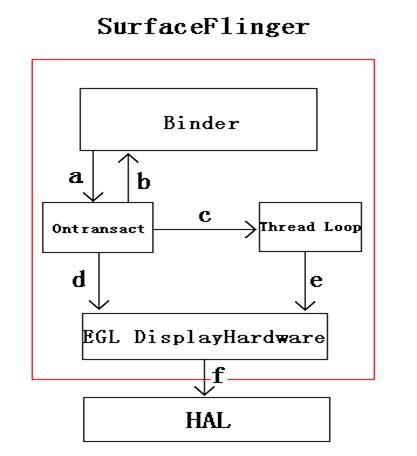
Surfaceflinger process流程分析
根据前面的介绍,surfaceflinger作为一个server process(其进程入口见main_surfaceflinger.cpp中的main函数),上层的应用程序(作为client)通过Binder方式与其进行通信。Surfaceflinger作为一个进程,这里把它分为3个部分,如下:
1、 Thread本身处理部分,包括初始化以及thread loop。
2、 Binder部分,负责接收上层应用的各个设置和命令,并反馈状态标志给上层。
3、 与底层的交互,负责调用底层接口(HAL)。
结构图如下:
注释:
a、 Binder接收到应用程序的命令(如创建surface、设置参数等),传递给flinger。
b、 Flinger完成对应命令后将相关结果状态反馈给上层。
c、 在处理上层命令过程中,根据需要设置event(主要和显示有关),通知Thread Loop进行处理。
d、 Flinger根据上层命令通知底层进行处理(主要是设置一些参数,Layer、position等)
e、 Thread Loop中进行surface的合成并通知底层进行显示(Post buffer)。
f、 DisplayHardware层根据flinger命令调用HAL进行HW的操作。
下面来具体分析一些SurfaceFlinger中重要的处理函数以及surface、Layer的属性
1. SurfaceFlinger::readyToRun
SurfaceFlinger thread的初始化函数,主要任务是分配内存和设置底层接口(EGL&HAL)。
- status_t SurfaceFlinger::readyToRun()
- {
- LOGI( "SurfaceFlinger's main thread ready to run. "
- "Initializing graphics H/W...");
- // we only support one display currently
- int dpy = 0;
- {
- // initialize the main display
- GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
- DisplayHardware* const hw = new DisplayHardware(this, dpy);
- plane.setDisplayHardware(hw);
- }
- // create the shared control-block
- mServerHeap = new MemoryHeapBase(4096,
- MemoryHeapBase::READ_ONLY, "SurfaceFlinger read-only heap");
- LOGE_IF(mServerHeap==0, "can't create shared memory dealer");
- mServerCblk = static_cast<surface_flinger_cblk_t*>(mServerHeap->getBase());
- LOGE_IF(mServerCblk==0, "can't get to shared control block's address");
- new(mServerCblk) surface_flinger_cblk_t;
- // initialize primary screen
- // (other display should be initialized in the same manner, but
- // asynchronously, as they could come and go. None of this is supported
- // yet).
- const GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
- const DisplayHardware& hw = plane.displayHardware();
- const uint32_t w = hw.getWidth();
- const uint32_t h = hw.getHeight();
- const uint32_t f = hw.getFormat();
- hw.makeCurrent();
- // initialize the shared control block
- mServerCblk->connected |= 1<<dpy;
- display_cblk_t* dcblk = mServerCblk->displays + dpy;
- memset(dcblk, 0, sizeof(display_cblk_t));
- dcblk->w = plane.getWidth();
- dcblk->h = plane.getHeight();
- dcblk->format = f;
- dcblk->orientation = ISurfaceComposer::eOrientationDefault;
- dcblk->xdpi = hw.getDpiX();
- dcblk->ydpi = hw.getDpiY();
- dcblk->fps = hw.getRefreshRate();
- dcblk->density = hw.getDensity();
- // Initialize OpenGL|ES
- glPixelStorei(GL_UNPACK_ALIGNMENT, 4);
- glPixelStorei(GL_PACK_ALIGNMENT, 4);
- glEnableClientState(GL_VERTEX_ARRAY);
- glEnable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
- glShadeModel(GL_FLAT);
- glDisable(GL_DITHER);
- glDisable(GL_CULL_FACE);
- const uint16_t g0 = pack565(0x0F,0x1F,0x0F);
- const uint16_t g1 = pack565(0x17,0x2f,0x17);
- const uint16_t wormholeTexData[4] = { g0, g1, g1, g0 };
- glGenTextures(1, &mWormholeTexName);
- glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, mWormholeTexName);
- glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
- glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
- glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
- glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
- glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, 2, 2, 0,
- GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT_5_6_5, wormholeTexData);
- const uint16_t protTexData[] = { pack565(0x03, 0x03, 0x03) };
- glGenTextures(1, &mProtectedTexName);
- glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, mProtectedTexName);
- glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
- glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
- glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
- glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
- glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, 1, 1, 0,
- GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT_5_6_5, protTexData);
- glViewport(0, 0, w, h);
- glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
- glLoadIdentity();
- // put the origin in the left-bottom corner
- glOrthof(0, w, 0, h, 0, 1); // l=0, r=w ; b=0, t=h
- mReadyToRunBarrier.open();
- /*
- * We're now ready to accept clients...
