JSON解析高手
前三篇博客分别介绍了xml的三种解析方法,分别是SAX,DOM,PULL解析XML,兴趣的朋友可以去看一下这【XML解析(一)】SAX解析XML,【XML解析(二)】DOM解析XML,【XML解析(三)】PULL解析XML三篇文章学习一下XML解析。我们知道客户端请求服务器,服务器给我们返回的数据通常不只是xml,还可以是json,html,当然json和xml是用的最多的了,下篇文章将会向大家解析如何解析html数据,这篇文章先向大家介绍如何解析服务器给我们返回的json数据。
一、概述
JSON是JavaScript Object Notation的简称,起源于js(javascript)它是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,JSON不仅在js中广泛使用,同时还在其他领域得到广泛使用,如c,c++,java,Php,swift等等,成为了一种通用的理想数据交换格式,它有两种数据结构,分别是对象,数组,它形式上有花括号{}和中括号[]嵌套,{}中的是代表对象,[]中的为数组,即对象中有数组,数组中又有对象,而且以及键/值对出现。
JSON语法:
json是javascript对象表示语法的子集
- 数据在键值对中
- 数据有逗号分隔
- 花括号保存对象
JSON的值:
- 数字(整数或浮点数)
- 字符串(在双引号中
- 逻辑值(true 或 false)
- 数组(在方括号中)
- 对象(在花括号中)
- null
json和xml比较:
- 数据体积小,耗费流量比xml少;
- 可读性比xml稍差,但格式化后也很直观;
- 与JavaScript交互比Xml方便;
- 速度比xml快;
- 拥有和xml同样多的解析方式。
更多信息参考:json官网,json百科
大概了解了JSON,下面将介绍在Android中通过采用android内置的org.json包,android 3.0 新出的JsonReader,google提供的gson解析json这三种常用的方式解析json。
二、JSON数据准备
要学习怎么解析json,咋们先要得到json数据,得到json数据方式有很多种,比如:webservice接口api,自己写个服务器端,或者自己在代码中写一个json格式的字符串。下面我们将通过金山词霸开放平台为我们提供的每日一句的api接口演示三种解析json的方法。
金山词霸每日一句api接口:http://open.iciba.com/dsapi
要解析json,我们得先知道要解析json的格式及内容,我们先用浏览器访问每日有一句api接口看看返回的数据。
访问结果:
{"sid":"1683","tts":"http:\/\/news.iciba.com\/admin\/tts\/2015-12-07-day.mp3","content":"You aspire to do great things? Begin with little ones.\t","note":"\u60f3\u6210\u5c31\u5927\u4e8b\uff0c\u5c31\u8981\u4ece\u5c0f\u4e8b\u5f00\u59cb\u3002\uff08Augustine of Hippo\uff09","love":"2437","translation":"\u8bcd\u9738\u5c0f\u7f16\uff1a\u62e5\u6709\u597d\u5fc3\u60c5\u7684\u6700\u4f73\u65b9\u5f0f\u5c31\u662f\u201c\u5e72\u6b63\u4e8b\u201d\u3002\u5b66\u4f1a\u4e86\u89c4\u5b9a\u7684\u5355\u8bcd\uff0c\u8bfb\u5b8c\u4e86\u5fc5\u8bfb\u7684\u4e66\uff0c\u6536\u5c3e\u4e86\u5de5\u4f5c\uff0c\u953b\u70bc\u6ca1\u6709\u5077\u61d2\u2026\u90a3\u4e48\u9047\u5230\u6001\u5ea6\u4e0d\u597d\u7684\u51fa\u79df\u53f8\u673a\uff0c\u591a\u6536\u94b1\u7684\u770b\u8f66\u5927\u5988\uff0c\u6392\u961f\u52a0\u585e\u7684\u65e0\u826f\u9752\u5e74\u4e5f\u4f1a\u4e00\u7b11\u7f6e\u4e4b\uff0c\u5fc3\u4e2d\u5145\u5b9e\uff0c\u624d\u6709\u5e95\u6c14\u5feb\u4e50\u3002\u3010\u5173\u6ce8\u8bcd\u9738\u5c0f\u59b9\u5fae\u4fe1\uff08\u5fae\u4fe1\u53f7\uff1aijinshanciba\uff09\uff0c\u6709\u60ca\u559c\u5466\uff01\u3011","picture":"http:\/\/cdn.iciba.com\/news\/word\/2015-12-07.jpg","picture2":"http:\/\/cdn.iciba.com\/news\/word\/big_2015-12-07b.jpg","caption":"\u8bcd\u9738\u6bcf\u65e5\u4e00\u53e5","dateline":"2015-12-07","s_pv":"6694","sp_pv":"121","tags":[{"id":"13","name":"\u540d\u4eba\u540d\u8a00"},{"id":"16","name":"\u6cbb\u6108\u7cfb"}],"fenxiang_img":"http:\/\/cdn.iciba.com\/web\/news\/longweibo\/imag\/2015-12-07.jpg"}哎呀,这尼玛!,这是什么啊,简直是无法直视啊,还要解析?不过不要紧,我们可以对该json数据先格式化一下,市场上有很多json格式化工具及在线json格式工具等等,这里我推荐一个工具,叫HiJson,点击这里下载:HiJson下载
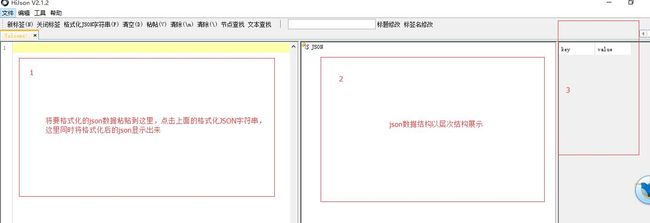
HiJson的使用非常简单,下面用一张图说明一下HiJson的使用:
