【MVC 4】2.使用 Razor
作者:[美]Adam Freeman 来源:《精通ASP.NET MVC 4》
Razor 是微软 MVC3 引入的视图引擎的名称,并在MVC 4 中进行了修订。视图引擎处理 ASP.NET内容,并查找指令,典型的是将动态内容插入到发送给浏览器的输出。
微软维持了两个视图引擎 —— 已经支持 ASP.NET 开发许多年的基于<% 和 %>标签的 ASPX 引擎,以及以@字符标注内容范围的 Razor 引擎。
1.创建示例项目
打开Microsoft Visual Studio 2012 ,新建MVC 4项目 Razor ,选择空模板。
1.1 定义模型
在 Models 文件夹下新建类文件 Product.cs
namespace Razor.Models { public class Product { public int ProductID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public string Description { get; set; } public decimal Price { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } } }
1.2 定义控制器
在 Controllers 文件夹下新建控制器 HomeController ,模板为空
namespace Razor.Controllers { /** * 此类定义了一个叫做 Index 的动作方法,创建了一个Product 对象,并对其进行属性填充。 * 将此Product 对象传递给了 View 方法,以便在渲染视图时使用它。 * */ public class HomeController : Controller { Product myProduct = new Product { ProductID = 1, Name = "Kayak", Description = "A boat for one person", Category = "Watersports", Price = 275M }; public ActionResult Index() { return View(myProduct); } } }
1.3 创建视图
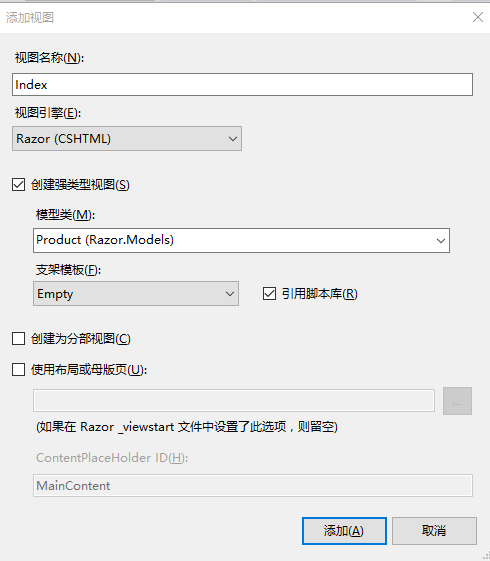
右击 HomeController 类的 Index 方法,添加视图文件 Index.cshtml ,模型类为 Razor.Models.Product
@model Razor.Models.Product @{ Layout = null; } <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> <title>Index</title> </head> <body> <div> </div> </body> </html>
2.使用模型对象
从视图第一行开始
...
@model Razor.Models.Product
...
Razor 语句以@字符开始。此处@model 语句声明了通过动作方法传递给该视图的模型对象的类型。这让用户能够通过@Model 来引用视图模型对象的方法、字段和属性。
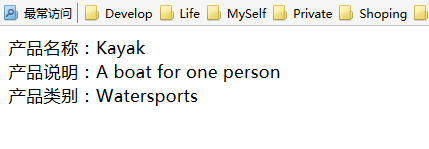
@model Razor.Models.Product @{ Layout = null; } <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> <title>Index</title> </head> <body> <div> 产品名称:@Model.Name </div> <div> 产品说明:@Model.Description </div> <div> 产品类别:@Model.Category </div> </body> </html>
显示效果:
* 声明视图模型对象的类型使用@model (小写m),而访问Name 属性使用@Model (大写M)。
3.使用布局
Index.cshtml 视图文件中的另一个 Razor 表达式如下所示:
...
@{
Layout = null;
}
...
