Bean装配细节
Bean装配细节
基本概述
在spring容器内拼凑bean叫做装配。装配bean的时候,需要告诉容器哪些bean以及容器如何使用依赖注入将它们配合在一起。
基本装配
使用XML装配
xml是最常见的spring应用系统配置源。几种spring容器都支持使用xml装配bean,包括:
1、XmlBeanFactory:调用ClassPathResource载入上下文定义文件(比如applicationContext.xml)。
2、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类路径载入上下文定义文件。
3、XmlWebApplicationContext:从web应用上下文中载入定义文件。
4、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:通过文件系统载入。
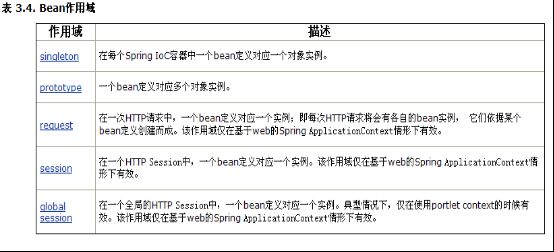
Scope
prototype、singleton、request 、session、global-sessionspring中的bean缺省情况下是单例模式。始终返回一个实例。若想返回不同的实例的话需要定义成原型模式。在Web应用中,可以使用后面三种方式。可以在<bean>元素中添加scope属性。
PS:尽量使用singleton,没有特殊用途建议不要使用prototype。
set方法注入依赖
通过<bean>元素的<property>子元素可以指明使用相应的set方法来注入依赖。可以注入任何东西,从基本类型到集合类,甚至是应用系统bean。设置null的话,可以在<property>元素下使用<null />元素。
案例1:简单Bean配置
<bean id=”xxx” class=”类全路径”>
<property name=”属性1” value=”值1” />
<property name=”属性2”>
<value>值2</value>
</property>
</bean>
案例2:引用其它Bean
<bean id="foo" class="...Foo">
<property name="name">
<ref bean="bar">
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="bar" class="...Bar">
</bean>
案例3:内部Bean
<bean id="foo" class="...Foo">
<property name="bar">
<bean class="...Bar">
</property>
</bean>
PS:内部Bean的缺点就是无法在其它地方重用,不过如果这个bean,只要为它服务的话,那么可以用内部Bean。
装配集合
除了基本类型和对象类型之外,集合类型的属性也是常用的,故有必要掌握集合在Spring的配置。
数组
<property name="empName"> <list> <value>zs</value> <value>ls</value> <value>ww</value> </list> </property>
List
<property name="empList"> <list> <ref bean="emp1" /> <ref bean="emp2" /> </list> </property>
Set
<property name="empSet"> <set> <ref bean="emp1" /> <ref bean="emp2" /> </set> </property>
Map
<property name="empMap"> <map> <entry key="1" value-ref="emp1"/> <entry key="2" value-ref="emp2"/> </map> </property>
属性集合
<property name="properties"> <props> <prop key="pp1">abcd</prop> <prop key="pp2">hello</prop> </props> </property>
案例
Bean类
package com.pc.collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 部门Bean
* @description
*
*/
public class Department {
private String name;
private String[] empName; // 数组
private List<Employee> empList; // list集合
private Set<Employee> empSet; // set集合
private Map<Integer, Employee> empMap; // map集合
private Properties properties; // Properties
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
public Map<Integer, Employee> getEmpMap() {
return empMap;
}
public void setEmpMap(Map<Integer, Employee> empMap) {
this.empMap = empMap;
}
public Set<Employee> getEmpSet() {
return empSet;
}
public void setEmpSet(Set<Employee> empSet) {
this.empSet = empSet;
}
public List<Employee> getEmpList() {
return empList;
}
public void setEmpList(List<Employee> empList) {
this.empList = empList;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String[] getEmpName() {
return empName;
}
public void setEmpName(String[] empName) {
this.empName = empName;
}
}
package com.pc.collection;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 雇员Bean
* @description
*
*/
public class Employee {
private String name;
private int id;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
配置文件:beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <!-- 在容器文件中配置bean(service/dao/domain/action/数据源) --> <bean id="department" class="com.pc.collection.Department"> <property name="name" value="开发部" /> <!-- 给数组注入值 --> <property name="empName"> <list> <value>zs</value> <value>ls</value> <value>ww</value> </list> </property> <!-- 给list注入值,可以有相同的对象 --> <property name="empList"> <list> <ref bean="emp1" /> <ref bean="emp2" /> </list> </property> <!-- 给set注入值,不可以有相同的对象 --> <property name="empSet"> <set> <ref bean="emp1" /> <ref bean="emp2" /> </set> </property> <!-- 给map注入值,只要key不一样就可以装配 --> <property name="empMap"> <map> <entry key="1" value-ref="emp1"/> <entry key="2" value-ref="emp2"/> </map> </property> <!-- 配置属性集合 --> <property name="properties"> <props> <prop key="pp1">abcd</prop> <prop key="pp2">hello</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <bean id="emp1" class="com.pc.collection.Employee"> <property name="name" value="张三" /> <property name="id" value="1" /> </bean> <bean id="emp2" class="com.pc.collection.Employee"> <property name="name" value="李四" /> <property name="id" value="2" /> </bean> </beans>
测试文件
package com.pc.collection;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 测试类