其中面板3显示面板2选择节点的键/值
将每日一句的json的数据格式化后的结果:
{
"caption": "词霸每日一句",
"content": "You aspire to do great things? Begin with little ones. ",
"dateline": "2015-12-07",
"fenxiang_img": "http://cdn.iciba.com/web/news/longweibo/imag/2015-12-07.jpg",
"love": "2437",
"note": "想成就大事,就要从小事开始。(Augustine of Hippo)",
"picture": "http://cdn.iciba.com/news/word/2015-12-07.jpg",
"picture2": "http://cdn.iciba.com/news/word/big_2015-12-07b.jpg",
"s_pv": "6694",
"sid": "1683",
"sp_pv": "121",
"tags": [
{
"id": "13",
"name": "名人名言"
},
{
"id": "16",
"name": "治愈系"
}
],
"translation": "词霸小编:拥有好心情的最佳方式就是“干正事”。学会了规定的单词,读完了必读的书,收尾了工作,锻炼没有偷懒…那么遇到态度不好的出租司机,多收钱的看车大妈,排队加塞的无良青年也会一笑置之,心中充实,才有底气快乐。【关注词霸小妹微信(微信号:ijinshanciba),有惊喜呦!】",
"tts": "http://news.iciba.com/admin/tts/2015-12-07-day.mp3"
}可以看到格式化后的数据结构非常清晰,这就是标准的json格式,有了json数据,下面我们就用org.json包(无需导入),JsonReader,Gson解析该json数据。
三、3种方式解析JSON实战(代码编写)
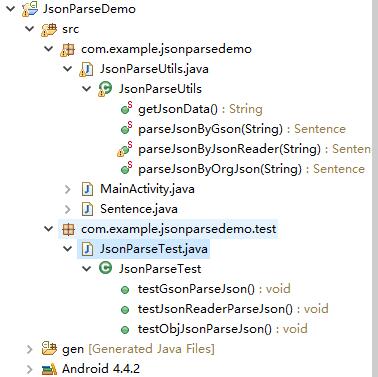
打开eclipse(这里只是演示一下解析json,就不用as(Android Studio)了)新建一个Android项目,为了方便,这里先将整个项目的目录结构贴出来,整个项目的代码将会在文章贴在文章末尾,方便下载。
目录结构:
代码编写:
1、 写一个工具类,JsonParseUtils.java,写一个请求得到json数据的方法
/** * 连接网络请求数据,这里使用HttpURLConnection */
public static String getJsonData() {
URL url = null;
String jsonData = ""; // 请求服务器返回的json字符串数据
InputStreamReader in = null; // 读取的内容(输入流)
try {
url = new URL("http://open.iciba.com/dsapi");
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
// 这一步会连接网络得到输入流
in = new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream());
// 为输入创建BufferedReader
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(in);
String inputLine = null;
while(((inputLine = br.readLine()) != null)){
jsonData += inputLine;
}
in.close(); // 关闭InputStreamReader
// 断开网络连接
conn.disconnect();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return jsonData;
}注意:HttpURLConnection默认是Get请求,如果要使用Post请求,需要对HttpURLConnection做一些配置,得到数据后记得关闭流和断开网络链接。
不要忘了添加请求网络的权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>2、解析JSON
- 方式一:使用org.json包解析
/** * 通过org.json解析json * @param jsonStr json字符串 * @throws JSONException 格式不对,转换异常 */
public static Sentence parseJsonByOrgJson(String jsonStr) throws JSONException{
// 使用该方法解析思路,遇到大括号用JsonObject,中括号用JsonArray
// 第一个是大括号{}
JSONObject jsonObj = new JSONObject(jsonStr);
// 新建Sentence对象
Sentence sentence = new Sentence();
// 以下是无脑操作
String caption = jsonObj.getString("caption");
String content = jsonObj.getString("content");
String dateline = jsonObj.getString("dateline");
String fenxiang_img = jsonObj.getString("fenxiang_img");
String love = jsonObj.getString("love");
String note = jsonObj.getString("note");
String picture = jsonObj.getString("picture");
String picture2 = jsonObj.getString("picture2");
String s_pv = jsonObj.getString("s_pv");
String sp_pv = jsonObj.getString("sp_pv");
String translation = jsonObj.getString("translation");
String tts = jsonObj.getString("tts");
