Playing with ptrace, Part II
In Part I of this article[LJ, November 2002], we saw how ptrace can beused to trace system calls and change system call arguments. Inthis article, we investigate advanced techniques like settingbreakpoints and injecting code into running programs. Debuggers usethese methods to set up breakpoints and execute debugging handlers.As with Part I, all code in this article is i386architecture-specific.
In Part I, we ran the process to be traced as a child aftercalling ptrace(PTRACE_TRACEME, ..). If you simply wanted to see howthe process is making system calls and trace the program, thiswould be sufficient. If you want to trace or debug a processalready running, then ptrace(PTRACE_ATTACH, ..) should beused.
When a ptrace(PTRACE_ATTACH, ..) is called with the pid to betraced, it is roughly equivalent to the process callingptrace(PTRACE_TRACEME, ..) and becoming a child of the tracingprocess. The traced process is sent a SIGSTOP, so we can examineand modify the process as usual. After we are done withmodifications or tracing, we can let the traced process continue onits own by calling ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, ..).
The following is the code for a small example tracingprogram:
int main()
{ int i;
for(i = 0;i < 10; ++i) {
printf("My counter: %d\n", i);
sleep(2);
}
return 0;
}
Save the program as dummy2.c. Compile and run it:
gcc -o dummy2 dummy2.c ./dummy2 &Now, we can attach to dummy2 by using the code below:
#include <sys/ptrace.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <linux/user.h> /* For user_regs_struct
etc. */
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{ pid_t traced_process;
struct user_regs_struct regs;
long ins;
if(argc != 2) {
printf("Usage: %s <pid to be traced>\n",
argv[0], argv[1]);
exit(1);
}
traced_process = atoi(argv[1]);
ptrace(PTRACE_ATTACH, traced_process,
NULL, NULL);
wait(NULL);
ptrace(PTRACE_GETREGS, traced_process,
NULL, ®s);
ins = ptrace(PTRACE_PEEKTEXT, traced_process,
regs.eip, NULL);
printf("EIP: %lx Instruction executed: %lx\n",
regs.eip, ins);
ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, traced_process,
NULL, NULL);
return 0;
}
The above program simply attaches to a process, waits for it tostop, examines its eip (instruction pointer) and detaches.
To inject code use ptrace(PTRACE_POKETEXT, ..) andptrace(PTRACE_POKEDATA, ..) after the traced process hasstopped.
How do debuggers set breakpoints? Generally, they replace theinstruction to be executed with a trap instruction, so that whenthe traced program stops, the tracing program, the debugger, canexamine it. It will replace the original instruction once thetracing program continues the traced process. Here's anexample:
#include <sys/ptrace.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <linux/user.h>
const int long_size = sizeof(long);
void getdata(pid_t child, long addr,
char *str, int len)
{ char *laddr;
int i, j;
union u {
long val;
char chars[long_size];
}data;
i = 0;
j = len / long_size;
laddr = str;
while(i < j) {
data.val = ptrace(PTRACE_PEEKDATA, child,
addr + i * 4, NULL);
memcpy(laddr, data.chars, long_size);
++i;
laddr += long_size;
}
j = len % long_size;
if(j != 0) {
data.val = ptrace(PTRACE_PEEKDATA, child,
addr + i * 4, NULL);
memcpy(laddr, data.chars, j);
}
str[len] = '\0';
}
void putdata(pid_t child, long addr,
char *str, int len)
{ char *laddr;
int i, j;
union u {
long val;
char chars[long_size];
}data;
i = 0;
j = len / long_size;
laddr = str;
while(i < j) {
memcpy(data.chars, laddr, long_size);
ptrace(PTRACE_POKEDATA, child,
addr + i * 4, data.val);
++i;
laddr += long_size;
}
j = len % long_size;
if(j != 0) {
memcpy(data.chars, laddr, j);
ptrace(PTRACE_POKEDATA, child,
addr + i * 4, data.val);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{ pid_t traced_process;
struct user_regs_struct regs, newregs;
long ins;
/* int 0x80, int3 */
char code[] = {0xcd,0x80,0xcc,0};
char backup[4];
if(argc != 2) {
printf("Usage: %s <pid to be traced>\n",
argv[0], argv[1]);
exit(1);
}
traced_process = atoi(argv[1]);
ptrace(PTRACE_ATTACH, traced_process,
NULL, NULL);
wait(NULL);
ptrace(PTRACE_GETREGS, traced_process,
NULL, ®s);
/* Copy instructions into a backup variable */
getdata(traced_process, regs.eip, backup, 3);
/* Put the breakpoint */
putdata(traced_process, regs.eip, code, 3);
/* Let the process continue and execute
the int 3 instruction */
ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, traced_process, NULL, NULL);
wait(NULL);
printf("The process stopped, putting back "
"the original instructions\n");
printf("Press <enter> to continue\n");
getchar();
putdata(traced_process, regs.eip, backup, 3);
/* Setting the eip back to the original
instruction to let the process continue */
ptrace(PTRACE_SETREGS, traced_process,
NULL, ®s);
ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, traced_process,
NULL, NULL);
return 0;
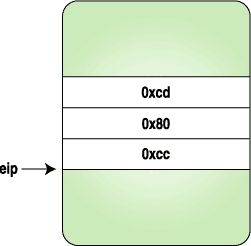
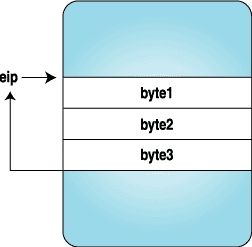
}Here we replace the three bytes with the code for a trapinstruction, and when the process stops, we replace the originalinstructions and reset the eip to original location. Figures 1-4clarify how the instruction stream looks when above program isexecuted.
