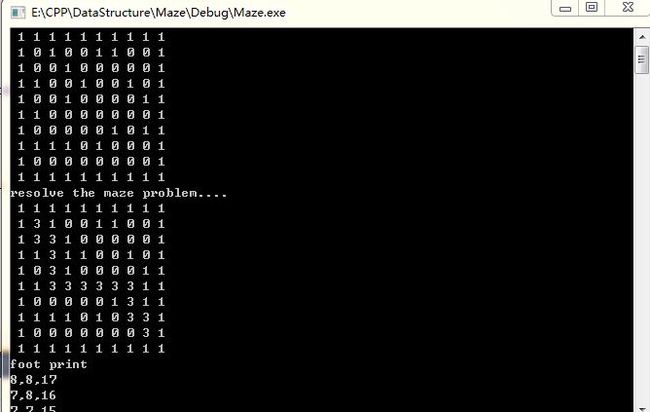
数据结构之迷宫求解 使用栈
// Maze.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
const int M=10;
const int N=10;
int maze[M][N]=
{
1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,
1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,
1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,
1,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,
1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,
1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,
1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,
1,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,
1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,
1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
}; // 定义迷宫
int next_xy[4][2]={{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}}; // 用于计算下一次搜索位置的计算量
typedef struct
{
int x;
int y;
}PosType; // 用于记录在迷宫中的位置
typedef struct
{
int ord;
PosType seat;
int di; // 记录方向
}SElemType; // 栈的元素类型
typedef struct node
{
SElemType data;
struct node *link;
}LinkedNode;
int Init(LinkedNode *&top);
int Push(LinkedNode *&top, SElemType e);
int Pop(LinkedNode *&top,SElemType &e);
int GetTop(LinkedNode *&top, SElemType &e);
int StackEmpty(LinkedNode *&top);
int Pass(PosType e);
int FootPrint(PosType e);
PosType NextPos(PosType &e,int di);
int MarkPrint(PosType e);
int MazePath(int MAZE[M][N],PosType start,PosType end,LinkedNode *&stack);
// 定义一个全局的栈
LinkedNode *stack;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
PosType start,end;
start.x=1;
start.y=1; // 起点
end.x=8;
end.y=8; // 终点
// 初始化栈
Init(stack);
// 打印当前迷宫
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
printf("%2d",maze[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("resolve the maze problem....\n");
MazePath(maze,start,end,stack); //调用迷宫求解函数
// 打印当前迷宫
for (int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
printf("%2d",maze[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("foot print\n");
SElemType e;
while(!StackEmpty(stack))
{
Pop(stack,e);
printf("%d,%d,%d",e.seat.x,e.seat.y,e.ord);
printf("\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
// 迷宫路径搜索,对全局栈的引用
int MazePath(int MAZE[M][N],PosType start,PosType end,LinkedNode *&stack)
{
//LinkedNode *stack;
//Init(stack); // 初始化栈
PosType currentPos;
SElemType e;
int curstep;
currentPos=start; // 开始位置
curstep=1;
do
{
if (Pass(currentPos)) // 如果当前结点可通,表示当前结点是第一次访问到
{
FootPrint(currentPos); //做访问标记
e.ord=curstep; // 搜索次数
e.seat.x=currentPos.x;
e.seat.y=currentPos.y; // 记录当前可通结点的情况
e.di=1; // 当前可通结点的访问方向为1,东南西北顺序访问
Push(stack,e); // 因为当前结点可通,所以将当前结点入栈,进一步判断当前结点的东南西北结点是否可通
// 同时,将当前结点入栈,防止下一步不可通的时候从当前结点获得下次可以访问的下个结点
if ((currentPos.x==end.x)&&(currentPos.y==end.y))
{
// 到了出口
return 1;
}
currentPos=NextPos(currentPos,1); // 当前点可通,访问当前点的第一个结点
curstep++; // 搜索次数加1
}
else
{
if (!StackEmpty(stack))
{
// 当前结点不可通,包括当前结点已经被修改了以后的情况
Pop(stack,e); // 回到上一个访问结点
while(e.di==4&&!StackEmpty(stack)) // 当前结点的所有下一步都访问过,且栈不为空,没有路可走,需要返回到上一步
{
MarkPrint(e.seat);
Pop(stack,e);
}
if (e.di<4)
{
// 还有其他的下一步没有访问到
e.di++;
Push(stack,e);
currentPos=NextPos(e.seat,e.di);
}
}
}
} while (!StackEmpty(stack)); // 栈不空,则继续寻找下一个可走的结点
return -1; // 当所有的栈元素出栈以后,栈为空,且没有返回找到的路径,那么说明已经没有其他的路可走,找不到通路
}
// 留下不能通过痕迹
int MarkPrint(PosType e)
{
int i,j;
i=e.x;
j=e.y;
maze[i][j]=1; //标记不能通过
return 1;
}
// 计算下一步的位置
PosType NextPos(PosType &e,int di)
{
e.x=e.x+next_xy[di-1][0];
e.y=e.y+next_xy[di-1][1];
return e;
}
// 判断当前点是否可通
int Pass(PosType e)
{
int i,j;
i=e.x;
j=e.y;
if(maze[i][j]==0)
{
// 0 表示当前路径可通
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int FootPrint(PosType e)
{
int i,j;
i=e.x;
j=e.y;
maze[i][j]=3; //进行已经访问过标记, 用3表示此点已经访问过
return 1;
}
int Init(LinkedNode *&top)
{
top=(LinkedNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkedNode));
if (!top)
{
return -1; // 初始化失败
}
top->link=NULL;
return 1;
}
int Push(LinkedNode *&top, SElemType e)
{
node *p=(LinkedNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkedNode));
if (!p)
{
return -1;
}
p->data=e;
p->link=top->link;
top->link=p; // 在链表的头部插入新的结点,入栈
return 1;
}
int Pop(LinkedNode *&top,SElemType &e)
{
if (top->link==NULL)
{
return -1;
}
e=top->link->data;
node *p=top->link;
top->link=top->link->link;
free(p);
return 1;
}
int GetTop(LinkedNode *&top, SElemType &e)
{
if (top->link==NULL)
{
return -1;
}
e=top->link->data;
return 1;
}
// 判断栈是否为空
int StackEmpty(LinkedNode *&top)
{
if (top->link==NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}