linux powerpc i2c驱动 之 i2c adapter层的注册过程
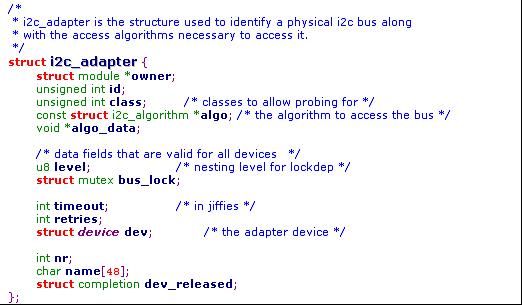
I2c的adapter层驱动,首先是其probe函数,adapter的结构体如下:
上面的结构体中其中algo实现i2c设备的读写操作函数
对于i2c_algorithm结构体,其中的functionality用来说明该算法所支持的i2c模式(有I2C_FUNC_I2C、I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR、I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BYTE、
I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA、I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WORD_DATA等模式,具体看i2c.h中的定义)
对于master_xfer是i2c的读写函数,主要是根据i2c的时序图实现i2c的读出与写入操作,而smbus_xfer则用来实现smbus的读写函数,有些adapter的algo只实现了i2c的读写函数,当支持smbus操作时,就会使用i2c的读写函数来模拟smbus操作。
(在i2c核心层,i2c的通用读写函数i2c_transfer、i2c_master_send就是通过调用adapter的algo来实现对不同cpu的i2c总线进行读写的,而用户只需调用i2c_transfer、i2c_master_send等函数就可以实现i2c/smbus的读写,而不必关心其底层是怎么实现的)
下面的结构体是用来注册总线adapter驱动的注册有关的,当进行platform驱动注册时,就会将具体的adapter设备与总线adapter驱动实现交互
在上面的结构体中,xx_i2c_of_match用于和adapter的设备id进行比较,以实现adapter驱动与adapter设备的比较。而xx_i2c_of_probe
则用来实现adapters的声明与注册以及i2c设备的发现与注册
在adapter的probe函数里,调用了iomap,该函数通过调用ioremap来实现地址映射,也就是将一个IO地址空间映射到内核的虚拟
地址空间中(因为在保护模式下,内核是不认物理地址的,当实现了地址映射后,就可以通过对虚拟地址的访问来实现对真正物理地
址的访问)。通过该函数就将i2c的基地址映射到内核虚拟地址了(可以查看具体cpu的datasheet获取i2c的物理基地址)
i2c_add_adapter 主要实现adapter的注册与添加,而
of_register_i2c_devices则实现了i2c client的发现与添加。
static int __devinit xx_i2c_of_probe(struct of_device *op,
const struct of_device_id *match)
{
struct xx_i2c_dev *i2c;
struct i2c_adapter *adap;
int result = 0;
u32 param1;
i2c = kzalloc(sizeof(*i2c), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!i2c)
return -ENOMEM;
i2c->dev = &op->dev; /* for debug and error output */
i2c->base = of_iomap(op->node, 0);
if (!i2c->base) {
dev_err(i2c->dev, "failed to map controller\n");
result = -ENOMEM;
goto fail_map;
}
i2c->irq = irq_of_parse_and_map(op->node, 0);
if (i2c->irq != NO_IRQ) { /* i2c->irq = NO_IRQ implies polling */
result = request_irq(i2c->irq, i2c_xx_isr,
0, "i2c-xx", i2c);
if (result < 0) {
dev_err(i2c->dev, "failed to attach interrupt\n");
goto fail_request;
}
}
i2c->write = writel;//master_xfer会调用这两个函数
i2c->read = readl;
init_completion(&i2c->cmd_complete);
mutex_init(&i2c->lock);
param1 = i2c->read(i2c->base + DW_IC_COMP_PARAM_1);
i2c->tx_fifo_depth = ((param1 >> 16) & 0xff) + 1;
i2c->rx_fifo_depth = ((param1 >> 8) & 0xff) + 1;
i2c_xx_init(i2c);
i2c->write(0,i2c->base + DW_IC_INTR_MASK); /* disable IRQ */
dev_set_drvdata(&op->dev, i2c);
adap = &i2c->adapter;
i2c_set_adapdata(adap, i2c);
adap->owner = THIS_MODULE;
adap->class = I2C_CLASS_HWMON;
strlcpy(adap->name, "Synopsys DesignWare I2C adapter",
sizeof(adap->name));
adap->algo = &i2c_xx_algo;
adap->dev.parent = &op->dev;
result = i2c_add_adapter(adap);
if (result) {
dev_err(i2c->dev, "failure adding adapter\n");
goto fail_add;
}
of_register_i2c_devices(adap, op->node);
return 0;
fail_add:
dev_set_drvdata(&op->dev, NULL);
//clk_disable(i2c->clk);
//clk_put(i2c->clk);
i2c->clk = NULL;
//fail_clk:
free_irq(i2c->irq, i2c);
fail_request:
irq_dispose_mapping(i2c->irq);
iounmap(i2c->base);
fail_map:
kfree(i2c);
return result;
}
在of_register_i2c_devices中,用到了一个重要的结构体:i2c_board_info,将会描述具体i2c设备的addr、type等(其中type为i2c client的id,这个值将会与i2c driver的id进行比较,若相同则说明i2c client与i2c driver是相同的,就会进行i2c client与i2c driver的对于)。下面是i2c_board_info的定义
struct i2c_board_info {
char type[I2C_NAME_SIZE];
unsigned short flags;
unsigned short addr;
void *platform_data;
struct dev_archdata *archdata;
int irq;
};