这是一个 Razor 代码块的例子,这种代码块能够在视图中包含C#语句。这种代码块以@{开始,以}结束,而其中的语句会在视图被渲染时进行执行。
此处将Layout 设置为null的效果是告诉 MVC 框架,改视图是自包含的,并且会渲染返回给客户端所需要的全部内容。
3.1 创建布局
右击Views 文件夹新建 "MVC 4布局页(Razor)",文件名为 _BaseLayout.cshtml 。布局的最初内容如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> <title>@ViewBag.Title</title> </head> <body> <div> @RenderBody() </div> </body> </html>
布局是特殊形式的视图。对@RenderBody 方法的调用会将动作方法所指定的视图内容插入到布局标记中。布局中的另一个 Razor 表达式会在 ViewBag 中查找一个叫做 Title 的属性,目的是设置 title 元素的内容。
修改布局文件如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> <title>@ViewBag.Title</title> </head> <body> <div> <h1>Product Information</h1> <div style="padding:20px;border:solid medium black;font-size:20pt;"> @RenderBody() </div> <h2>Visit <a href="http://apress.com">Apress</a></h2> </div> </body> </html>
3.2 运用布局
为了将布局文件运用于视图,只需要设置 Layout 属性的值。修改 Index.cshtml 如下:
@model Razor.Models.Product @{ ViewBag.Title = "Product Info"; Layout = "~/Views/_BaseLayout.cshtml"; } <div> 产品名称:@Model.Name </div> <div> 产品说明:@Model.Description </div> <div> 产品类别:@Model.Category </div> <div> 产品价格:[email protected] </div>
显示效果如下图所示:
3.3 使用视图起始文件
还有个小问题要解决,这就是,必须在每一个视图中都要指定布局文件。这意味着,要重新命名布局文件,那么必须找出引用该布局的每一个视图并进行修改,这将是一个易错的过程。
通过使用视图起始文件可以解决此问题。在渲染一个视图时,MVC 框架会查找一个叫作 _ViewStart.cshtml 的文件。框架会将此文件的内容视为视图文件的一部分,于是用户可以使用这一特性为 Layout 属性自动的设置一个值。
同样,在Views 文件夹下新建"MVC 4布局页(Razor)",文件名为 _ViewStart.cshtml ,修改文件内容为:
@{
Layout = "~/Views/_BaseLayout.cshtml";
}
此视图起始文件含有 Layout 属性的值,这意味着用户可以去除 Index.cshtml 文件中相应的语句:
@model Razor.Models.Product @{ ViewBag.Title = "Product Info"; } <div> 产品名称:@Model.Name </div> <div> 产品说明:@Model.Description </div> <div> 产品类别:@Model.Category </div> <div> 产品价格:[email protected] </div>
不必以任何方式指定希望使用的视图起始文件。MVC 框架会对此文件进行定位,并自动地使用其内容。若在视图文件中重新定义了 Layout 值,会覆盖视图起始文件中所指定的布局。
3.4 演示共享布局
在控制器文件 HomeController 中新建方法 NameAndPrice 如下:
public ActionResult NameAndPrice()
{
return View(myProduct);
}
添加对应的视图文件 NameAndPrice.cshtml 如下
@model Razor.Models.Product @{ ViewBag.Title = "NameAndPrice"; Layout = "~/Views/_BaseLayout.cshtml"; } <h2>NameAndPrice</h2> The product name is @Model.Name and it costs [email protected]
启动并导航到 /Home/NameAndPrice ,显示效果如下:
4.使用 Razor 表达式
在一个好的MVC框架应用程序中,动作方法与视图所起的作用是清晰分离的。
| 动作方法与视图所起的作用 | ||
| 组件 | 要做的事 | 不做的事 |
| 动作方法 | 向视图传递一个视图模型 | 向视图传递格式化的数据 |
| 视图 | 使用视图模型对象向用户表现内容 | 修改视图模型对象的任何方面 |