- */
- // start boot animation
- property_set("ctl.start", "bootanim");
- return NO_ERROR;
- }
status_t SurfaceFlinger::readyToRun()
{
LOGI( "SurfaceFlinger's main thread ready to run. "
"Initializing graphics H/W...");
// we only support one display currently
int dpy = 0;
{
// initialize the main display
GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
DisplayHardware* const hw = new DisplayHardware(this, dpy);
plane.setDisplayHardware(hw);
}
// create the shared control-block
mServerHeap = new MemoryHeapBase(4096,
MemoryHeapBase::READ_ONLY, "SurfaceFlinger read-only heap");
LOGE_IF(mServerHeap==0, "can't create shared memory dealer");
mServerCblk = static_cast<surface_flinger_cblk_t*>(mServerHeap->getBase());
LOGE_IF(mServerCblk==0, "can't get to shared control block's address");
new(mServerCblk) surface_flinger_cblk_t;
// initialize primary screen
// (other display should be initialized in the same manner, but
// asynchronously, as they could come and go. None of this is supported
// yet).
const GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
const DisplayHardware& hw = plane.displayHardware();
const uint32_t w = hw.getWidth();
const uint32_t h = hw.getHeight();
const uint32_t f = hw.getFormat();
hw.makeCurrent();
// initialize the shared control block
mServerCblk->connected |= 1<<dpy;
display_cblk_t* dcblk = mServerCblk->displays + dpy;
memset(dcblk, 0, sizeof(display_cblk_t));
dcblk->w = plane.getWidth();
dcblk->h = plane.getHeight();
dcblk->format = f;
dcblk->orientation = ISurfaceComposer::eOrientationDefault;
dcblk->xdpi = hw.getDpiX();
dcblk->ydpi = hw.getDpiY();
dcblk->fps = hw.getRefreshRate();
dcblk->density = hw.getDensity();
// Initialize OpenGL|ES
glPixelStorei(GL_UNPACK_ALIGNMENT, 4);
glPixelStorei(GL_PACK_ALIGNMENT, 4);
glEnableClientState(GL_VERTEX_ARRAY);
glEnable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
glShadeModel(GL_FLAT);
glDisable(GL_DITHER);
glDisable(GL_CULL_FACE);
const uint16_t g0 = pack565(0x0F,0x1F,0x0F);
const uint16_t g1 = pack565(0x17,0x2f,0x17);
const uint16_t wormholeTexData[4] = { g0, g1, g1, g0 };
glGenTextures(1, &mWormholeTexName);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, mWormholeTexName);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, 2, 2, 0,
GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT_5_6_5, wormholeTexData);
const uint16_t protTexData[] = { pack565(0x03, 0x03, 0x03) };
glGenTextures(1, &mProtectedTexName);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, mProtectedTexName);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, 1, 1, 0,
GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT_5_6_5, protTexData);
glViewport(0, 0, w, h);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
// put the origin in the left-bottom corner
glOrthof(0, w, 0, h, 0, 1); // l=0, r=w ; b=0, t=h
mReadyToRunBarrier.open();
/*
* We're now ready to accept clients...