sentence.caption = caption;
sentence.content = content;
sentence.dateline = dateline;
sentence.fenxiang_img = fenxiang_img;
sentence.love = love;
sentence.note = note;
sentence.picture = picture;
sentence.picture2 = picture2;
sentence.s_pv = s_pv;
sentence.sp_pv = sp_pv;
sentence.translation = translation;
sentence.tts = tts;
// 解析关键字tags,它是一个JsonArray,遇到[]
JSONArray jsonArray = jsonObj.getJSONArray("tags");
// 新建Tag集合
List<Sentence.Tag> tags = new ArrayList<Sentence.Tag>();
for(int i=0;i<jsonArray.length();i++){
Sentence.Tag tag = new Sentence.Tag();
// jsonArray里的每一项都是JsonObject
JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
tag.id = jsonObject.getInt("id");
tag.name = jsonObject.getString("name");
tags.add(tag);
}
sentence.tags = tags;
return sentence;
}使用这种方法解析JSON,看注释,没什么好多的,总结一句话就是:遇到{}用JSONObject,遇到[]用JSONArray,这样你就可以说你精通org.json解析JSON了。
- 方式二:使用JsonReader解析JSON,JsonReader解析JSON有点类似PULL解析XML,主要的方法还是nextName()将游标后移。
/** * Call requires API level 11 (current min is 8): new * android.util.JsonReader 通过org.json解析json * * @param jsonStr * json字符串 * @throws Exception */
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
public static Sentence parseJsonByJsonReader(String jsonStr)
throws Exception {
// 新建Sentence
Sentence sentence = new Sentence();
// 新建Tag集合
List<Sentence.Tag> tags = new ArrayList<Sentence.Tag>();
JsonReader reader = new JsonReader(new StringReader(jsonStr));
// 遇到{,开始解析对象
reader.beginObject();
while (reader.hasNext()) {
String name = reader.nextName();
if ("caption".equals(name)) {
sentence.caption = reader.nextString();
}
if ("content".equals(name)) {
sentence.content = reader.nextString();
}
if ("dateline".equals(name)) {
sentence.dateline = reader.nextString();
}
if ("fenxiang_img".equals(name)) {
sentence.fenxiang_img = reader.nextString();
}
if ("love".equals(name)) {
sentence.love = reader.nextString();
}
if ("note".equals(name)) {
sentence.note = reader.nextString();
}
if ("picture".equals(name)) {
sentence.picture = reader.nextString();
}
if ("picture2".equals(name)) {
sentence.picture2 = reader.nextString();
}
if ("s_pv".equals(name)) {
sentence.s_pv = reader.nextString();
}
if ("sid".equals(name)) {
sentence.sid = reader.nextString();
}
if ("sp_pv".equals(name)) {
sentence.sp_pv = reader.nextString();
}
if ("translation".equals(name)) {
sentence.translation = reader.nextString();
}
if ("tts".equals(name)) {
sentence.tts = reader.nextString();
}
if ("tags".equals(name)) {
// 遇到[,开始解析数组
reader.beginArray();
while (reader.hasNext()) {
// 遇到{,开始解析对象
reader.beginObject();
Sentence.Tag tag = new Sentence.Tag();
if ("id".equals(reader.nextName())) {
tag.id = reader.nextInt();
}
if ("name".equals(reader.nextName())) {
tag.name = reader.nextString();
}
// 遇到},对象解析结束
reader.endObject();
tags.add(tag);
}
sentence.tags = tags;
// 遇到],数组解析结束
reader.endArray();
}
