1057. Stack (30)五种解法总结(大杂烩)
题面
1057. Stack (30)
Stack is one of the most fundamental data structures, which is based on the principle of Last In First Out (LIFO). The basic operations include Push (inserting an element onto the top position) and Pop (deleting the top element). Now you are supposed to implement a stack with an extra operation: PeekMedian -- return the median value of all the elements in the stack. With N elements, the median value is defined to be the (N/2)-th smallest element if N is even, or ((N+1)/2)-th if N is odd.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (<= 105). Then N lines follow, each contains a command in one of the following 3 formats:
Push keyPop
PeekMedian
where key is a positive integer no more than 105.
Output Specification:
For each Push command, insert key into the stack and output nothing. For each Pop or PeekMedian command, print in a line the corresponding returned value. If the command is invalid, print "Invalid" instead.
Sample Input:17 Pop PeekMedian Push 3 PeekMedian Push 2 PeekMedian Push 1 PeekMedian Pop Pop Push 5 Push 4 PeekMedian Pop Pop Pop PopSample Output:
Invalid Invalid 3 2 2 1 2 4 4 5 3 Invalid
解题思路
1.树状数组+二分查找
树状数组(Binary Indexed Tree(BIT))是一种能高效查找前缀和的数据结构,具体实现原理见鄙人还没写好的拙作《树状数组的复习》。使用树状数组是为了能进行二分查找,原先遍历Count数组,最多的时候能遍历10^5次,运用二分查找可以将查找次数优化为lg(10^5)/lg(2) < 15
下面是代码
# include <cstdio>
# include <stack>
using namespace std;
class BIT
{
private:
int *Elem;
int Size;
int lowbit(int n)
{
return n&(-n);
}
public:
BIT(int size):Size(size+1) /*想想看还是+1好了,要不申请了100的空间只能用到99感觉太奇怪了*/
{
Elem = new int[Size];
for (int i=0;i<Size;i++)/*还没试过用memset初始化,下次试试*/
Elem[i] = 0;
}
int GetSum(int right)/*[0,right]*/
{
int sum = 0;
while (right)
{
sum += Elem[right];
right -= lowbit(right);
}
return sum;
}
int GetSum(int left,int right)/*[left,right]*/
{
return GetSum(left-1) - GetSum(right);
}
void Add(int value,int index)
{
while (index < Size)
{
Elem[index] += value;
index += lowbit(index);
}
}
~BIT()
{
delete[] Elem;
}
};
BIT bit(100000);
int getmid(int size)
{
int index = (size+1)/2;
int left = 1,right = 100000,mid;
while(left<right)
{
mid = (left+right)/2;
if(bit.GetSum(mid)<index)
left = mid+1;
else
right = mid;
}
return left;
}
int main()
{
int n,tmp;
scanf("%d",&n);
stack<int> s;
char str[10];
while (n--)
{
scanf("%s",str);
switch(str[1])
{
case 'e':
{
if (s.empty())
printf("Invalid\n");
else
printf("%d\n",getmid(s.size()));
break;
}
case 'o':
{
if (s.empty())
printf("Invalid\n");
else
{
tmp = s.top();s.pop();
printf("%d\n",tmp);
bit.Add(-1,tmp);
}
break;
}
case 'u':
{
scanf("%d",&tmp);s.push(tmp);
bit.Add(1,tmp);
}
break;
}
}
return 0;
}</span>
2.分桶法(分治,分层HASH,平方分割)本人快乐的原创
分桶法的基本思路是分治,在一开始的暴力解法中,我们可以认为Count数组是一个大的桶,这个大的桶里有5*10^5个小桶,每个小桶能装一个数,在分桶法中,我们建立多个大桶,每个桶中又有小桶,比如,我们建立多个500个大桶,每个桶的容量是100,同时记录每个大桶中存放的数据的个数,在查找的时候我们可以通过每个大桶中元素的快速定位到放置中位数的那个小桶。当然你可以认为这是一种HASH,hash(key) = key/10。设每个大桶中含有k个小桶,共有m个大桶,m*k = n为定值。则一开始我们需要遍历大小为m的大桶数组,后来要遍历大小为k的单个大桶,时间复杂度为O(max(k,m))在n*k为定值的情况下,易知m = k = (m*k)^(1/2)的时候效率最高为n^(1/2)。
