《机器学习实战》之ID3决策树算法
ID3决策树算法类似算法流程图。
决策树算法
优点:计算复杂度不高,输出结果易于理解,对中间值的缺失不敏感,可以处理不相关特征数据。
缺点:可能会产生过度匹配问题。
适用数据类型:数值型和标称型
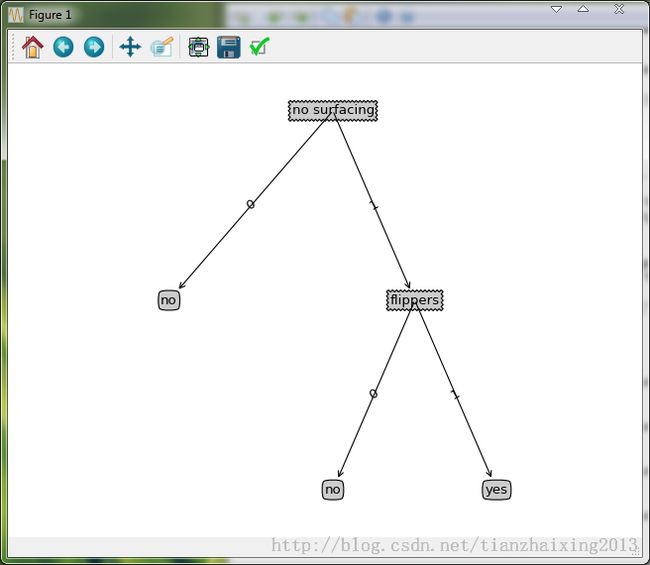
基于python的实现代码:
1)准备子函数
# -*- coding: cp936 -*-
from math import log
import operator
def createDataSet():#创建数据集
dataSet = [[1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 'no']]
labels = ['no surfacing','flippers']
#change to discrete values
return dataSet, labels
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
numEntries = len(dataSet) #计算数据集的长度
labelCounts = {} #定义一个label字典,统计每个label出现的次数,键值为label,值为对应label出现的次数
for featVec in dataSet: #the the number of unique elements and their occurance
currentLabel = featVec[-1]#数据集每个元素都是一个列表,每个元素列表的最后一列为label
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0 #判断当前label是否已经存在字典键值列表中,没有存在的话,将当前label加入字典,并设置对应值为0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 #否则,当前label出现次数累加
shannonEnt = 0.0
for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries #计算每个label出现的概率
shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob,2) #计算数据集的(香农信息熵)信息熵,其中log base 2
return shannonEnt
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):#按照给定特征划分数据集:待划分数据集,划分数据集的特征,需要返回的特征值
retDataSet = [] #定义一个空列表,即:子数据集
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value: #判断待划分数据集中元素列表指定位置的特征是否与需要返回的特征值匹配
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #chop out axis used for splitting
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) #获取待划分数据集中元素列表的子元素列表(已经裁剪掉指定数据集的特征)
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec) #添加获取的子元素列表到子数据集中
return retDataSet
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet): #选择最好的数据集划分方式--以不同特征划分子数据集的信息熵增益(或者数据集信息熵减少)大小为依据!
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #the last column is used for the labels
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) #计算整个数据集的信息熵
bestInfoGain = 0.0; bestFeature = -1
for i in range(numFeatures): #iterate over all the features
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]#create a list of all the examples of this feature 运用到列表推导式
uniqueVals = set(featList) #get a set of unique values
newEntropy = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value)
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #calculate the info gain; ie reduction in entropy
if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #compare this to the best gain so far
bestInfoGain = infoGain #if better than current best, set to best
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature #returns an integer2) 构建决策树
def majorityCnt(classList): #运用多数表决方法判定label不唯一时,叶子节点的分类
classCount={}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys(): classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.iteritems(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0] #返回label出现次数最多的所属分类
def createTree(dataSet,labels): #创建决策树
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): #list.count(list[0])返回指定位置0对应值list[0],出现的次数
return classList[0] #stop splitting when all of the classes are equal
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #stop splitting when there are no more features in dataSet
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet)
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}}
del(labels[bestFeat]) #删除已经使用的最佳划分数据集特征
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featValues)
for value in uniqueVals:
subLabels = labels[:] #copy all of labels, so trees don't mess up existing labels
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value),subLabels)
return myTree