对于powerpc,其设备的物理地址是写在设备树dts中的。设备的寄存器基地址、中断号等信息都写在dts中,内核通过platform_get_resource等标准接口即可自动获取这些值,实现了驱动和资源的分离。(在系统启动阶段会解析DTB文件,将相关资源注册到Platform bus上,这样就可以通过platform_get_resource等进行访问。)
在of_register_i2c_devices里通过of_modalias_node与
of_get_property就可以获得i2c设备的type与addr了;接着会调用
i2c_new_device,添加新的i2c client
void of_register_i2c_devices(struct i2c_adapter *adap,
struct device_node *adap_node)
{
void *result;
struct device_node *node;
/*注册依附在该adapter上的所有 i2c client*/
for_each_child_of_node(adap_node, node)
{
struct i2c_board_info info = {};
struct dev_archdata dev_ad = {};
const u32 *addr;
int len;
/*获取i2c 设备的名称,并将名称赋值到
i2c_board_info的type*/
if (of_modalias_node(node, info.type, sizeof(info.type)) < 0)
continue;
/*获取i2c设备的地址*/
addr = of_get_property(node, "reg", &len);
if (!addr || len < sizeof(int) || *addr > (1 << 10) - 1) {
printk(KERN_ERR
"of-i2c: invalid i2c device entry\n");
continue;
}
info.irq = irq_of_parse_and_map(node, 0);
info.addr = *addr;
dev_archdata_set_node(&dev_ad, node);
info.archdata = &dev_ad;
request_module("%s", info.type);
result = i2c_new_device(adap, &info);
if (result == NULL) {
printk(KERN_ERR
"of-i2c: Failed to load driver for %s\n",
info.type);
irq_dispose_mapping(info.irq);
continue;
}
/*
* Get the node to not lose the dev_archdata->of_node.
* Currently there is no way to put it back, as well as no
* of_unregister_i2c_devices() call.
*/
of_node_get(node);
}
}
在i2c_new_device里,将会初始化一个i2c client。然后会调用device_register来注册一个i2c设备
struct i2c_client *
i2c_new_device(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_board_info const *info)
{
struct i2c_client *client;
int status;
client = kzalloc(sizeof *client, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!client)
return NULL;
client->adapter = adap;
client->dev.platform_data = info->platform_data;
if (info->archdata)
client->dev.archdata = *info->archdata;
client->flags = info->flags;
client->addr = info->addr;
client->irq = info->irq;
strlcpy(client->name, info->type, sizeof(client->name));
/* Check for address business */
status = i2c_check_addr(adap, client->addr);
if (status)
goto out_err;
client->dev.parent = &client->adapter->dev;
client->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type;//这句很重要i2c client将会注册在该总线上
client->dev.type = &i2c_client_type;
dev_set_name(&client->dev, "%d-%04x", i2c_adapter_id(adap),
client->addr);
status = device_register(&client->dev);
if (status)
goto out_err;
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "client [%s] registered with bus id %s\n",
client->name, dev_name(&client->dev));
return client;
out_err:
dev_err(&adap->dev, "Failed to register i2c client %s at 0x%02x "
"(%d)\n", client->name, client->addr, status);
kfree(client);
return NULL;
}
1、进行设备的初始化;2、调用device_add
int device_register(struct device *dev)
{
device_initialize(dev);
return device_add(dev);
}
在device_add里,将会调用device_add_class_symlinks、device_add_attrs、bus_add_device,其中在bus_add_device就会将i2c client注册到i2c总线上的列表上,与i2c driver驱动注册到i2c总线的驱动列表上相似
int device_add(struct device *dev)
{
struct device *parent = NULL;
struct class_interface *class_intf;
int error = -EINVAL;
dev = get_device(dev);
if (!dev)
goto done;
if (!dev->p) {
error = device_private_init(dev);
if (error)
goto done;
}
if (dev->init_name) {
dev_set_name(dev, "%s", dev->init_name);
dev->init_name = NULL;
}
if (!dev_name(dev))
goto name_error;
pr_debug("device: '%s': %s\n", dev_name(dev), __func__);