本题中为了方便,采用分层hash的策略,将值为key的元素放入bucke[k/100][k%100]中。
# include <cstdio>
# include <stack>
using namespace std;
const int _size = 100000;
const int capi = 500;
int bucket[_size/capi][capi];
int count[_size/capi];
int getmid(int size)
{
int ind = (size+1)/2,cnt=0,i,j;
for (i=0;i<_size/capi;i++)
{
if (cnt + count[i]>=ind)
break;
cnt += count[i];
}
for (j=0;j<capi;j++)
{
cnt += bucket[i][j];
if (cnt>=ind)
return j+i*capi;
}
}
char str[10];
int main()
{
int n,tmp;
scanf("%d",&n);
stack<int> s;
while (n--)
{
scanf("%s",str);
switch(str[1])
{
case 'e':
{
if (s.empty())
printf("Invalid\n");
else
printf("%d\n",getmid(s.size())+1);
break;
}
case 'o':
{
if (s.empty())
printf("Invalid\n");
else
{
tmp = s.top();s.pop();
printf("%d\n",tmp);
tmp--;
bucket[tmp/capi][tmp%capi]--;
count[tmp/capi]--;
}
break;
}
case 'u':
{
scanf("%d",&tmp);s.push(tmp);
tmp--;
bucket[tmp/capi][tmp%capi]++;
count[tmp/capi]++;
}
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
最后我想说的就是,
1.这个方法和树状数组+二分的方法并无矛盾,你同样可以用树状数组优化大桶元素的前缀和。
2.还有就是如果你乐意你完全可以多分几个层玩,比如key放在bucket[...][...][...],分层分多了以后,你会发现这个桶变成了一棵树,如果你分层的依据是二分法,你还会发现,你分出了一棵线段树。
3.如果数据范围增大,你可以修改hash使其映射到更小的空间,同时将每个大桶改为vector<int>数组,查询是对每个vector<int>中的元素排序,个人感觉不会很慢
3.线段树(分治)有种杀鸡用牛刀的感觉
# include <cstdio>
# include <stack>
using namespace std;
typedef int Node;
class zkw_segtree
{
private:
Node *T;
int size;
public:
zkw_segtree(int range)
{
for (size = 1;size < range+2;size<<=1);
T = new Node[2*size];
for (int i=1;i<size+size;i++)
T[i] = 0;
}
void Add(int value,int i)
{
for (i+=size;i;i>>=1)
T[i] += value;
}
int Query(int s,int t)
{
int ret = 0;
for (s+=size-1,t+=size+1;s^t^1;s>>=1,t>>=1)
{
if (~s^1) ret += T[s^1];
if (t^1) ret += T[t^1];
}
return ret;
}
int Find_Kth(int k,int root = 1)
{
while (root<<1 < size<<1)
{
if (T[root<<1]>=k) root = root<<1;
else
{
k -= T[root<<1];
root = (root<<1) + 1;
}
}
return root - size;
}
~zkw_segtree()
{
delete[] T;
}
};
zkw_segtree segtree(100000);
int main()
{
int n,tmp;
scanf("%d",&n);
stack<int> s;
char str[10];
while (n--)
{
scanf("%s",str);
switch(str[1])
{
case 'e':
{
if (s.empty())
printf("Invalid\n");
else
printf("%d\n",segtree.Find_Kth((s.size()+1)/2));
break;
}
case 'o':
{
if (s.empty())
printf("Invalid\n");
else
{
tmp = s.top();s.pop();
printf("%d\n",tmp);
segtree.Add(-1,tmp);
}
break;
}
case 'u':
{
scanf("%d",&tmp);s.push(tmp);
segtree.Add(1,tmp);
}
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
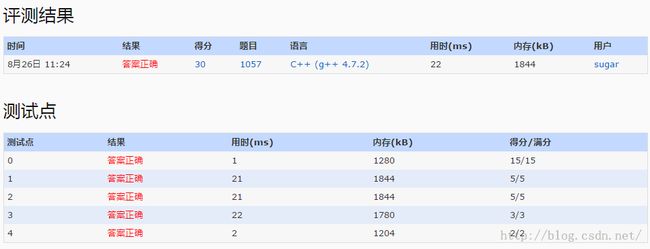
4.Prioriry Queue On Multiset(红黑树是支持插入与删除的堆)真正的牛刀
以下是代码
# include <cstdio>
# include <stack>
# include <set>
using namespace std;
const int debug = 1;
typedef int T;
class Find_Median
{
private:
multiset<T,greater<T> > maxheap;
multiset<T,less<T> > minheap;
public:
void Push(T data)
{