*/
// start boot animation
property_set("ctl.start", "bootanim");
return NO_ERROR;
}
2. SurfaceFlinger::threadLoop
Surfaceflinger的loop函数,主要是等待其他接口发送的event,进行显示数据的合成以及显示。
- bool SurfaceFlinger::threadLoop()
- {
- waitForEvent(); //等待其他接口的signal event
- // post surfaces (if needed)
- handlePageFlip(); //处理翻页机制
- if (UNLIKELY(mHwWorkListDirty)) {
- // build the h/w work list
- handleWorkList();
- }
- const DisplayHardware& hw(graphicPlane(0).displayHardware());
- if (LIKELY(hw.canDraw())) {
- // repaint the framebuffer (if needed)
- const int index = hw.getCurrentBufferIndex();
- GraphicLog& logger(GraphicLog::getInstance());
- logger.log(GraphicLog::SF_REPAINT, index);
- handleRepaint(); //合并所有layer并填充到buffer中去
- // inform the h/w that we're done compositing
- logger.log(GraphicLog::SF_COMPOSITION_COMPLETE, index);
- hw.compositionComplete();
- logger.log(GraphicLog::SF_SWAP_BUFFERS, index);
- postFramebuffer(); //互换front buffer和back buffer,调用EGL接口进行显示
- logger.log(GraphicLog::SF_REPAINT_DONE, index);
- } else {
- // pretend we did the post
- hw.compositionComplete();
- usleep(16667); // 60 fps period,每秒刷新60次
- }
- return true;
- }
bool SurfaceFlinger::threadLoop()
{
waitForEvent(); //等待其他接口的signal event
// post surfaces (if needed)
handlePageFlip(); //处理翻页机制
if (UNLIKELY(mHwWorkListDirty)) {
// build the h/w work list
handleWorkList();
}
const DisplayHardware& hw(graphicPlane(0).displayHardware());
if (LIKELY(hw.canDraw())) {
// repaint the framebuffer (if needed)
const int index = hw.getCurrentBufferIndex();
GraphicLog& logger(GraphicLog::getInstance());
logger.log(GraphicLog::SF_REPAINT, index);
handleRepaint(); //合并所有layer并填充到buffer中去
// inform the h/w that we're done compositing
logger.log(GraphicLog::SF_COMPOSITION_COMPLETE, index);
hw.compositionComplete();
logger.log(GraphicLog::SF_SWAP_BUFFERS, index);
postFramebuffer(); //互换front buffer和back buffer,调用EGL接口进行显示
logger.log(GraphicLog::SF_REPAINT_DONE, index);
} else {
// pretend we did the post
hw.compositionComplete();
usleep(16667); // 60 fps period,每秒刷新60次
}
return true;
}
3. SurfaceFlinger::createSurface
提供给应用程序的主要接口,该接口可以创建一个surface,底层会根据参数创建layer以及分配内存(共2个buffer:front/back buffer),surface相关参数会反馈给上层。
- sp<ISurface> SurfaceFlinger::createSurface(
- ISurfaceComposerClient::surface_data_t* params,
- const String8& name,
- const sp<Client>& client,
- DisplayID d, uint32_t w, uint32_t h, PixelFormat format,
- uint32_t flags)
- {
- sp<LayerBaseClient> layer;
- sp<ISurface> surfaceHandle;
- if (int32_t(w|h) < 0) {
- LOGE("createSurface() failed, w or h is negative (w=%d, h=%d)",
- int(w), int(h));
- return surfaceHandle;
- }
- //LOGD("createSurface for pid %d (%d x %d)", pid, w, h);
- sp<Layer> normalLayer;
- //创建layer,根据参数(宽高格式)分配内存(共2个buffer:front/back buffer)
- switch (flags & eFXSurfaceMask) {
- case eFXSurfaceNormal:
- normalLayer = createNormalSurface(client, d, w, h, flags, format);
- layer = normalLayer;
- break;
- case eFXSurfaceBlur:
- // for now we treat Blur as Dim, until we can implement it
- // efficiently.
- case eFXSurfaceDim:
- layer = createDimSurface(client, d, w, h, flags);
- break;
- case eFXSurfaceScreenshot:
- layer = createScreenshotSurface(client, d, w, h, flags);
- break;
- }
- if (layer != 0) {
- layer->initStates(w, h, flags);
- layer->setName(name);
- ssize_t token = addClientLayer(client, layer);
- //创建surface
- surfaceHandle = layer->getSurface();
- if (surfaceHandle != 0) {
- params->token = token;
- params->identity = layer->getIdentity();
- if (normalLayer != 0) {
- Mutex::Autolock _l(mStateLock);
- mLayerMap.add(layer->getSurfaceBinder(), normalLayer);
- }
- }
- setTransactionFlags(eTransactionNeeded);
- }
- return surfaceHandle;
- }
sp<ISurface> SurfaceFlinger::createSurface(
ISurfaceComposerClient::surface_data_t* params,
const String8& name,
const sp<Client>& client,
DisplayID d, uint32_t w, uint32_t h, PixelFormat format,
uint32_t flags)
{
sp<LayerBaseClient> layer;
sp<ISurface> surfaceHandle;
if (int32_t(w|h) < 0) {
LOGE("createSurface() failed, w or h is negative (w=%d, h=%d)",
int(w), int(h));
return surfaceHandle;
}
//LOGD("createSurface for pid %d (%d x %d)", pid, w, h);
sp<Layer> normalLayer;
//创建layer,根据参数(宽高格式)分配内存(共2个buffer:front/back buffer)
switch (flags & eFXSurfaceMask) {
case eFXSurfaceNormal:
normalLayer = createNormalSurface(client, d, w, h, flags, format);
layer = normalLayer;
break;
case eFXSurfaceBlur:
// for now we treat Blur as Dim, until we can implement it
// efficiently.
