【Android界面实现】自定义滑动开关控件的实现与使用
在IPhone中,滑动开关控件非常常见,而且效果也非常好,但是在Android平台下,却没有自带的这种控件,只有功能类似的ToggleButton控件。本篇文章主要介绍自定义的滑动开关控件的实现与使用。在实现的过程中,也参考了其他类似自定义控件的实现,同时对代码进行了优化。
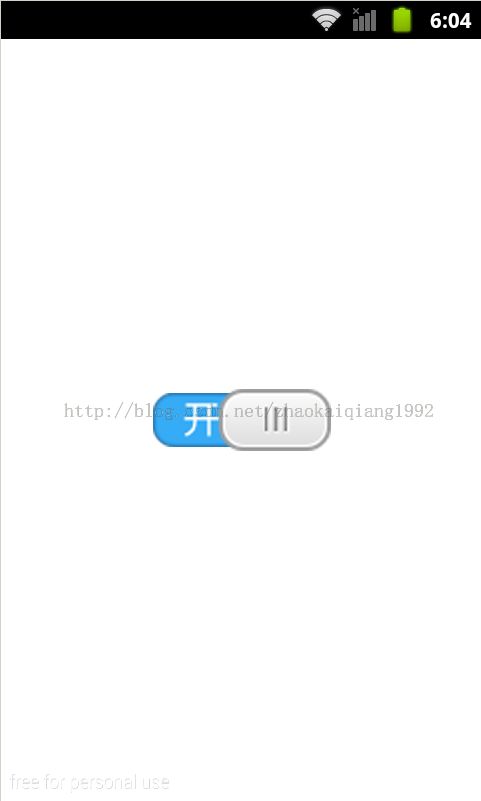
首先看实现的效果图
下面讲解这个自定义控件如何实现
/**
* 滑动控件
*
* @Time 2014-6-17 下午2:35:17
*/
public class SlipSwitch extends View implements OnTouchListener {
// 开关开启时的背景,关闭时的背景,滑动按钮
private Bitmap switch_on_bg, switch_off_bg, slip_Btn;
// 是否正在滑动
private boolean isSlipping = false;
// 当前开关状态,true为开启,false为关闭
private boolean isSwitchOn = false;
// 手指按下时的水平坐标X,当前的水平坐标X
private float previousX, currentX;
// 开关监听器
private OnSwitchListener onSwitchListener;
// 是否设置了开关监听器
private boolean isSwitchListenerOn = false;
// 矩阵
private Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
// 画笔
private Paint paint = new Paint();
// 滑动按钮的左边坐标
private float left_SlipBtn;
// 松开前开关的状态
private boolean previousSwitchState;
public SlipSwitch(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public SlipSwitch(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
//初始化
protected void init() {
setOnTouchListener(this);
setSwitchState(true);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
// 手指滑动到左半边的时候表示开关为关闭状态,滑动到右半边的时候表示开关为开启状态
if (currentX < (switch_on_bg.getWidth() / 2)) {
canvas.drawBitmap(switch_off_bg, matrix, paint);
} else {
canvas.drawBitmap(switch_on_bg, matrix, paint);
}
// 判断当前是否正在滑动
if (isSlipping) {
if (currentX > switch_on_bg.getWidth()) {
left_SlipBtn = switch_on_bg.getWidth() - slip_Btn.getWidth();
} else {
left_SlipBtn = currentX - slip_Btn.getWidth() / 2;
}
} else {
// 根据当前的开关状态设置滑动按钮的位置
if (isSwitchOn) {
left_SlipBtn = switch_off_bg.getWidth();
} else {
left_SlipBtn = 0;
}
}
// 对滑动按钮的位置进行异常判断
if (left_SlipBtn < 0) {
left_SlipBtn = 0;
} else if (left_SlipBtn > switch_on_bg.getWidth() - slip_Btn.getWidth()) {
left_SlipBtn = switch_on_bg.getWidth() - slip_Btn.getWidth();
}
canvas.drawBitmap(slip_Btn, left_SlipBtn, 0, paint);
}
// 告诉父控件,要占多大的空间
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(switch_on_bg.getWidth(), switch_on_bg.getHeight());
}
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
// 滑动
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
currentX = event.getX();
break;
// 按下
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
isSlipping = true;
previousX = event.getX();
currentX = previousX;
break;
// 松开
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
isSlipping = false;
previousSwitchState = isSwitchOn;
if (event.getX() >= (switch_on_bg.getWidth() / 2)) {
isSwitchOn = true;
} else {
isSwitchOn = false;
}
// 如果设置了监听器,则调用此方法
if (isSwitchListenerOn && (previousSwitchState != isSwitchOn)) {
onSwitchListener.onSwitched(isSwitchOn);
}
break;
}
// 重新绘制控件
invalidate();
return true;
}
protected void setImageResource(int switchOnBkg, int switchOffBkg,
int slipBtn) {
switch_on_bg = BitmapFactory
.decodeResource(getResources(), switchOnBkg);
switch_off_bg = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),
switchOffBkg);
slip_Btn = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), slipBtn);
}
protected void setSwitchState(boolean switchState) {
isSwitchOn = switchState;
}
protected boolean getSwitchState() {
return isSwitchOn;
}
protected void updateSwitchState(boolean switchState) {
isSwitchOn = switchState;
invalidate();
}
public void setOnSwitchListener(OnSwitchListener listener) {
onSwitchListener = listener;
isSwitchListenerOn = true;
}
// 监听器接口
public interface OnSwitchListener {
abstract void onSwitched(boolean isSwitchOn);
}
}
在这个实现过程中,有几个方法至关重要。
一个是onMeasure(),这个方法主要是告诉父控件,自定义控件要占多大的控件,我们把背景图片的宽高设置即可。
另外一个onDraw(),这个方法负责自定义界面的绘制,当手指按下、滑动、松开的时候,这个方法都需要对更改后的界面进行重新的绘制。
最后一个方法便是onTouch(),因为自定义控件实现了OnTouchListener接口,所以要重写这个方法。当手指在屏幕点击和滑动的时候,就会出发这个事件,我们需要根据用户操作的不同,对按下、放开、滑动等事件,进行不一样的处理。但是无论如何处理,在方法的最后,我们都要调用invalidate();方法,对界面进行刷新,我们可以看到这个方法的介绍
Invalidate the whole view. If the view is visible, onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas) will be called at some point in the future. This must be called from a UI thread. To call from a non-UI thread, call postInvalidate().
意思就是说,如果控件可见,我们在调用这个方法之后,系统会调用onDraw方法进行界面的刷新,而且这个方法必须在主线程调用,如果在非主线程想完成界面刷新的功能,我们可以调用postInvalidate()这个方法实现。
而且onTouch()的返回值为true,我们可以看一下这个方法的介绍
好了,通过这几个方法,我们就实现了一个简单的自定义的滑动开关控件,下面我们看一下如何使用这个自定义的控件。
布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="@android:color/white"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<edu.qust.SlipSwitch
android:id="@+id/main_myslipswitch"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
Activity中的代码
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private SlipSwitch slipswitch;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
slipswitch = (SlipSwitch) findViewById(R.id.main_myslipswitch);
slipswitch.setImageResource(R.drawable.bkg_switch,
R.drawable.bkg_switch, R.drawable.btn_slip);
slipswitch.setOnSwitchListener(new OnSwitchListener() {
@Override
public void onSwitched(boolean isSwitchOn) {
if (isSwitchOn) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "开关已经开启",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} else {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "开关已经关闭",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
});
}
}
使用非常简单,不过多介绍了
使用到的素材文件