}
// 遇到},对象解析结束
reader.endObject();
return sentence;
}JsonReader解析JSON:
- 当开始解析对象时(遇到”{“就JsonReader.beginObject()),当这个对象解析结束了(遇到”}”)就endObject()结束对象的解析。
- 当开始解析数组时(遇到”[“就JsonReader.beginArray()),当这个数组解析结束了(遇到”]”)就endArray()结束数组的解析。
注意nextXXX()都会是游标后移,如果有数据忘了解析等等导致游标错位,将会导致数据类型错乱,这个时候就会很容易发生:java.lang.IllegalStateException: Expected a X but was Y …参数匹配异常。所以一定不要漏了数据和注意每一次移动游标。
方式三:使用GSON解析
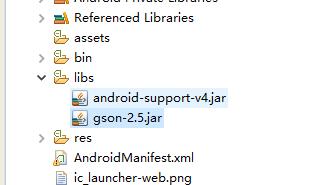
1、下载Gson包放到项目lib目录下面,并添加到构建路径中
gson的jar包下载:gson-2.5.jar
2、编写JavaBean
package com.example.jsonparsedemo;
import java.util.List;
// 由于简单起见,直接用public
public class Sentence {
public String caption;
public String content;
public String dateline;
public String fenxiang_img;
public String love;
public String note;
public String picture;
public String picture2;
public String s_pv;
public String sid;
public String sp_pv;
public String translation;
public String tts;
public List<Tag> tags;
static class Tag{
public int id;
public String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "id=" + id + "\n" +
"name=" + name + "\n" ;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "caption=" + caption + "\n" +
"content=" + content+ "\n" +
"dateline=" + dateline+ "\n" +
"fenxiang_img=" + fenxiang_img+ "\n" +
"love=" + love + "\n" +
"note=" + note + "\n" +
"picture=" + picture + "\n" +
"picture2=" + picture2 + "\n" +
"s_pv=" + s_pv + "\n" +
"sid=" + sid + "\n" +
"sp_pv="+ sp_pv + "\n" +
"translation=" + translation + "\n" +
"tts=" + tts + "\n" +
"tags=" + tags + "\n";
}
}
JavaBean的编写(重点):
- 其中属性名称和json数据的键名必须相同
- 内部类不必是static(亲测)
- 类属性可以是其他权限修饰符,包括private,并且可以不用写setter和getter(亲测)
3、新建gson对象解析json,
/** * 通过GSON解析json * @param jsonStr * @return */
public static Sentence parseJsonByGson(String jsonStr){
Gson gson = new Gson();
Sentence sentence = gson.fromJson(jsonStr, Sentence.class);
return sentence;
}就三行代码,没什么说的,到这里三种解析json的方式都介绍完了,感觉每种方式都好简单,想不精通JSON解析都难。
JsonParseUtils.java的完整代码:
package com.example.jsonparsedemo;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.StringReader;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.util.JsonReader;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
public class JsonParseUtils {
/** * 连接网络请求数据,这里使用HttpURLConnection */
public static String getJsonData() {
URL url = null;
String jsonData = ""; // 请求服务器返回的json字符串数据
InputStreamReader in = null; // 读取的内容(输入流)
try {
url = new URL("http://open.iciba.com/dsapi");
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
// 这一步会连接网络得到输入流
in = new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream());
// 为输入创建BufferedReader
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(in);
String inputLine = null;
while (((inputLine = br.readLine()) != null)) {
jsonData += inputLine;
}
in.close(); // 关闭InputStreamReader
// 断开网络连接
conn.disconnect();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return jsonData;