def classify(inputTree,featLabels,testVec): #使用决策树分类函数进行分类
firstStr = inputTree.keys()[0]
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr]
featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr)
key = testVec[featIndex]
valueOfFeat = secondDict[key]
if isinstance(valueOfFeat, dict): #判断是否为字典类型的节点,如果是,则该节点为判断节点,否则,该节点为叶子节点
classLabel = classify(valueOfFeat, featLabels, testVec)
else: classLabel = valueOfFeat
return classLabel
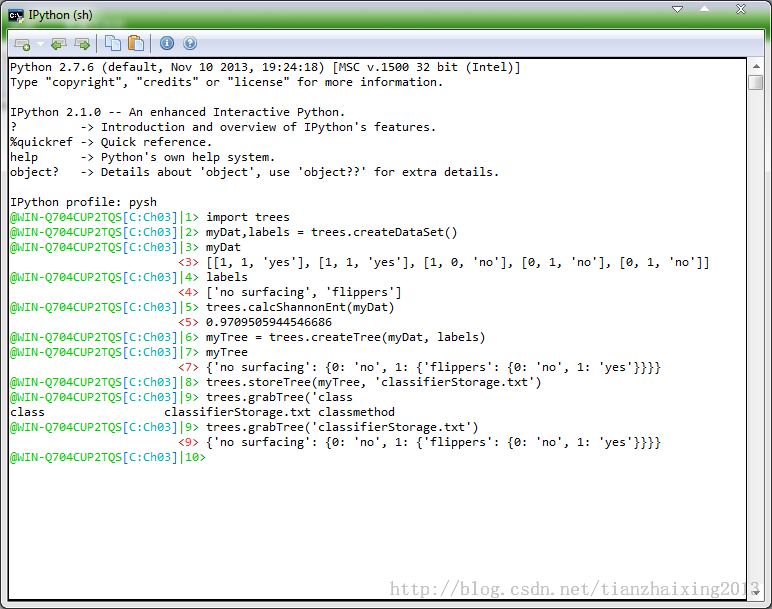
def storeTree(inputTree,filename): #利用pickle模块存储已经创建好的决策树,以便后续使用中无需重新构建
import pickle
fw = open(filename,'w')
pickle.dump(inputTree,fw)
fw.close()
def grabTree(filename):
import pickle
fr = open(filename)
return pickle.load(fr)
3) 程序运行截图:(这里用的pythonxy里面的IPython(sh)交换环境)
实例测试:
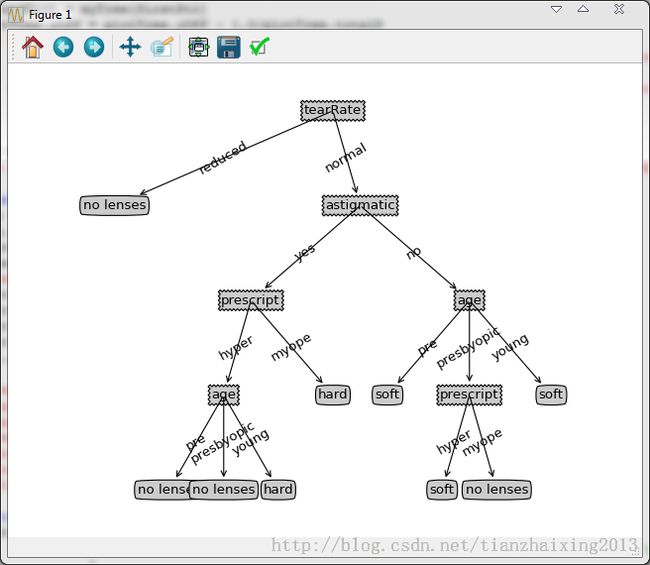
lenses.txt内容如下所示:
young myope no reduced no lenses young myope no normal soft young myope yes reduced no lenses young myope yes normal hard young hyper no reduced no lenses young hyper no normal soft young hyper yes reduced no lenses young hyper yes normal hard pre myope no reduced no lenses pre myope no normal soft pre myope yes reduced no lenses pre myope yes normal hard pre hyper no reduced no lenses pre hyper no normal soft pre hyper yes reduced no lenses pre hyper yes normal no lenses presbyopic myope no reduced no lenses presbyopic myope no normal no lenses presbyopic myope yes reduced no lenses presbyopic myope yes normal hard presbyopic hyper no reduced no lenses presbyopic hyper no normal soft presbyopic hyper yes reduced no lenses presbyopic hyper yes normal no lenses
基于matplotlib模块的Python绘图代码如下所示:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
firstStr = myTree.keys()[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else: numLeafs +=1
return numLeafs
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = myTree.keys()[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else: thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args )
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30)
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):#if the first key tells you what feat was split on
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) #this determines the x width of this tree
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstStr = myTree.keys()[0] #the text label for this node should be this
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict': #test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes
plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key)) #recursion
else: #it's a leaf node print the leaf node
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD
#if you do get a dictonary you know it's a tree, and the first element will be another dict
def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops) #no ticks
#createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) #ticks for demo puropses
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW; plotTree.yOff = 1.0;
plotTree(inTree, (0.5,1.0), '')
plt.show()
#def createPlot():
# fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
# fig.clf()
# createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) #ticks for demo puropses
# plotNode('a decision node', (0.5, 0.1), (0.1, 0.5), decisionNode)
# plotNode('a leaf node', (0.8, 0.1), (0.3, 0.8), leafNode)
# plt.show()
def retrieveTree(i):
listOfTrees =[{'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}}},
{'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: {'head': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}, 1: 'no'}}}}
]
return listOfTrees[i]
#createPlot(thisTree)