if (maxheap.size() < minheap.size())
maxheap.insert(data);
else
minheap.insert(data);
}
bool Erase(T data)
{
multiset<T>::iterator it;
if ((it=maxheap.find(data))!=maxheap.end())
maxheap.erase(it);
else if ((it=minheap.find(data))!=minheap.end())
minheap.erase(it);
else
return false;
return true;
}
T Query()
{
while (maxheap.size() < minheap.size())
{
maxheap.insert(*minheap.begin());
minheap.erase(minheap.begin());
}
while (minheap.size() < maxheap.size())
{
minheap.insert(*maxheap.begin());
maxheap.erase(maxheap.begin());
}
if (maxheap.size()==0) return *minheap.begin();
if (minheap.size()==0) return *maxheap.begin();
multiset<T>::iterator maxtop = maxheap.begin();
multiset<T>::iterator mintop = minheap.begin();
while (*maxtop > *mintop)
{
maxheap.insert(*mintop);
minheap.insert(*maxtop);
maxheap.erase(maxtop);
minheap.erase(mintop);
maxtop = maxheap.begin();
mintop = minheap.begin();
}
return *(maxheap.size() >= minheap.size()?maxtop:mintop);
}
};
Find_Median FM;
int main()
{
int n,tmp;
scanf("%d",&n);
stack<int> s;
char str[10];
while (n--)
{
scanf("%s",str);
switch(str[1])
{
case 'e':
{
if (s.empty()) printf("Invalid\n");
else
printf("%d\n",FM.Query());
break;
}
case 'o':
{
if (s.empty()) printf("Invalid\n");
else
{
tmp = s.top();s.pop();
printf("%d\n",tmp);
FM.Erase(tmp);
}
break;
}
case 'u':
{
scanf("%d",&tmp);s.push(tmp);
FM.Push(tmp);
}
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
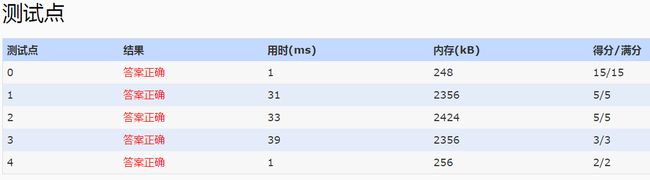
5. 平衡搜索树——Treap(我觉得从前维护两个set求中间值是牛刀,那时我还小)
很久没有更新这篇文章了,这段时间我考完了PAT,虽然没有拿到满分,但是这个成绩我也比较满意了,后来发生一些乱七八糟的事,现在也总算混进了集训队,也学到了一些东西吧。
Treap就是其中一个东西,不过主标题是平衡搜索树,就是说这道题可以使用平衡搜索树来实现,而treap只是其中一种方法。
我们先考虑不是平衡搜索树,而是一棵普通搜索树的情况,对于每棵树我们记录这个树中总共有几个节点。
现在记lsize是左子树的规模,rsize是右子树的规模。
当我们需要查找第K小的数时
如果K<=lsize,说明我们要到左子树中去查找第K大的数。
如果K>lsize+1,说明我们要到右子树中查找第第K-(lsize+1)的数
如果前两项不符合,说明当前节点就是我们需要寻找的第K小值,直接返回结果
然后解释为什么要使用平衡树,不用平衡树查找时间会很长,虽然我没有试过会不会超时。
最后安利一下Treap这个数据结构,毫无疑问是最好写的平衡二叉树,没有之一。我至今不会写红黑书,AVL树写了两次,差点把我写哭出来。但是Treap能在需要的时候随手敲出一个来。
以下是代码,虽然这段代码看起来很长,但是前头那个名片可以删除,头文件可以删除一部分,正文部分比较长是因为我出于效率考虑在单个节点中添加cnt记录重复节点的个数,这让代码变得很长,不这样做应该也是可以过的。
PS:习惯使用cin,cout的同学请小心,这道题目如果不取消cin,cout和标准输入输出流的同步,输入输出起码能用掉80ms,不要问我是怎么知道的。
/***************************************************************** > File Name: tmp.cpp > Author: Uncle_Sugar > Mail: [email protected] > Created Time: 2016年02月29日 星期一 13时28分28秒 *****************************************************************/ # include <cstdio> # include <cstring> # include <cmath> # include <cstdlib> # include <climits> # include <iostream> # include <iomanip> # include <set> # include <map> # include <vector> # include <stack> # include <queue> # include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int debug = 1; const int size = 5000 + 10; typedef long long ll; struct Treap_Node{ int value; int fix,cnt,size; Treap_Node *left,*right; Treap_Node():cnt(0),size(0),left(NULL),right(NULL){} Treap_Node(int _value):value(_value),cnt(0),size(0),left(NULL),right(NULL){} }*root = NULL; inline void Treap_SetSize(Treap_Node *&P){ if (P){ P->size = P->cnt; if (P->left) P->size += P->left->size; if (P->right) P->size += P->right->size; } } inline int lsize(Treap_Node *&P){ return P->left?P->left->size:0; } inline int rsize(Treap_Node *&P){ return P->right?P->right->size:0; } void Treap_Left_Rotate(Treap_Node *&a){ Treap_Node *b = a->right; a->right = b->left; b->left = a; a = b; Treap_SetSize(a->left); Treap_SetSize(a->right); Treap_SetSize(a); } void Treap_Right_Rotate(Treap_Node *&a){ Treap_Node *b = a->left; a->left = b->right; b->right = a; a = b; Treap_SetSize(a->left); Treap_SetSize(a->right); Treap_SetSize(a); } void Treap_Insert(Treap_Node *&P,int value){ if (!P){ P = new Treap_Node; P->value = value; P->fix = rand(); } if (value < P->value){ Treap_Insert(P->left,value); if (P->left->fix < P->fix) Treap_Right_Rotate(P); } else if (P->value < value){ Treap_Insert(P->right,value); if (P->right->fix < P->fix) Treap_Left_Rotate(P); } else { P->cnt++; } Treap_SetSize(P); } bool Treap_Delete(Treap_Node *&P,int value){ bool ret = false; if (!P) { ret = false; } else { if (value < P->value) Treap_Delete(P->left,value); else if (P->value < value) Treap_Delete(P->right,value); else { if (P->cnt==0||(--P->cnt)==0){ if (!P->left||!P->right){ Treap_Node *t = P; if (!P->right) P = P->left; else P = P->right; delete t; ret = true; } else if (P->left->fix < P->right->fix){ Treap_Right_Rotate(P); ret = Treap_Delete(P->right,value); } else { Treap_Left_Rotate(P); ret = Treap_Delete(P->left,value); } } } Treap_SetSize(P); } return ret; } Treap_Node* Treap_Findkth(Treap_Node *&P,int k){ if (k <= lsize(P)) return Treap_Findkth(P->left,k); else if (k > lsize(P)+P->cnt) return Treap_Findkth(P->right,k-(lsize(P)+P->cnt)); else return P; } void Treap_Clear(Treap_Node *&root){ if (root->left) Treap_Clear(root->left); if (root->right) Treap_Clear(root->right); delete root; root = NULL; } stack<int> stk; void push(){ int tmp; cin >> tmp; stk.push(tmp); Treap_Insert(root,tmp); } void pop(){ if (stk.empty()){ cout << "Invalid\n"; }else{ cout << stk.top() << '\n'; Treap_Delete(root,stk.top()); stk.pop(); } } void peekmedian(){ if (stk.empty()) cout << "Invalid\n"; else { Treap_Node *T = Treap_Findkth(root,(stk.size()+1)/2); cout << T->value << '\n'; } } void InOrderTravel(Treap_Node* root){ if (root->left) InOrderTravel(root->left); cout << root->value << ' ' << root->cnt << '\n'; if (root->right) InOrderTravel(root->right); } int main() { std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0); int i,j,k; int n; cin >> n; char cmd[100]; for (i=1;i<=n;i++){ cin >> cmd; switch (cmd[1]){ case 'u':push();break; case 'o':pop();break; case 'e':peekmedian();break; } } return 0; }
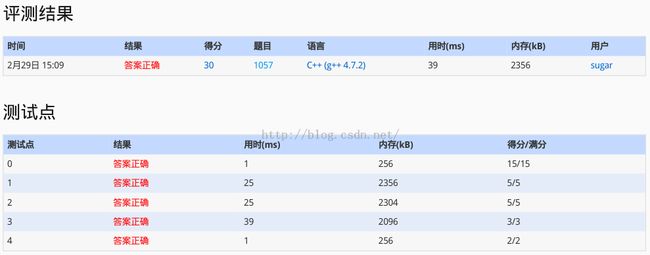
速度吗,还是可以的,貌似3号样例有一点点化时间