Directx11学习笔记【五】 基本的数学知识----向量篇
本文参考dx11龙书 Chapter1 vector algebra(向量代数)
要想学好游戏编程,扎实的数学知识是尤为重要的,下面将对dx11龙书中有关向量的数学知识做一下总结。
在数学中,几何向量(也称为欧几里得向量,通常简称向量、矢量),指具有大小(magnitude)和方向(direction)的几何对象,可以形象化地表示为带箭头的线段,箭头所指:代表向量的方向、线段长度:代表向量的大小。
向量的表示方式一般有3种:
1.代数表示:一般印刷用黑体小写字母α、β、γ…或a、b、c… 等来表示,手写用在a、b、c…等字母上加一箭头表示
2.几何表示:用有向线段表示
3.坐标表示
(注:directx使用的是左手系,下面不作说明均以左手系为准)
向量的一些基本操作(部分摘自百度百科):
1.向量的模,即向量的长度。
向量a的模记作|a|。向量的模是非负实数,是可以比较大小的。向量a=(x,y), ![]() 。因为方向不能比较大小,所以向量也就不能比较大小。对于向量来说“大于”和“小于”的概念是没有意义的。例如,“向量AB>向量CD”是没有意义的。
。因为方向不能比较大小,所以向量也就不能比较大小。对于向量来说“大于”和“小于”的概念是没有意义的。例如,“向量AB>向量CD”是没有意义的。
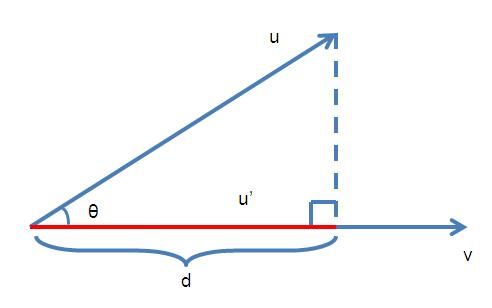
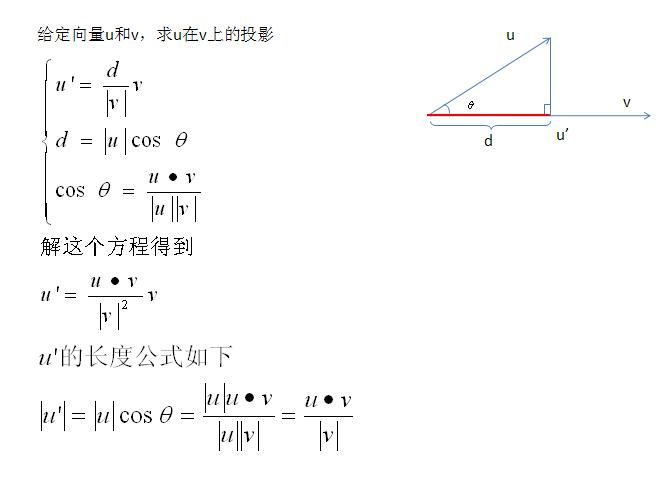
给定一个向量u和v,求u在v上的投影向量,如下图。
假设u在v上的投影向量是u’,且向量u和v的夹角为theta。一个向量有两个属性,大小和方向,我们先确定u’的大小(即长度,或者模),从u的末端做v的垂线,那么d就是u’的长度。而u’和v的方向是相同的,v的方向v/|v|也就是u’的方向。所以有
再求d的长度。
![]() (2)
(2)
最后求cos(theta)
联合求解方程(1)(2)(3)得到
这就是最终的投影向量。
而这个向量的长度d是
============================
以下是旧的推导,也保留。
XNA MathVectors
下面介绍一些xna math库中常用的向量结构及方法
1.向量类型
有XMVECTOR,XMFLOAT2,XMFLOAT3,XMFLOAT4等几种类型,具体可以看dx11龙书1.6.1节
在这一章中作者给出使用向量类型应注意的5点:
(1)、 对局部变量和全局变量,使用XMVECTOR类型;
(2)、 对类的数据成员,使用XMFLOAT2, XMFLOAT3和XMFLOAT4数据成员;
(3)、 在进行计算之前,使用载入函数(loading functions)来将XMFLOAT*类型转换成XMVECTOR类型;
(4)、 用XMVECTOR的实例进行计算;
(5)、 使用存储函数(storage functions)来将XMVECTOR转换成XMFLOAT*类型
2.Loading and Storage Methods(载入和存储函数)
我们用下面的方法来加载数据,从XMFLOAT*到XMVECTOR
XMVECTOR XMLoadFloat3(CONST XMFLOAT3 *pSource);
XMVECTOR XMLoadInt3(CONST UINT* pSource);
XMVECTOR XMLoadColor(CONST XMCOLOR *pSource);
用下面的方法存储数据,从XMVECTOR到XMFLOAT*
VOID XMStoreFloat3(XMFLOAT3 *pDestination,FXMVECTOR V);
......