* @description
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过applicationContext获取Bean
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/pc/collection/beans.xml");
Department department = (Department) applicationContext.getBean("department");
System.out.println(department.getName());
// 测试数组
for(String empName : department.getEmpName()) {
System.out.println(empName);
}
// 测试List
System.out.println("----------通过list集合取出数据---------");
for(Employee employee : department.getEmpList()) {
System.out.println(employee.getName());
}
// 测试Set
System.out.println("----------通过set集合取出数据---------");
for(Employee employee : department.getEmpSet()) {
System.out.println(employee.getName());
}
// 测试Map
System.out.println("----------通过map集合取出数据,迭代器---------");
// 迭代器
Iterator<Integer> iterator = department.getEmpMap().keySet().iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer integer = iterator.next();
Employee employee = department.getEmpMap().get(integer);
System.out.println(integer + " " + employee.getName());
}
System.out.println("----------通过map集合取出数据,for增强---------");
// for增强
for(Entry<Integer, Employee> entry : department.getEmpMap().entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue().getName());
}
System.out.println("----------通过Properties取出数据,For增强---------");
Properties properties = department.getProperties();
for (Entry<Object, Object> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("----------通过Properties取出数据,枚举---------");
Enumeration enumeration = properties.keys();
while(enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String) enumeration.nextElement();
System.out.println(key + " " + properties.getProperty(key));
}
}
}
继承配置
当需要从父对象中继承属性配置的时候,可以采用继承配置的方式。
配置方法
<!-- 配置一个学生对象 --> <bean id="student" class="com.pc.inherit.Student"> <property name="name" value="张三" /> <property name="age" value="20" /> </bean> <!-- 配置Graduate对象 --> <bean id="graduate" parent="student" class="com.pc.inherit.Graduate"> <!-- 如果配置父对象属性,则会替换 --> <property name="name" value="李四" /> <property name="degree" value="学士" /> </bean>
案例
Bean类
package com.pc.inherit;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 学生类
* @description
*
*/
public class Student {
protected String name;
protected int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package com.pc.inherit;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 毕业生类
* @description
*
*/
public class Graduate extends Student {
private String degree;
public String getDegree() {
return degree;
}
public void setDegree(String degree) {
this.degree = degree;
}
}
配置文件:beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <!-- 在容器文件中配置bean(service/dao/domain/action/数据源) --> <!-- 配置一个学生对象 --> <bean id="student" class="com.pc.inherit.Student"> <property name="name" value="张三" /> <property name="age" value="20" /> </bean> <!-- 配置Graduate对象 --> <bean id="graduate" parent="student" class="com.pc.inherit.Graduate"> <!-- 如果配置父对象属性,则会替换 --> <property name="name" value="李四" /> <property name="degree" value="学士" /> </bean> </beans>
测试文件
package com.pc.inherit;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 通过applicationContext获取bean
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/pc/inherit/beans.xml");
Graduate graduate = (Graduate) applicationContext.getBean("graduate");
System.out.println(graduate.getName() + " " + graduate.getAge() + " " + graduate.getDegree());
}
}
通过构造方法注入值
除了通过Set方法注入外,也可以使用构造方法的方法来注入值。同时,这种注入方式带来的好处就是,可以明确知道哪些属性必须要赋值,也就是说通过构造强制依赖关系,不可能实例化不完全或者无法使用的bean。
<!-- 配置一个员工对象 --> <bean id="employee" class="com.pc.constructor.Employee"> <!-- 通过构造方法来注入属性值 --> <constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" value="张三"/> <constructor-arg index="1" type="int" value="20" /> </bean>
案例
Bean类
package com.pc.constructor;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 员工类
* @description
*
*/
public class Employee {
private String name;
private int age;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
配置文件:beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <!-- 在容器文件中配置bean(service/dao/domain/action/数据源) --> <!-- 配置一个员工对象 --> <bean id="employee" class="com.pc.constructor.Employee"> <!-- 通过构造方法来注入属性值 --> <constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" value="张三"/> <constructor-arg index="1" type="int" value="20" /> </bean> </beans>
