SQL之存储过程
1:定义
存储过程(stored procedure)是一组为了完成特定功能的SQL语句集合,经编译后存储在服务器端的数据库中,利用存储过程可以加速SQL语句的执行。
存储过程分为系统存储过程和自定义存储过程。
*系统存储过程在master数据库中,但是在其他的数据库中可以直接调用,并且在调用时不必在存储过程前加上数据库名,因为在创建一个新数据库时,系统存储过程
在新的数据库中会自动创建
*自定义存储过程,由用户创建并能完成某一特定功能的存储过程,存储过程既可以有参数又有返回值,但是它与函数不同,存储过程的返回值只是指明执行是否成功,
并不能像函数那样被直接调用,只能利用execute来执行存储过程。
2:存储过程的优点
*提高应用程序的通用性和可移植性:存储过程创建后,可以在程序中被多次调用,而不必重新编写该存储过程的SQL语句。并且数据库专业人员可以随时对存储过程进行
修改,且对程序源代码没有影响,这样就极大的提高了程序的可移植性。
*可以更有效的管理用户操作数据库的权限:在Sql Server数据库中,系统管理员可以通过对执行某一存储过程的权限进行限制,从而实现对相应的数据访问进行控制,
避免非授权用户对数据库的访问,保证数据的安全。
*可以提高SQL的速度,存储过程是编译过的,如果某一个操作包含大量的SQL代码或分别被执行多次,那么使用存储过程比直接使用单条SQL语句执行速度快的多。
*减轻服务器的负担:当用户的操作是针对数据库对象的操作时,如果使用单条调用的方式,那么网络上还必须传输大量的SQL语句,如果使用存储过程,
则直接发送过程的调用命令即可,降低了网络的负担。
3:创建存储过程
SQL Server创建存储过程:
create procedure 过程名
@parameter 参数类型
@parameter 参数类型
。。。
as
begin
end
执行存储过程:execute 过程名
Oracle创建存储过程:
create procedure 过程名
parameter in|out|in out 参数类型
.......
parameter in|out|in out 参数类型
........
as
begin
命令行或者命令块
exception
命令行或者命令块
end
4:不带参数的存储过程
create procedure proc_sql1
as
begin
declare @i int
set @i=0
while @i<26
begin
print char(ascii('a') + @i) + '的ASCII码是: ' + cast(ascii('a') + @i as varchar(5))
set @i = @i + 1
end
end
exec proc_sql1;
a的ASCII码是: 97 b的ASCII码是: 98 c的ASCII码是: 99 d的ASCII码是: 100 e的ASCII码是: 101 f的ASCII码是: 102 g的ASCII码是: 103 h的ASCII码是: 104 i的ASCII码是: 105 j的ASCII码是: 106 k的ASCII码是: 107 l的ASCII码是: 108 m的ASCII码是: 109 n的ASCII码是: 110 o的ASCII码是: 111 p的ASCII码是: 112 q的ASCII码是: 113 r的ASCII码是: 114 s的ASCII码是: 115 t的ASCII码是: 116 u的ASCII码是: 117 v的ASCII码是: 118 w的ASCII码是: 119 x的ASCII码是: 120 y的ASCII码是: 121 z的ASCII码是: 122
5:数据查询功能的不带参数的存储过程
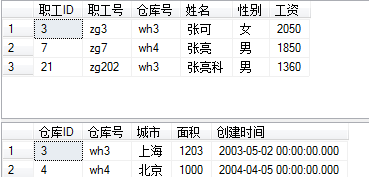
create procedure proc_sql2 as begin select * from 职工 where 工资>2000 end
execute proc_sql2
在存储过程中可以包含多个select语句,显示姓名中含有”张“字职工信息及其所在的仓库信息,
create procedure pro_sql5 as begin select * from 职工 where 姓名 like '%张%' select * from 仓库 where 仓库号 in(select 仓库号 from 职工 where 姓名 like '%张%') end go execute pro_sql5
6:带有输入参数的存储过程
找出三个数字中的最大数:
create proc proc_sql6
@num1 int,
@num2 int,
@num3 int
as
begin
declare @max int
if @num1>@num2
set @max = @num1
else set @max = @num2
if @num3 > @max
set @max = @num3
print '3个数中最大的数字是:' + cast(@max as varchar(20))
end
execute proc_sql6 15, 25, 35
3个数中最大的数字是:35
7:求阶乘之和 如6! + 5! + 4! + 3! + 2! + 1
alter proc proc_sql7
@dataSource int
as
begin
declare @sum int, @temp int, @tempSum int
set @sum = 0
set @temp = 1
set @tempSum = 1
while @temp <= @dataSource
begin
set @tempSum = @tempSum * @temp
set @sum = @sum + @tempSum
set @temp = @temp + 1
end
print cast(@dataSource as varchar(50)) + '的阶乘之和为:' + cast(@sum as varchar(50))
end
execute proc_sql7 6
6的阶乘之和为:873
8:带有输入参数的数据查询功能的存储过程
create proc proc_sql8 @mingz int, @maxgz int as begin select * from 职工 where 工资>@mingz and 工资<@maxgz end
execute proc_sql8 2000,5000
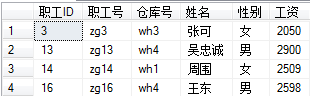
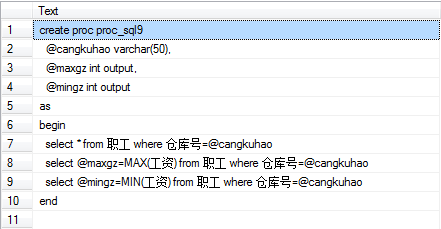
9:带输入和输出参数的存储过程:显示指定仓库号的职工信息和该仓库号的最大工资和最小工资