}
/** * 通过org.json解析json * * @param jsonStr * json字符串 * @throws JSONException * 格式不对,转换异常 */
public static Sentence parseJsonByOrgJson(String jsonStr)
throws JSONException {
// 使用该方法解析思路,遇到大括号用JsonObject,中括号用JsonArray
// 第一个是大括号
JSONObject jsonObj = new JSONObject(jsonStr);
// 新建Sentence对象
Sentence sentence = new Sentence();
// 以下是无脑操作
String caption = jsonObj.getString("caption");
String content = jsonObj.getString("content");
String dateline = jsonObj.getString("dateline");
String fenxiang_img = jsonObj.getString("fenxiang_img");
String love = jsonObj.getString("love");
String note = jsonObj.getString("note");
String picture = jsonObj.getString("picture");
String picture2 = jsonObj.getString("picture2");
String s_pv = jsonObj.getString("s_pv");
String sid = jsonObj.getString("sid");
String sp_pv = jsonObj.getString("sp_pv");
String translation = jsonObj.getString("translation");
String tts = jsonObj.getString("tts");
sentence.caption = caption;
sentence.content = content;
sentence.dateline = dateline;
sentence.fenxiang_img = fenxiang_img;
sentence.love = love;
sentence.note = note;
sentence.picture = picture;
sentence.picture2 = picture2;
sentence.s_pv = s_pv;
sentence.sid = sid;
sentence.sp_pv = sp_pv;
sentence.translation = translation;
sentence.tts = tts;
// 解析关键字tags,它是一个JsonArray
JSONArray jsonArray = jsonObj.getJSONArray("tags");
// 新建Tag集合
List<Sentence.Tag> tags = new ArrayList<Sentence.Tag>();
for (int i = 0; i < jsonArray.length(); i++) {
Sentence.Tag tag = new Sentence.Tag();
// jsonArray里的每一项都是JsonObject
JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
tag.id = jsonObject.getInt("id");
tag.name = jsonObject.getString("name");
tags.add(tag);
}
sentence.tags = tags;
return sentence;
}
/** * Call requires API level 11 (current min is 8): new * android.util.JsonReader 通过org.json解析json * * @param jsonStr * json字符串 * @throws Exception */
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
public static Sentence parseJsonByJsonReader(String jsonStr)
throws Exception {
// 新建Sentence
Sentence sentence = new Sentence();
// 新建Tag集合
List<Sentence.Tag> tags = new ArrayList<Sentence.Tag>();
JsonReader reader = new JsonReader(new StringReader(jsonStr));
// 遇到{,开始解析对象
reader.beginObject();
while (reader.hasNext()) {
String name = reader.nextName();
if ("caption".equals(name)) {
sentence.caption = reader.nextString();
}
if ("content".equals(name)) {
sentence.content = reader.nextString();
}
if ("dateline".equals(name)) {
sentence.dateline = reader.nextString();
}
if ("fenxiang_img".equals(name)) {
sentence.fenxiang_img = reader.nextString();
}
if ("love".equals(name)) {
sentence.love = reader.nextString();
}
if ("note".equals(name)) {
sentence.note = reader.nextString();
}
if ("picture".equals(name)) {
sentence.picture = reader.nextString();
}
