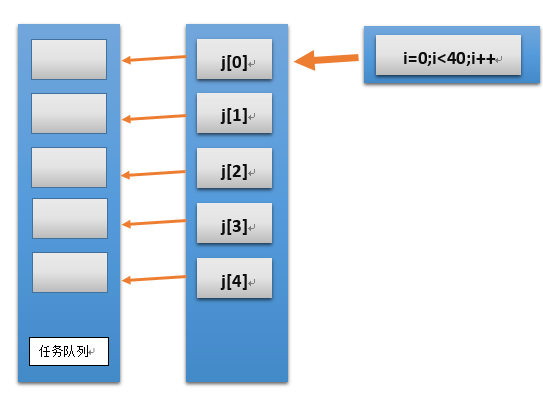
原理图:
解决办法
将
main()
函数中代码添加一个j[40]保存i的数字即可。
如图
修改后代码:
int main(void)
{
struct threadpool * pool = threadpool_init(10,20);
int i;
int *j = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * 40);
for(i = 0; i < 40; i++)
{
j[i] = i;
threadpool_add_job(pool, work, &j[i]);
}
//可以添加更多任务,如果你想的话
sleep(4);
threadpool_destroy(pool);
return 0;
}
参考资料
linux c线程池简单实现_kankan231
一个Linux下C线程池的实现_XscKernel