create proc proc_sql9 @cangkuhao varchar(50), @maxgz int output, @mingz int output as begin select * from 职工 where 仓库号=@cangkuhao select @maxgz=MAX(工资) from 职工 where 仓库号=@cangkuhao select @mingz=MIN(工资) from 职工 where 仓库号=@cangkuhao end
declare @maxgz int, @mingz int execute proc_sql9 'wh1', @maxgz output, @mingz output select @maxgz as 职工最大工资, @mingz as 职工最小工资
10:带有登录判断功能的存储过程
create proc proc_sql10
@hyuer varchar(50),
@hypwd varchar(50)
as
begin
if @hyuer = 'hystu1'
begin
if @hypwd = '1111'
print '用户名和密码输入正确'
else
print '密码输入错误'
end
else if @hyuer = 'hystu2'
begin
if @hypwd = '2222'
print '用户名和密码输入正确'
else
print '密码输入错误'
end
else if @hyuer = 'hystu3'
begin
if @hypwd = '3333'
print '用户名和密码输入正确'
else
print '密码输入错误'
end
else
print '您输入的用户名不正确,请重新输入'
end
execute proc_sql10 'hystu1', '11'
密码输入错误
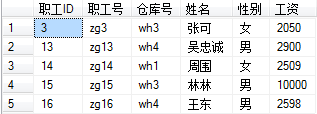
11:带有判断条件的插入功能的存储过程
create proc proc_sq111
@zghao varchar(30),
@ckhao varchar(30),
@sname varchar(50),
@sex varchar(10),
@gz int
as
begin
if Exists(select * from 职工 where 职工号=@zghao)
print '该职工已经存在,请重新输入'
else
begin
if Exists(select * from 仓库 where 仓库号=@ckhao)
begin
insert into 职工(职工号, 仓库号, 姓名, 性别, 工资)
values(@zghao, @ckhao, @sname, @sex, @gz)
end
else
print '您输入的仓库号不存在,请重新输入'
end
end
execute proc_sq111 'zg42', 'wh1', '张平', '女', 1350
12: 创建加密存储过程
create proc proc_enerypt with encryption as begin select * from 仓库 end
所谓加密存储过程,就是将create proc 语句的原始文本转换为模糊格式,模糊代码的输出在SQL Server的任何目录视图中都能直接显示
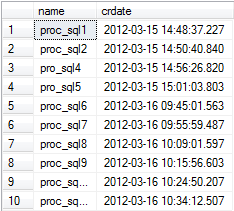
13: 查看存储过程和功能代码信息
select name, crdate from sysobjects where type='p'
查看指定存储过程的属性信息:
execute sp_help proc_sql1
查看存储过程所使用的数据对象的信息
execute sp_depends proc_sql2
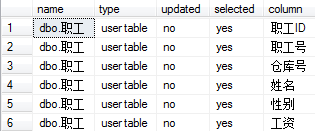
查看存储过程的功能代码
execute sp_helptext proc_sql9
14:重命名存储过程名
execute sp_rename 原存储过程名, 新存储过程名
15:删除存储过程
drop 过程名
带有判断条件的删除存储过程
if Exists(select * from dbo.sysobjects where name='proc_sql6' and xtype='p')
begin
print '要删除的存储过程存在'
drop proc proc_sq16
print '成功删除存储过程proc_sql6'
end
else
print '要删除的存储过程不存在'
16:存储过程的自动执行
使用sp_procoption系统存储过程即可自动执行一个或者多个存储过程,其语法格式如下:
sp_procoption [@procName=] 'procedure', [@optionName=] 'option', [@optionValue=] 'value'
各个参数含义如下:
[@procName=] 'procedure': 即自动执行的存储过程
[@optionName=] 'option':其值是startup,即自动执行存储过程
[@optionValue=] 'value':表示自动执行是开(true)或是关(false)
sp_procoption @procName='masterproc', @optionName='startup', @optionValue='true'
利用sp_procoption系统函数设置存储过程masterproc为自动执行
17:监控存储过程
可以使用sp_monitor可以查看SQL Server服务器的各项运行参数,其语法格式如下:
sp_monitor
该存储过程的返回值是布尔值,如果是0,表示成功,如果是1,表示失败。该存储过程的返回集的各项参数的含义如下:
*last_run: 上次运行时间
*current_run:本次运行的时间
*seconds: 自动执行存储过程后所经过的时间
*cpu_busy:计算机CPU处理该存储过程所使用的时间
*io_busy:在输入和输出操作上花费的时间
*idle:SQL Server已经空闲的时间
*packets_received:SQL Server读取的输入数据包数
*packets_sent:SQL Server写入的输出数据包数
*packets_error:SQL Server在写入和读取数据包时遇到的错误数
*total_read: SQL Server读取的次数
*total_write: SQLServer写入的次数
*total_errors: SQL Server在写入和读取时遇到的错误数
*connections:登录或尝试登录SQL Server的次数