if ("picture2".equals(name)) {
sentence.picture2 = reader.nextString();
}
if ("s_pv".equals(name)) {
sentence.s_pv = reader.nextString();
}
if ("sid".equals(name)) {
sentence.sid = reader.nextString();
}
if ("sp_pv".equals(name)) {
sentence.sp_pv = reader.nextString();
}
if ("translation".equals(name)) {
sentence.translation = reader.nextString();
}
if ("tts".equals(name)) {
sentence.tts = reader.nextString();
}
if ("tags".equals(name)) {
// 遇到[,开始解析数组
reader.beginArray();
while (reader.hasNext()) {
// 遇到{,开始解析对象
reader.beginObject();
Sentence.Tag tag = new Sentence.Tag();
if ("id".equals(reader.nextName())) {
tag.id = reader.nextInt();
}
if ("name".equals(reader.nextName())) {
tag.name = reader.nextString();
}
// 遇到},对象解析结束
reader.endObject();
tags.add(tag);
}
sentence.tags = tags;
// 遇到],数组解析结束
reader.endArray();
}
}
// 遇到},对象解析结束
reader.endObject();
return sentence;
}
/** * 通过GSON解析json * @param jsonStr * @return */
public static Sentence parseJsonByGson(String jsonStr){
Gson gson = new Gson();
Sentence sentence = gson.fromJson(jsonStr, Sentence.class);
return sentence;
}
}
四 、3种方式解析JSON实战(测试结果)
由于本篇文章并不打算将解析的数据用android控件显示出来,只是解析json数据,有了数据还不会用吗,哈哈,数据在手,天下我有。下面我们通过Android的单元测试3种方式解析的结果。
其实Android的单元测试已经在【XML解析(一)】SAX解析XML文章中介绍过了,这里为了完整性及照顾新手,这里在说一遍吧,也可以去看那篇文章。
Android单元测试
第一步:环境搭建
- 在 AndroidManifest.xml的根节点下面添加一个instrumentation
<instrumentation android:targetPackage="com.example.jsonparsedemo" android:name="android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner"></instrumentation>第二步: 新建一个测试类JsonParseTest.java(测试的类可以放在该应用的任何包下面,但必须继承AndroidTestCase)
- 写一个测试方法测试obj.json解析json
/** * 测试obj.json解析json */
public void testObjJsonParseJson() throws Exception{
Log.e("obj.json", "-------------------------");
String jsonData = JsonParseUtils.getJsonData();
Sentence sentence = JsonParseUtils.parseJsonByOrgJson(jsonData);
Log.e("result", sentence.toString());
}- 写一个测试方法测试JsonReader解析json
/** * 测试JsonReader解析json */
public void testJsonReaderParseJson() throws Exception{
Log.e("JsonReader", "-------------------------");
String jsonData = JsonParseUtils.getJsonData();
Sentence sentence = JsonParseUtils.parseJsonByJsonReader(jsonData);
Log.e("result", sentence.toString());
}- 写一个测试方法测试JsonReader解析json
/** * 测试JsonReader解析json */
public void testGsonParseJson() throws Exception{
Log.e("gson", "-------------------------");
String jsonData = JsonParseUtils.getJsonData();
Sentence sentence = JsonParseUtils.parseJsonByGson(jsonData);
Log.e("result", sentence.toString());
}分别运行上面的三个方法,Run As Android JUnit Test
测试结果:
- org.json解析结果
- JsonReader解析结果
- gson解析结果
OK,三种方法都成功解析json,是不是感觉json解析简直是太简单了,简单到不想解析。
总结:无论是XML还是JSON,或者HTML的解析都很简单,我们只要知道解析的原理和技巧就能解析任何的XML,JSON数据了,虽然在这之前还没写过解析HTML,但HTML解析也非常简单,下篇文章将会介绍如何解析HTML,实现网络爬虫,敬请期待。
由于个人水平有限,文章所介绍的知识有错误的地方,欢迎大家指出,与君共勉,一起进步。
下篇文章:【解析HTML】HTML解析,网络爬虫。敬请期待。