parent = get_device(dev->parent);
setup_parent(dev, parent);
/* use parent numa_node */
if (parent)
set_dev_node(dev, dev_to_node(parent));
/* first, register with generic layer. */
/* we require the name to be set before, and pass NULL */
error = kobject_add(&dev->kobj, dev->kobj.parent, NULL);
if (error)
goto Error;
/* notify platform of device entry */
if (platform_notify)
platform_notify(dev);
error = device_create_file(dev, &uevent_attr);
if (error)
goto attrError;
if (MAJOR(dev->devt)) {
error = device_create_file(dev, &devt_attr);
if (error)
goto ueventattrError;
error = device_create_sys_dev_entry(dev);
if (error)
goto devtattrError;
devtmpfs_create_node(dev);
}
error = device_add_class_symlinks(dev);
if (error)
goto SymlinkError;
error = device_add_attrs(dev);
if (error)
goto AttrsError;
error = bus_add_device(dev);//
if (error)
goto BusError;
error = dpm_sysfs_add(dev);
if (error)
goto DPMError;
device_pm_add(dev);
if (dev->bus)
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,
BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE, dev);
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
bus_probe_device(dev);
if (parent)
klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_parent,
&parent->p->klist_children);
if (dev->class) {
mutex_lock(&dev->class->p->class_mutex);
/* tie the class to the device */
klist_add_tail(&dev->knode_class,
&dev->class->p->class_devices);
/* notify any interfaces that the device is here */
list_for_each_entry(class_intf,
&dev->class->p->class_interfaces, node)
if (class_intf->add_dev)
class_intf->add_dev(dev, class_intf);
mutex_unlock(&dev->class->p->class_mutex);
}
done:
put_device(dev);
return error;
DPMError:
bus_remove_device(dev);
BusError:
device_remove_attrs(dev);
AttrsError:
device_remove_class_symlinks(dev);
SymlinkError:
if (MAJOR(dev->devt))
device_remove_sys_dev_entry(dev);
devtattrError:
if (MAJOR(dev->devt))
device_remove_file(dev, &devt_attr);
ueventattrError:
device_remove_file(dev, &uevent_attr);
attrError:
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_REMOVE);
kobject_del(&dev->kobj);
Error:
cleanup_device_parent(dev);
if (parent)
put_device(parent);
name_error:
kfree(dev->p);
dev->p = NULL;
goto done;
}
在该函数里, sysfs_create_link用来建立dev与bus之间的链接;然后调用
klist_add_tail,将device的dev->p->knode_bus添加到
bus->p->klist_devices,就实现将device添加到i2c 总线的device列表。这样,在i2c driver注册时,通过调用
bus_for_each_dev(i2c_register_driver-->driver_register
-->bus_add_driver-->driver_attach-->bus_for_each_dev),就会查找我们注册在bus->p->klist_devices上的每一个i2c设备,实现i2c总线上设备与驱动的对应。
int bus_add_device(struct device *dev)
{
struct bus_type *bus = bus_get(dev->bus);
int error = 0;
if (bus) {
pr_debug("bus: '%s': add device %s\n", bus->name, dev_name(dev));
error = device_add_attrs(bus, dev);
if (error)
goto out_put;
error = sysfs_create_link(&bus->p->devices_kset->kobj,
&dev->kobj, dev_name(dev));
if (error)
goto out_id;
error = sysfs_create_link(&dev->kobj,
&dev->bus->p->subsys.kobj, "subsystem");
if (error)
goto out_subsys;
error = make_deprecated_bus_links(dev);
if (error)
goto out_deprecated;
klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_bus, &bus->p->klist_devices);
}
return 0;
out_deprecated:
sysfs_remove_link(&dev->kobj, "subsystem");
out_subsys:
sysfs_remove_link(&bus->p->devices_kset->kobj, dev_name(dev));
out_id:
device_remove_attrs(bus, dev);
out_put:
bus_put(dev->bus);
return error;
}