poj1609 Tiling Up Blocks
Tiling Up Blocks
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 4964 | Accepted: 1946 |
Description
Michael The Kid receives an interesting game set from his grandparent as his birthday gift. Inside the game set box, there are n tiling blocks and each block has a form as follows:
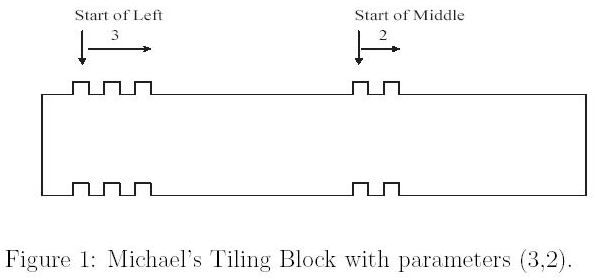
Each tiling block is associated with two parameters (l,m), meaning that the upper face of the block is packed with l protruding knobs on the left and m protruding knobs on the middle. Correspondingly, the bottom face of an (l,m)-block is carved with l caving dens on the left and m dens on the middle.
It is easily seen that an (l,m)-block can be tiled upon another (l,m)-block. However,this is not the only way for us to tile up the blocks. Actually, an (l,m)-block can be tiled upon another (l',m')-block if and only if l >= l' and m >= m'.
Now the puzzle that Michael wants to solve is to decide what is the tallest tiling blocks he can make out of the given n blocks within his game box. In other words, you are given a collection of n blocks B = {b1, b2, . . . , bn} and each block bi is associated with two parameters (li,mi). The objective of the problem is to decide the number of tallest tiling blocks made from B.

Each tiling block is associated with two parameters (l,m), meaning that the upper face of the block is packed with l protruding knobs on the left and m protruding knobs on the middle. Correspondingly, the bottom face of an (l,m)-block is carved with l caving dens on the left and m dens on the middle.
It is easily seen that an (l,m)-block can be tiled upon another (l,m)-block. However,this is not the only way for us to tile up the blocks. Actually, an (l,m)-block can be tiled upon another (l',m')-block if and only if l >= l' and m >= m'.
Now the puzzle that Michael wants to solve is to decide what is the tallest tiling blocks he can make out of the given n blocks within his game box. In other words, you are given a collection of n blocks B = {b1, b2, . . . , bn} and each block bi is associated with two parameters (li,mi). The objective of the problem is to decide the number of tallest tiling blocks made from B.
Input
Several sets of tiling blocks. The inputs are just a list of integers.For each set of tiling blocks, the first integer n represents the number of blocks within the game box. Following n, there will be n lines specifying parameters of blocks in B; each line contains exactly two integers, representing left and middle parameters of the i-th block, namely, li and mi. In other words, a game box is just a collection of n blocks B = {b1, b2, . . . , bn} and each block bi is associated with two parameters (li,mi).
Note that n can be as large as 10000 and li and mi are in the range from 1 to 100.
An integer n = 0 (zero) signifies the end of input.
Note that n can be as large as 10000 and li and mi are in the range from 1 to 100.
An integer n = 0 (zero) signifies the end of input.
Output
For each set of tiling blocks B, output the number of the tallest tiling blocks can be made out of B. Output a single star '*' to signify the end of
outputs.
outputs.
Sample Input
3 3 2 1 1 2 3 5 4 2 2 4 3 3 1 1 5 5 0
Sample Output
2 3 *
这道题按照第一维降序排序后,就是LIS了,不过数据量大,需要O(nlogn)的算法。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct block{
int l,m;
bool operator<(const block &a)const{
if(l==a.l) return m>a.m;
return l>a.l;
}
}p[10010];
struct cmp{
bool operator()(const int &a,const int &b)const{
return a>b;
}
};
int dp[10010];
int main()
{
int n,a,b;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&p[i].l,&p[i].m);
}
sort(p,p+n);
dp[0]=p[0].m;
int tot=1;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int id=upper_bound(dp,dp+tot,p[i].m,cmp())-dp;
dp[id]=p[i].m;
if(id==tot) ++tot;
}
printf("%d\n",tot);
}
puts("*");
return 0;
}
但是此题有更好的解法,dp[i][j]表示第一维小于等于i并且第二维小于等于j的最优解,那么dp[i][j]=max(dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j]}+w[i][j];