测试文件
package com.pc.constructor;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 测试类
* @description
*
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/pc/constructor/beans.xml");
Employee employee = (Employee) applicationContext.getBean("employee");
System.out.println(employee.getName() + " " + employee.getAge());
}
}
自动装配
通过在<bean>元素中添加autowire属性来进行配置。
基本类型
1、byName:寻找和属性名相同的bean,若找不到,则装不上。
2、byType:寻找和属性类型相同的bean,找不到,装不上,找到多个抛异常。
3、constructor:查找和bean的构造参数一致的一个或多个bean,若找不到或找到多个,抛异常。
4、autodetect::(3)和(2)之间选一个方式。不确定性的处理与(3)和(2)一致。如果发现默认的构造器,那么将使用byType的方法。
5、default:这个需要在<beans defualt-autorwire=”指定” />,也就是说autowire的值继承自default-autowire的值。
6、no:不自动装配,这也是autowrite的默认值。
PS:不推荐使用自动装配,因为自动装配往往不能直观的看出哪些属性被配置了。
PS:如果<beans>指定了default-autowire属性,那么所有bean的default属性值就是这个。如果没有指定default-autowire属性,则default-autowire的默认值是no。
PS:如果使用自动装配同时使用手动装配,那么自动装配的属性,将被手动装配的属性覆盖。
案例
Bean类
package com.pc.autowire;
public class Dog {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package com.pc.autowire;
public class Master {
private String name;
private Dog dog;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
}
配置文件:beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd">
<!-- 在容器文件中配置bean(service/dao/domain/action/数据源) -->
<!-- 配置一个master对象 -->
<bean id="master" class="com.pc.autowire.Master" autowire="byName">
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
<!-- 传统set -->
<!-- <property name="dog" ref="dog" /> -->
</bean>
<!-- 配置dog对象 -->
<bean id="dog" class="com.pc.autowire.Dog">
<property name="name" value="小白" />
<property name="age" value="3" />
</bean>
</beans>
测试文件
package com.pc.autowire;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/pc/autowire/beans.xml");
Master master = (Master) applicationContext.getBean("master");
System.out.println(master.getName() + " " + master.getDog().getName());
}
}
注解装配
通过在<beans>元素下配置<context:annotation-config/>可以激活在类中探测各种注解。比如说:@Required @Autowire @PostConstrct @PreDestroy @Resource @EJB @PersistenceContext @WebServiceRef等等
装配特殊Bean
1、通过配置后加工bean,涉及到Bean和Bean工厂生命周期。
2、改变依赖注入,将字符串转换成其它类型。
3、从属性文本装载信息,包括信息国际化。
4、监听并处理其它bean及spring发布的系统消息。
5、知道自己在spring中的唯一表识。
案例
Bean类
package com.pc.dispatch;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 数据库连接信息Bean
* @description
*
*/
public class DBUtil {
private String drivername;
private String uri;
private String name;
private String pwd;
public String getDrivername() {
return drivername;
}
public void setDrivername(String drivername) {
this.drivername = drivername;
}
public String getUri() {
return uri;
}
public void setUri(String uri) {
this.uri = uri;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
}
属性文件:db.properties
#key = value name=scott drivername=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver uri=jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:SWITCH pwd=123456
配置文件:beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd">
<!-- 在容器文件中配置bean(service/dao/domain/action/数据源) -->
<!-- 配置一个DBUtil对象 -->
<!-- 普通方式 -->
<!--
<bean id="dbutil" class="com.pc.dispatch.DBUtil">
<property name="name" value="scott" />
<property name="drivername" value="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"/>
<property name="uri" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:SWITCH" />
<property name="pwd" value="123456" />
</bean>
-->
<!-- 分散配置,引入db.properties文件 -->
<!-- location属性值中的classpath可以通过,隔开,配置多个属性文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:com/pc/dispatch/db.properties"/>
<bean id="dbutil" class="com.pc.dispatch.DBUtil">
<!-- $占位符,使用占位符代替硬编码 -->
<property name="name" value="${name}" />
<property name="drivername" value="${drivername}" />
<property name="uri" value="${uri}" />
<property name="pwd" value="${pwd}" />
</bean>
</beans>
测试文件
package com.pc.dispatch;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/pc/dispatch/beans.xml");
DBUtil dbUtil = (DBUtil) applicationContext.getBean("dbutil");
System.out.println(dbUtil.getDrivername());
System.out.println(dbUtil.getUri());
System.out.println(dbUtil.getName());
System.out.println(dbUtil.getPwd());
}
}
PS:除了分散配置的Bean之外,还有后处理器BeanPostProcessor,三个感知Bean,分别感知自己的名字BeanNameAware,感知自己所处的Bean工厂BeanFactoryAware,感知所在上下文ApplicationContexAware。