Figure 1. After the Process Is Stopped Figure 2. After the Trap Instruction Bytes AreSet
Figure 3. Trap Is Hit and Control Is Given to theTracing Program Figure 4. After the Original Instructions Are Replacedand eip Is Reset to the Original Location
Now that we have a clear idea of how breakpoints are set,let's inject some code bytes into a running program. These codebytes will print “hello world”.
The following program is a simple “hello world” programwith modifications to fit our needs. Compile the following programwith:
gcc -o hello hello.c
void main()
{
__asm__("
jmp forward
backward:
popl %esi # Get the address of
# hello world string
movl $4, %eax # Do write system call
movl $2, %ebx
movl %esi, %ecx
movl $12, %edx
int $0x80
int3 # Breakpoint. Here the
# program will stop and
# give control back to
# the parent
forward:
call backward
.string \"Hello World\\n\""
);
}
The jumping backward and forward here is required to find theaddress of the “hello world” string.
We can get the machine code for the above assembly from GDB.Fire up GDB and disassemble the program:
(gdb) disassemble main Dump of assembler code for function main: 0x80483e0 <main>: push %ebp 0x80483e1 <main+1>: mov %esp,%ebp 0x80483e3 <main+3>: jmp 0x80483fa <forward> End of assembler dump. (gdb) disassemble forward Dump of assembler code for function forward: 0x80483fa <forward>: call 0x80483e5 <backward> 0x80483ff <forward+5>: dec %eax 0x8048400 <forward+6>: gs 0x8048401 <forward+7>: insb (%dx),%es:(%edi) 0x8048402 <forward+8>: insb (%dx),%es:(%edi) 0x8048403 <forward+9>: outsl %ds:(%esi),(%dx) 0x8048404 <forward+10>: and %dl,0x6f(%edi) 0x8048407 <forward+13>: jb 0x8048475 0x8048409 <forward+15>: or %fs:(%eax),%al 0x804840c <forward+18>: mov %ebp,%esp 0x804840e <forward+20>: pop %ebp 0x804840f <forward+21>: ret End of assembler dump. (gdb) disassemble backward Dump of assembler code for function backward: 0x80483e5 <backward>: pop %esi 0x80483e6 <backward+1>: mov $0x4,%eax 0x80483eb <backward+6>: mov $0x2,%ebx 0x80483f0 <backward+11>: mov %esi,%ecx 0x80483f2 <backward+13>: mov $0xc,%edx 0x80483f7 <backward+18>: int $0x80 0x80483f9 <backward+20>: int3 End of assembler dump.
We need to take the machine code bytes from main+3 tobackward+20, which is a total of 41 bytes. The machine code can beseen with the x command in GDB:
(gdb) x/40bx main+3 <main+3>: eb 15 5e b8 04 00 00 00 <backward+6>: bb 02 00 00 00 89 f1 ba <backward+14>: 0c 00 00 00 cd 80 cc <forward+1>: e6 ff ff ff 48 65 6c 6c <forward+9>: 6f 20 57 6f 72 6c 64 0a
Now we have the instruction bytes to be executed. Why wait? We caninject them using the same method as in the previous example. Thefollowing is the source code; only the main function is given here:
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{ pid_t traced_process;
struct user_regs_struct regs, newregs;
long ins;
int len = 41;
char insertcode[] =
"\xeb\x15\x5e\xb8\x04\x00"
"\x00\x00\xbb\x02\x00\x00\x00\x89\xf1\xba"
"\x0c\x00\x00\x00\xcd\x80\xcc\xe8\xe6\xff"
"\xff\xff\x48\x65\x6c\x6c\x6f\x20\x57\x6f"
"\x72\x6c\x64\x0a\x00";
char backup[len];
if(argc != 2) {
printf("Usage: %s <pid to be traced>\n",
argv[0], argv[1]);
exit(1);
}
traced_process = atoi(argv[1]);
ptrace(PTRACE_ATTACH, traced_process,
NULL, NULL);
wait(NULL);
ptrace(PTRACE_GETREGS, traced_process,
NULL, ®s);
getdata(traced_process, regs.eip, backup, len);
putdata(traced_process, regs.eip,
insertcode, len);
ptrace(PTRACE_SETREGS, traced_process,
NULL, ®s);
ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, traced_process,
NULL, NULL);
wait(NULL);
printf("The process stopped, Putting back "
"the original instructions\n");
putdata(traced_process, regs.eip, backup, len);
ptrace(PTRACE_SETREGS, traced_process,
NULL, ®s);
printf("Letting it continue with "
"original flow\n");
ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, traced_process,
NULL, NULL);
return 0;
}
Injecting the Code into Free Space
In the previous example we injected the code directly intothe executing instruction stream. However, debuggers can getconfused with this kind of behaviour, so let's find the free spacein the process and inject the code there. We can find free space byexamining the /proc/pid/maps file of the traced process. Thefollowing function will find the starting address of thismap:
long freespaceaddr(pid_t pid)
{
FILE *fp;
char filename[30];
char line[85];
long addr;
char str[20];
sprintf(filename, "/proc/%d/maps", pid);
fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if(fp == NULL)
exit(1);
while(fgets(line, 85, fp) != NULL) {
sscanf(line, "%lx-%*lx %*s %*s %s", &addr,
str, str, str, str);
if(strcmp(str, "00:00") == 0)
break;
}
fclose(fp);
return addr;
}
Each line in /proc/pid/maps represents a mapped region of theprocess. An entry in /proc/pid/maps looks like this:
map start-mapend protection offset device inode process file 08048000-0804d000 r-xp 00000000 03:08 66111 /opt/kde2/bin/kdeinit
The following program injects code into free space. It's similar tothe previous injection program except the free space address isused for keeping our new code. Here is the source code for the mainfunction:
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{ pid_t traced_process;
struct user_regs_struct oldregs, regs;
long ins;
int len = 41;
char insertcode[] =
"\xeb\x15\x5e\xb8\x04\x00"
"\x00\x00\xbb\x02\x00\x00\x00\x89\xf1\xba"
"\x0c\x00\x00\x00\xcd\x80\xcc\xe8\xe6\xff"
"\xff\xff\x48\x65\x6c\x6c\x6f\x20\x57\x6f"
"\x72\x6c\x64\x0a\x00";
char backup[len];
long addr;
if(argc != 2) {
printf("Usage: %s <pid to be traced>\n",
argv[0], argv[1]);
exit(1);
}
traced_process = atoi(argv[1]);
ptrace(PTRACE_ATTACH, traced_process,
NULL, NULL);
wait(NULL);
ptrace(PTRACE_GETREGS, traced_process,
NULL, ®s);
addr = freespaceaddr(traced_process);
getdata(traced_process, addr, backup, len);
putdata(traced_process, addr, insertcode, len);
memcpy(&oldregs, ®s, sizeof(regs));
regs.eip = addr;
ptrace(PTRACE_SETREGS, traced_process,
NULL, ®s);
ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, traced_process,
NULL, NULL);
wait(NULL);
printf("The process stopped, Putting back "
"the original instructions\n");
putdata(traced_process, addr, backup, len);
ptrace(PTRACE_SETREGS, traced_process,
NULL, &oldregs);
printf("Letting it continue with "
"original flow\n");
ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, traced_process,
NULL, NULL);
return 0;
}
Behind the Scenes
So what happens within the kernel now? How is ptraceimplemented? This section could be an article on its own; however,here's a brief description of what happens.
When a process calls ptrace with PTRACE_TRACEME, the kernelsets up the process flags to reflect that it is beingtraced:
Source: arch/i386/kernel/ptrace.c
if (request == PTRACE_TRACEME) {
/* are we already being traced? */
if (current->ptrace & PT_PTRACED)
goto out;
/* set the ptrace bit in the process flags. */
current->ptrace |= PT_PTRACED;
ret = 0;
goto out;
}
When a system call entry is done, the kernel checks this flagand calls the trace system call if the process is being traced. Thegory assembly details can be found in arch/i386/kernel/entry.S.
Now, we are in the sys_trace() function as defined inarch/i386/kernel/ptrace.c. It stops the child and sends a signal tothe parent notifying that the child is stopped. This wakes up thewaiting parent, and it does the ptrace magic. Once the parent isdone, and it calls ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, ..) orptrace(PTRACE_SYSCALL, ..), it wakes up the child by calling thescheduler function wake_up_process(). Some other architectures canimplement this by sending a SIGCHLD to child.
Conclusion
ptrace may appear to bemagic to some people, because it can examine and modify a runningprogram. It is generally used by debuggers and system call tracingprograms, such as ptrace. It opens up interesting possibilities fordoing user-mode extensions as well. There have been a lot ofattempts to extend the operating system on the user level. SeeResources to read about UFO, a user-level extension to filesystems.ptrace also is used to employsecurity mechanisms.
All example code from this article and from Part I isavailable as a tar archive on the Linux Journal FTP site[ftp.linuxjournal.com/pub/lj/listings/issue104/6210.tgz].