Class字节码文件结构详解
Class字节码中有两种数据类型:
字节数据直接量:这是基本的数据类型。共细分为u1、u2、u4、u8四种,分别代表连续的1个字节、2个字节、4个字节、8个字节组成的整体数据。
表:表是由多个基本数据或其他表,按照既定顺序组成的大的数据集合。表是有结构的,它的结构体现在,组成表的成分所在的位置和顺序都是已经严格定义好的。
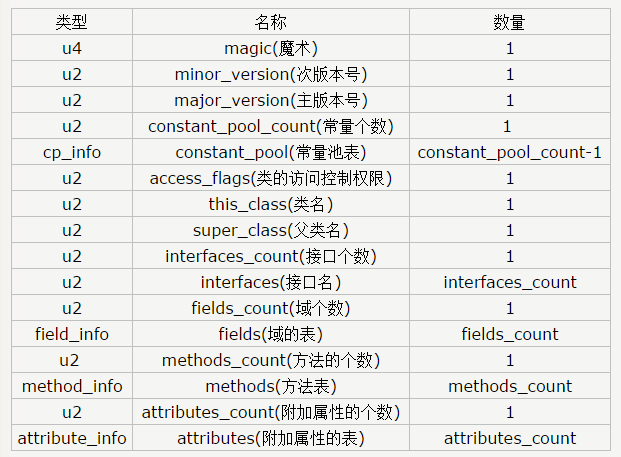
Class字节码总体结构如下:
具体详解请参考http://www.blogjava.net/DLevin/archive/2011/09/05/358033.html
我在这里要说明几个细节问题:
为什么说常量表的数量是constant_pool_count-1,且索引从1开始而不是0。其实根本原因在于,索引为0也是一个常量(保留常量),只不过它不存在常量表,这个常量就对应null值。因此加上这个系统保留常量,常量个数共为constant_pool_count个,但是常量表数量要减1。
在常量池中,如果存在long型或double型字面量,它们会占用两个连续索引。比如:假设一个类中只有一个int型字面量1和一个double型字面量1(当然这种假设是不可能的,因为总会有类名字面量等),则常量池个数为3,而不是2。这正是因为double字面量占用了两个连续的索引。
接下来,贴出一个小demo来展示如何读取字节码:
ClassParser负责把握Class字节码整体结构的解析。
package com.lixin;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class ClassParser {
private InputStream in;
public ClassParser(InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
public void parse() throws IOException {
// 魔数
magicNumber();
// 主次版本号
version();
// 常量池
constantPool();
// 类或接口修饰符
accessFlag();
// 继承关系(当前类、父类、父接口)
inheritence();
// 字段集合
fieldList();
// 方法集合
methodList();
// 属性集合
attributeList();
}
private void attributeList() throws IOException {
line();
int attrLength = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("共有"+attrLength+"个属性");
for (int i=0;i<attrLength;i++) {
line();
attribute();
}
}
private void attribute() throws IOException {
int nameIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int length = StreamUtils.read4(in);
byte[] info = StreamUtils.read(in, length);
System.out.println("nameIndex:"+nameIndex);
System.out.println("length:"+length);
System.out.println("info:"+info);
}
private void methodList() throws IOException {
int length = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("共有"+length+"个方法");
for (int i=0;i<length;i++)
method();
}
private void method() throws IOException {
System.out.println("---------------------");
int accessFlag = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int nameIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int descriptorIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("accessFlag:"+accessFlag);
System.out.println("nameIndex:"+nameIndex);
System.out.println("descriptorIndex:"+descriptorIndex);
attributeList();
}
private void fieldList() throws IOException {
line();
int length = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("共有"+length+"个字段");
for (int i=0;i<length;i++) {
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
int accessFlag = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int nameIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int descriptorIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("accessFlag:"+accessFlag);
System.out.println("nameIndex:"+nameIndex);
System.out.println("descriptorIndex:"+descriptorIndex);
attributeList();
}
}
private void inheritence() throws IOException {
line();
int thisClassRef = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int superClassRef = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("thisClassRef:"+thisClassRef);
System.out.println("superClassRef:"+superClassRef);
int interfaceLen = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("接口数量:"+interfaceLen);
for (int i=0;i<interfaceLen;i++) {
int interfaceRef = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("interfaceRef:"+interfaceRef);
}
}
private void accessFlag() throws IOException {
line();
int accessFlag = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("accessFlag:0x"+Integer.toHexString(accessFlag)+"("+accessFlag+")");
}
private void constantPool() throws IOException {
new ConstantPoolParser(in).constPool();
}
private void version() throws IOException {
line();
int minorVersion = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int majorVersion = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("版本:"+majorVersion+"."+minorVersion);
}
private void magicNumber() throws IOException {
line();
int magic = StreamUtils.read4(in);
System.out.println("魔数:"+Integer.toHexString(magic).toUpperCase());
}
private void line() {
System.out.println("----------------------");
}
}
ConstPoolParser负责常量池的解析(因为常量池表较多,且数据量也较大,因此单独拉出来解析)
package com.lixin;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class ConstPoolParser {
public static final int Utf8_info = 1;
public static final int Integer_info = 3;
public static final int Float_info = 4;
public static final int Long_info = 5;
public static final int Double_info = 6;
public static final int Class_info = 7;
public static final int String_info = 8;
public static final int Fieldref_info = 9;
public static final int Methodref_info = 10;
public static final int InterfaceMethodref_info = 11;
public static final int NameAndType_info = 12;
public static final int MethodHandle_info = 15;
public static final int MethodType_info = 16;
public static final int InvokeDynamic_info = 18;
private InputStream in;
public ConstPoolParser(InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
public void constPool() throws IOException {
line();
int length = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("共有"+length+"个常量");
boolean doubleBytes = false;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
if (doubleBytes) {
doubleBytes = false;
continue;
}
line();
System.out.println("常量索引:"+i);
int flag = StreamUtils.read1(in);
// System.out.println("标志:"+flag);
switch (flag) {
case Utf8_info:
utf8Info();
continue;
case Integer_info:
integerInfo();
continue;
case Float_info:
floatInfo();
continue;
case Long_info:
doubleBytes = true;
longInfo();
continue;
case Double_info:
doubleBytes = true;
doubleInfo();
continue;
case Class_info:
classInfo();
continue;
case String_info:
stringInfo();
continue;
case Fieldref_info:
fieldrefInfo();
continue;
case Methodref_info:
methodrefInfo();
continue;
case InterfaceMethodref_info:
interfaceMethodrefInfo();
continue;
case NameAndType_info:
nameAndTypeInfo();
continue;
case MethodHandle_info:
methodHandleInfo();
continue;
case MethodType_info:
methodTypeInfo();
continue;
case InvokeDynamic_info:
invokeDynamicInfo();
continue;
default:
System.err.println(flag);
throw new RuntimeException("unknown");
}
}
}
private void line() {
System.out.println("----------------------");
}
private void utf8Info() throws IOException {
int length = StreamUtils.read2(in);
byte[] buf = StreamUtils.read(in, length);
String s = new String(buf,0,buf.length);
System.out.println("utf8Info表:");
System.out.println("值:"+s);
}
private void integerInfo() throws IOException {
System.out.println("integerInfo表:");
int value = StreamUtils.read4(in);
System.out.println("值:"+value);
}
private void floatInfo() throws IOException {
System.out.println("floatInfo表:");
int value = StreamUtils.read4(in);
float f = Float.intBitsToFloat(value);
System.out.println("值:"+f);
}
private void longInfo() throws IOException {
System.out.println("longInfo表:");
long value = StreamUtils.read8(in);
System.out.println("值:"+value);
}
private void doubleInfo() throws IOException {
System.out.println("doubleInfo表:");
long value = StreamUtils.read8(in);
double d = Double.longBitsToDouble(value);
System.out.println("值:"+d);
}
private void classInfo() throws IOException {
System.out.println("classInfo表:");
int index = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("index:" + index);
}
private void stringInfo() throws IOException {
System.out.println("stringInfo表:");
int index = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("index:" + index);
}
private void fieldrefInfo() throws IOException {
int classIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int nameAndTypeIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("fieldrefInfo表:");
System.out.println("classIndex:" + classIndex);
System.out.println("nameAndTypeIndex:" + nameAndTypeIndex);
}
private void methodrefInfo() throws IOException {
int classIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int nameAndTypeIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("methodrefInfo表:");
System.out.println("classIndex:" + classIndex);
System.out.println("nameAndTypeIndex:" + nameAndTypeIndex);
}
private void interfaceMethodrefInfo() throws IOException {
int classIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int nameAndTypeIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("interfaceMethodrefInfo表:");
System.out.println("classIndex:" + classIndex);
System.out.println("nameAndTypeIndex:" + nameAndTypeIndex);
}
private void nameAndTypeInfo() throws IOException {
int nameIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int typeIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("nameAndTypeInfo表:");
System.out.println("nameIndex:" + nameIndex);
System.out.println("typeIndex:" + typeIndex);
}
private void methodHandleInfo() throws IOException {
int referenceKind = StreamUtils.read1(in);
int referenceIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("methodHandleInfo表:");
System.out.println("referenceKind:"+referenceKind);
System.out.println("referenceIndex:"+referenceIndex);
}
private void methodTypeInfo() throws IOException {
System.out.println("methodTypeInfo表:");
int descriptorIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("descriptorIndex:"+descriptorIndex);
}
private void invokeDynamicInfo() throws IOException {
int bootstrapMethodAttrIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
int nameAndTypeIndex = StreamUtils.read2(in);
System.out.println("bootstrapMethodAttrIndex:"+bootstrapMethodAttrIndex);
System.out.println("nameAndTypeIndex:"+nameAndTypeIndex);
}
}
StreamUtils负责从输入字节流中读取数据
package com.lixin;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class StreamUtils {
public static int read1(InputStream in) throws IOException {
return in.read() & 0xff;
}
public static int read2(InputStream in) throws IOException{
return (read1(in) << 8) | read1(in);
}
public static int read4(InputStream in) throws IOException {
return (read2(in) <<16) | read2(in);
}
public static long read8(InputStream in) throws IOException {
long high = read4(in) & 0xffffffffl;
long low = read4(in) & 0xffffffffl;
return (high << 32) | (low);
}
public static byte[] read(InputStream in,int length) throws IOException {
byte[] buf = new byte[length];
in.read(buf, 0, length);
return buf;
}
}
TestClass为待解析的目标类,读者可以任意改写此类来多做实验
package com.lixin;
public class TestClass {
private int a = 5;
protected char c = 'c';
double x = 1.1;
long y = 111;
public void show() {
}
}
测试方法入口:
package com.lixin;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* 程序入口
* @author lixin
*
*/
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InputStream in = Class.class.getResourceAsStream("/com/lixin/TestClass.class");
ClassParser parser = new ClassParser(in);
parser.parse();
}
}
最后,我们可以使用jdk中的javap进行字节码反编译,来对比我们的读取与反编译结果差别,用于查错。
javap -v TestClass.class >./out.txt