jpivot联MS的XMLA,详细配置(英文版)
Summary: This paper is intended for anyone who is interested in providing access to SQL Server 2005 Analysis Services through HTTP protocol.The paper explains the steps required to set up HTTP access and discusses different performance and security settings.All the instructions in this paper are specific to the Microsoft Windows® Server™ 2003 operating system.
On This Page
Overview
Getting binaries
Creating an application pool
Creating a virtual directory
Setting up virtual directory properties
Selecting security settings
Setting up Web Service Extension
Selecting the target Analysis Services server
Getting it all together
Overview
Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2005 Analysis Services uses the same architecture for providing HTTP access as did SQL Server 2000 Analysis Services.
The pump component is loaded into IIS (Internet Information Services) and serves as an ISAPI extension, pumping data from the client to an Analysis Services server and back.
This white paper walks you through the process of setting up HTTP access to Analysis Services when using Microsoft Windows Server™ 2003 SP1.
Getting binaries
To get binaries:
Copy the contents of the %Installation folder%/OLAP/bin/isapi directory into the folder you would like to become the base for the virtual directory in IIS.
In this example, we are going to copy all the files from the C:/Program Files/Microsoft SQL Server/MSSQL.1/OLAP/bin/isapi folder into the C:/inetpub/wwwroot/olap directory.
| Notes: To take advantage of the full set of security settings, it is important to make sure that the folder to become the base for the virtual directory is located on the drive formatted for the NTFS file system. Due to IIS limitations, the path to your directory should not contain spaces. |
If you are planning to run the HTTP pump on a different server than the Analysis Services server, please make sure that you also install OLEDB for Analysis Redistributable package.
Creating an application pool
To create an application pool:
-
To open the Computer Management console, open Control Panel, then Administrative Tools, then Computer Management.
(Or, right-click the My Computer icon and select Manage on the shortcut menu.)
-
In the Computer Management console, expand the Services and Applications node and then the Internet Information Services node.
If you can’t find the Internet Information Services node, IIS is probably not installed on your machine. To install it, open Add or Remove Programs in Control Panel. Select Add/Remove Windows Components. Then add IIS to Windows.
-
Right-click the Application pools to open the shortcut menu and select New, then Application Pool.
-
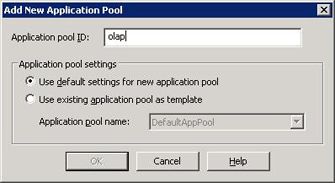
Name the application pool. In this example, we call it OLAP. (See Figure 2.)
Figure 2
Creating a virtual directory
To create a virtual directory:
-
To open the Computer Management console, open Control Panel, then Administrative Tools, then Computer Management.
(Or, right-click the My Computer icon and select Manage on the shortcut menu.)
-
In the Computer Management console, expand the Services and Applications node and then the Internet Information Services node.
If you can’t find the Internet Information Services node, IIS is probably not installed on your machine. To install it, open Add or Remove Programs in Control Panel. Select Add/Remove Windows Components. Then add IIS to Windows.
-
Right-click the Web site to open the shortcut menu and select New, then Virtual directory.
-
Name the virtual directory. In this example, we call it OLAP.
The Content Directory should point to the folder you’ve just created. In our example, this is C:/inetpub/wwroot/olap.
-
Make sure that under the Access Permissions, only the second check box, Run Scripts (Such as ASP) is selected. (See Figure 3.)
Figure 3
Setting up virtual directory properties
To set properties for the virtual directory:
-
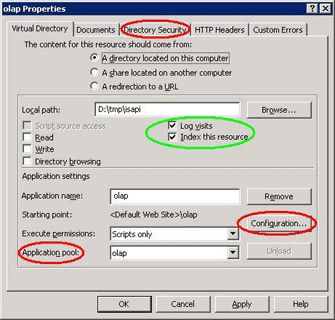
Right-click your virtual directory node and select Properties from the menu.
You should see the screen shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4Properties that need to be changed are circled in red.
Properties that are not required to be changed but which play an important role in the security and performance of the virtual directory are circled in green.
-
Choose the application pool as one you’ve just created.
-
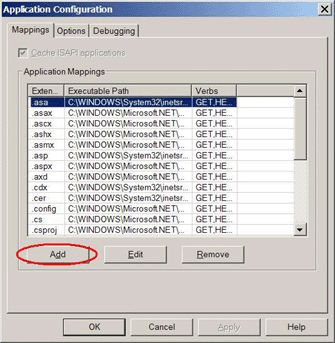
Click the Configuration button and you will see the screen shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 -
Click the Add button.