4.1插入数据值
用 Razor 表达式能做的最简单的事情是将数据值插入到标记中。用户可以用@Model 表达式来做这件事情,以引用视图模型对象所定义的属性和方法,或者使用@Viewbag 表达式,以引用通过视图包特性动态定义的属性。
在 Home 控制器中新增动作方法 DemoExpressions
public ActionResult DemoExpressions() { ViewBag.ProductCount = 1; ViewBag.ExpressShip = true; ViewBag.ApplyDiscount = false; ViewBag.Supplier = null; return View(myProduct); }
并创建对应的视图文件 DemoExpression.cshtml
@model Razor.Models.Product @{ ViewBag.Title = "DemoExpressions"; } <table> <thead> <tr><th>Property</th><th>Value</th></tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr><th>Name</th><th>@Model.Name</th></tr> <tr><th>Price</th><th>@Model.Price</th></tr> <tr><th>Stock Level</th><th>@ViewBag.ProductCount</th></tr> </tbody> </table>
导航到对应的URL /Home/DemoExpressions ,显示效果如下:
4.2 设置标签属性的值
到此为止的所有例子都是设置元素内容,但用户也可以使用Razor 表达式来设置元素标签的值。修改视图文件 DemoExpressions.cshtml 文件如下:
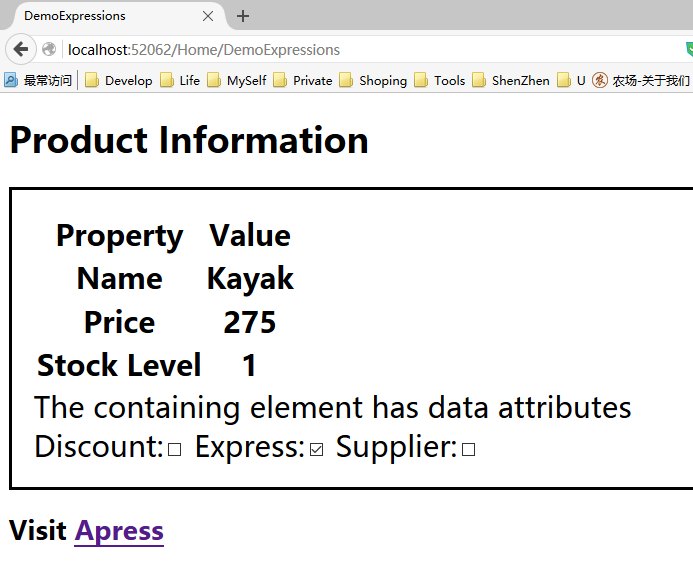
@model Razor.Models.Product @{ ViewBag.Title = "DemoExpressions"; } <table> <thead> <tr><th>Property</th><th>Value</th></tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr><th>Name</th><th>@Model.Name</th></tr> <tr><th>Price</th><th>@Model.Price</th></tr> <tr><th>Stock Level</th><th>@ViewBag.ProductCount</th></tr> </tbody> </table> <div data-discount="@ViewBag.ApplyDiscount" data-express="@ViewBag.ExpressShip" data-supplier="@ViewBag.Supplier"> The containing element has data attributes </div> Discount:<input type="checkbox" checked="@ViewBag.ApplyDiscount"/> Express:<input type="checkbox" checked="@ViewBag.ExpressShip" /> Supplier:<input type="checkbox" checked="@ViewBag.Supplier" />
显示效果如下:
4.3 使用条件语句
修改视图文件 DemoExpressions.cshtml 文件如下:
@model Razor.Models.Product @{ ViewBag.Title = "DemoExpressions"; } <table> <thead> <tr><th>Property</th><th>Value</th></tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr><th>Name</th><th>@Model.Name</th></tr> <tr><th>Price</th><th>@Model.Price</th></tr> <tr><th>Stock</th> <th> @switch ((int)ViewBag.ProductCount) { case 0: @:Out of Stock break; case 1: <b>Low Stock (@ViewBag.ProductCount)</b> break; default: @ViewBag.ProductCount break; } </th> </tr> </tbody> </table>
为了开始一个条件语句,要在C# 的条件关键字前放一个@字符。在此例中,此条件关键字 switch。就像在规则的C# 代码块中的一样,要以闭花括号{}来终止代码块
在 Razor 代码块的内部,只要通过定义HTML 以及Razor 表达式,就可以将HTML 元素和数值插入到视图输出,例如:
... <b>Low Stock (@ViewBag.ProductCount)</b> ...