case eFXSurfaceDim:
layer = createDimSurface(client, d, w, h, flags);
break;
case eFXSurfaceScreenshot:
layer = createScreenshotSurface(client, d, w, h, flags);
break;
}
if (layer != 0) {
layer->initStates(w, h, flags);
layer->setName(name);
ssize_t token = addClientLayer(client, layer);
//创建surface
surfaceHandle = layer->getSurface();
if (surfaceHandle != 0) {
params->token = token;
params->identity = layer->getIdentity();
if (normalLayer != 0) {
Mutex::Autolock _l(mStateLock);
mLayerMap.add(layer->getSurfaceBinder(), normalLayer);
}
}
setTransactionFlags(eTransactionNeeded);
}
return surfaceHandle;
}
4. SurfaceFlinger::setTransactionState
处理上层的各个命令,并根据flag设置event通知Threadloop进行处理。
- void SurfaceFlinger::setTransactionState(const Vector<ComposerState>& state,
- int orientation) {
- Mutex::Autolock _l(mStateLock);
- uint32_t flags = 0;
- if (mCurrentState.orientation != orientation) {
- if (uint32_t(orientation)<=eOrientation270 || orientation==42) {
- mCurrentState.orientation = orientation;
- flags |= eTransactionNeeded;
- mResizeTransationPending = true;
- } else if (orientation != eOrientationUnchanged) {
- LOGW("setTransactionState: ignoring unrecognized orientation: %d",
- orientation);
- }
- }
- const size_t count = state.size();
- for (size_t i=0 ; i<count ; i++) {
- const ComposerState& s(state[i]);
- sp<Client> client( static_cast<Client *>(s.client.get()) );
- flags |= setClientStateLocked(client, s.state);
- }
- if (flags) {
- setTransactionFlags(flags);
- }
- signalEvent();
- // if there is a transaction with a resize, wait for it to
- // take effect before returning.
- while (mResizeTransationPending) {
- status_t err = mTransactionCV.waitRelative(mStateLock, s2ns(5));
- if (CC_UNLIKELY(err != NO_ERROR)) {
- // just in case something goes wrong in SF, return to the
- // called after a few seconds.
- LOGW_IF(err == TIMED_OUT, "closeGlobalTransaction timed out!");
- mResizeTransationPending = false;
- break;
- }
- }
- }
void SurfaceFlinger::setTransactionState(const Vector<ComposerState>& state,
int orientation) {
Mutex::Autolock _l(mStateLock);
uint32_t flags = 0;
if (mCurrentState.orientation != orientation) {
if (uint32_t(orientation)<=eOrientation270 || orientation==42) {
mCurrentState.orientation = orientation;
flags |= eTransactionNeeded;
mResizeTransationPending = true;
} else if (orientation != eOrientationUnchanged) {
LOGW("setTransactionState: ignoring unrecognized orientation: %d",
orientation);
}
}
const size_t count = state.size();
for (size_t i=0 ; i<count ; i++) {
const ComposerState& s(state[i]);
sp<Client> client( static_cast<Client *>(s.client.get()) );
flags |= setClientStateLocked(client, s.state);
}
if (flags) {
setTransactionFlags(flags);
}
signalEvent();
// if there is a transaction with a resize, wait for it to
// take effect before returning.
while (mResizeTransationPending) {
status_t err = mTransactionCV.waitRelative(mStateLock, s2ns(5));
if (CC_UNLIKELY(err != NO_ERROR)) {
// just in case something goes wrong in SF, return to the
// called after a few seconds.
LOGW_IF(err == TIMED_OUT, "closeGlobalTransaction timed out!");
mResizeTransationPending = false;
break;
}
}
}
5. SurfaceFlinger::composeSurfaces
该接口在threadLoop->handleRepaint中被调用,负责将所有存在的surface进行合并,OpenGL模块负责这个部分。
6. SurfaceFlinger::postFramebuffer
该接口在threadLoop中被调用,负责将合成好的数据(存在于back buffer中)推入front buffer中,然后调用HAL接口命令底层显示。
7. surface与layer
从3中可知,上层每创建一个surface的时候,底层都会同时创建一个layer,下面看一下surface及layer的相关属性。
Note:code中相关结构体太大,就不全部罗列出来了
A、Surface相关属性(详细参考文件surface.h)
a1:SurfaceID:根据此ID把相关surface和layer对应起来
a2:SurfaceInfo
包括宽高格式等信息
a3:2个buffer指针、buffer索引等信息
B、Layer相关属性(详细参考文件layer.h/layerbase.h/layerbitmap.h)
包括Layer的ID、宽高、位置、layer、alpha指、前后buffer地址及索引、layer的状态信息(如eFlipRequested、eBusy、eLocked等)