-
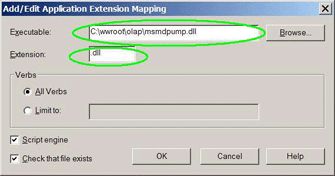
In the Executable option, enter the full path name to msmdpump.dll. In this example, it would be: C:/wwroot/olap/msmdpump.dll
-
Enter .dll in the Extension text box.
Your screen should look something like the dialog box shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6 -
Click the OK button to accept the settings.
Selecting security settings
To select security settings;
-
Select the Directory security tab and then click to Edit on Authentication and access control. You will see a dialog box similar to the one in Figure 7.
Figure 7 -
You are presented with three options. Choose one of them.
This section briefly describes these options, citing the advantages, disadvantages, and security concerns of each one.
Anonymous access
When this mode is selected, the pump ( msmdpump.dll) is running with credentials; in our case, these are the credentials of IUSR_MACHINENAME user. Therefore, every connection to Analysis Services is opened as IUSR_MACHINENAME user. When this mode is selected, there is no distinction between which user is connecting to IIS and which to Analysis Services. There is no way to distinguish between users.
This mode is to be used when the security infrastructure does not take advantage of the security functionality of Analysis Services. This is most likely an extremely controlled environment, where users are given or denied access to the virtual directory.
Integrated Windows authentication
This is the most secure and the recommended mode.
It requires that IIS Server be able to access user domain credentials. This could be done using Microsoft Active Directory® or another mechanism. It is beyond the scope of this paper to discuss all the possible configurations.
Digest authentication for Windows domain servers
This paper does not discuss this option. You can use Help for IIS to read more about it.
Basic authentication
This mode requires that the user enter a user name and password. The user name and password are transmitted over the HTTP connection to IIS. IIS will try to impersonate the user using the provided credentials.
Please note that it is absolutely imperative for anyone building a system where the password is transmitted to have ways of securing the communication channel. IIS provides a great set of tools for setting up and requiring that all communications be encrypted using HTTPS protocol.
The steps required for setting up HTTPS for a virtual directory are described later in this paper.
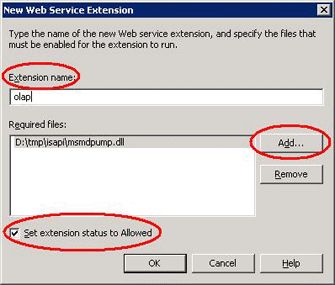
Setting up Web Service Extension
To set up Web Service Extension:
-
In Computer Management, right-click the Web Service Extensions node and select Add new Web Service Extension.
-
Name the extension.
-
Click the Add button and provide a path to your msmdpump.dll file.
-
Check the Set extension status to Allowed check box.
Your screen should look something like the dialog box shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8
Selecting the target Analysis Services server
As you can see in the architectural diagram in Figure 1, every pump component uses its own configuration file.
Open the msmdpump.ini file located in your folder and take a look at the contents of this file. It should look like the following:
<ConfigurationSettings>
<ServerName>localhost</ServerName>
<SessionTimeout>3600</SessionTimeout>
<ConnectionPoolSize>100</ConnectionPoolSize>
<MinThreadPoolSize>0</MinThreadPoolSize>
<MaxThreadPoolSize>0</MaxThreadPoolSize>
<MaxThreadsPerClient>4</MaxThreadsPerClient>
</ConfigurationSettings>
The only setting you are interested in at this point is <ServerName>.
If the Analysis Services instance that you need to provide access to is located on the local machine and installed as a default instance, there is no reason to change this setting. Otherwise, you need to specify the machine name and instance name ( mymachine/inst1).
It is also possible to specify a pointer to the virtual directory on another IIS server that is set up for HTTP access to Analysis Services.
For example, you could have <ServerName>http://secondmachine/olap/msmdpump.dll</ServerName>
Getting it all together
At this point you should have configured your HTTP pump and should be ready to connect from your application.
If your application provides you with a way to specify the server name, all you need to do is to substitute your server name with the path to your virtual directory concatenated with “msmdpump.dll”.
As in SQL Server 2000 Analysis Services, the MSOLAP OLEDB provider will understand that the server name includes an URL path and will automatically start using HTTP protocol.
For example, to connect to “MyMachine” from the MDX sample application, you should be able to connect to the Analysis Services server using “http://MyMachine/olap/msmdpump.dll” as a server name.
引用原文:http://technet.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/cc917711(en-us).aspx