@ViewBag.ProductCount
...
不必将元素或表达式放在引号内或以特殊的方式来表示它们——Razor 引擎会将这些解释为正常方式处理的输出。然而,如果想将未包含在HTML 元素中的文字文本插入到视图,则需要使用Razor 的一个辅助工具,并以它作为这一行的前缀,例如:
...
@:Out of Stock
...
@:字符阻止Razor 将此行解释为一条C# 语句,这是Razor 遇到文本时的默认行为。
此例显示效果如下:
把此例的switch语句改成if语句,也可产生同样的效果:
@if (ViewBag.ProductCount == 0) { @:Out of Stock } else if (ViewBag.ProductCount == 1) { <b>Low Stock (@ViewBag.ProductCount)</b> } else { @ViewBag.ProductCount }
4.4 枚举数组和集合
在编写MVC 应用程序时,用户会经常希望枚举一个数组或一些其他形式对象集合的内容,并生成一种细节内容。
在 Home 控制器文件 HomeController.cs 中新建动作方法 DemoArray
public ActionResult DemoArray() { Product[] array = { new Product{Name="Kayak",Price=275M}, new Product{Name="Lifejacket",Price=48.95M}, new Product{Name="Soccer",Price=19.50M}, new Product{Name="Corner flag",Price=34.95M} }; return View(array); }
然后创建对应的视图文件DemoArray.cshtml
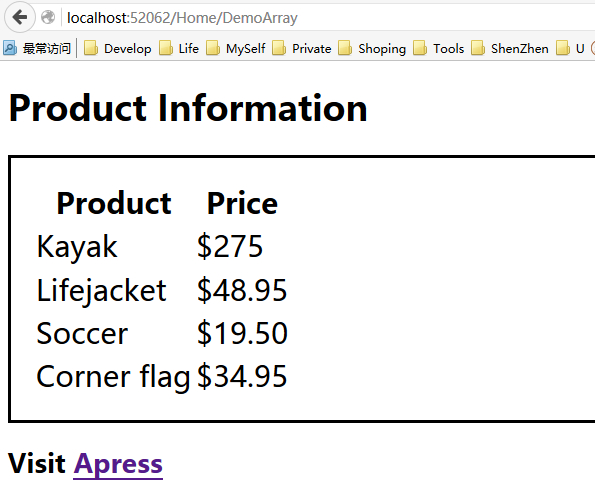
@model Razor.Models.Product[] @{ ViewBag.Title = "DemoArray"; } @if (Model.Length > 0) { <table> <thead><tr><th>Product</th><th>Price</th></tr></thead> <tbody> @foreach(Razor.Models.Product p in Model){ <tr> <td>@p.Name</td> <td>[email protected]</td> </tr> } </tbody> </table> }
导航到对应的URL地址:/Home/DemoArray ,效果图如下:
4.5 处理命名空间
此例在最好的foreach 循环中使用了全限定名的Product 类:
...
@foreach(Razor.Models.Product p in Model)
...
可以对一个视图运用@using 表达式,以引入命名空间:
@using Razor.Models; @model Product[] @{ ViewBag.Title = "DemoArray"; } @if (Model.Length > 0) { <table> <thead><tr><th>Product</th><th>Price</th></tr></thead> <tbody> @foreach(Product p in Model){ <tr> <td>@p.Name</td> <td>[email protected]</td> </tr> } </tbody> </table> }