3.Parameter Passing参数传递
龙书中主要介绍了CXMVECTOR 和FXMVECTOR 这两种参数类型,并告诉了我们在定义函数时,参数类型的注意事项:
函数的前三个XMVECTOR类型必须是FXMVECTOR,而后面的都是CXMVECTOR。
4.Constant Vectors常向量
需要初始化的XMVECTOR常量应该定义为XMVECTORF32类型(用于存储浮点向量)或XMVECTORU32类型(用于存储整数向量).
5.Vector Functions一些向量运算有关的函数
XMVECTOR XMVectorZero();//返回零向量
XMVECTOR XMVectorSplatOne();//返回(1,1,1,1)
XMVECTOR XMVectorSet(FLOAT x,FLOAT y,FLOAT z,FLOAT w);//返回(x,y,z,w)
XMVECTOR XMVectorReplicate(FLOAT s);//返回(s,s,s,s)
XMVECTOR XMVectorSplatX(FXMVECTOR V);//返回(vx,vx,vx,vx)
XMVECTOR XMVector3Length(FXMVECTOR V);//返回向量v的模所构成的新的向量,例如向量v模为2,则返回(2,2,2)
XMVECTOR XMVector3LengthSq(FXMVECTOR V);//模的平方
XMVECTOR XMVector3Dot(FXMVECTOR V1,FXMVECTOR V2);//点积
XMVECTOR XMVector3Cross(FXMVECTOR V1,FXMVECTOR V2);//叉积
XMVECTOR XMVector3Normalize(FXMVECTOR V);//单位化
XMVECTOR XMVector3Orthogonal(FXMVECTOR V);//得到一个与其垂直的向量
XMVECTOR XMVector3AngleBetweenVectors(FXMVECTOR V1,FXMVECTOR V2);//两个向量的夹角
VOID XMVector3ComponentsFromNormal(XMVECTOR* pParallel,XMVECTOR* pPerpendicular,FXMVECTOR V,FXMVECTOR Normal);//向量的投影
BOOL XMVector3Equal(FXMVECTOR V1,FXMVECTOR V2);//判断两个向量是否相等
6.Floating-Point Error浮点数计算误差
用浮点数进行计算(甚至单纯地表示)时,会出现误差,所以等判断相等时,需要定义一个容许误差。
附:dx11龙书测试的源码及测试结果
1.
1 #include <windows.h> 2 #include <xnamath.h> 3 #include <iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //重载<<操作符 7 ostream& operator<<(ostream &os, FXMVECTOR v) 8 { 9 XMFLOAT3 dest; 10 XMStoreFloat3(&dest, v); 11 os << "(" << dest.x << "," << dest.y << "," << dest.z << ")"; 12 return os; 13 } 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 cout.setf(ios_base::boolalpha);//cout格式化 输入输出bool值可以为true和false 18 19 //检查是否支持SSE2 20 if (!XMVerifyCPUSupport()) 21 { 22 cout << "xna math not supported" << endl; 23 return 0; 24 } 25 XMVECTOR p = XMVectorZero(); 26 XMVECTOR q = XMVectorSplatOne(); 27 XMVECTOR u = XMVectorSet(1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 0.0f); 28 XMVECTOR v = XMVectorSplatX(u); 29 XMVECTOR w = XMVectorReplicate(-3.5f); 30 31 cout << "p = " << p << endl; 32 cout << "q = " << q << endl; 33 cout << "u = " << u << endl; 34 cout << "v = " << v << endl; 35 cout << "w = " << w << endl; 36 37 return 0; 38 }
2.
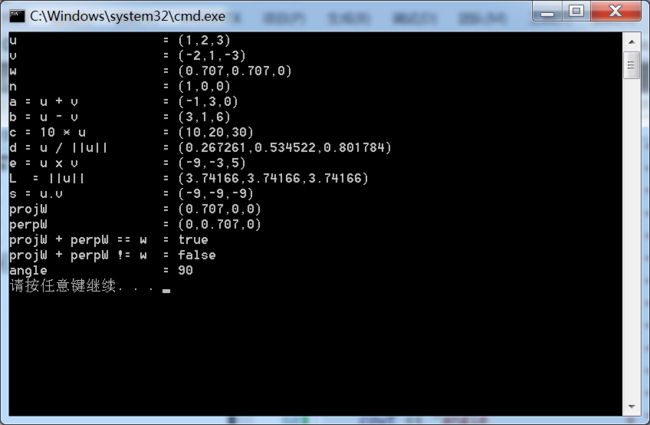
1 #include <windows.h> 2 #include <xnamath.h> 3 #include <iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 ostream& operator<<(ostream &os, FXMVECTOR v) 7 { 8 XMFLOAT3 dest; 9 XMStoreFloat3(&dest, v); 10 os << "(" << dest.x << "," << dest.y << "," << dest.z << ")"; 11 return os; 12 } 13 14 int main() 15 { 16 cout.setf(ios_base::boolalpha); 17 if (!XMVerifyCPUSupport()) 18 { 19 cout << "xna math not supported" << endl; 20 return 0; 21 } 22 XMVECTOR n = XMVectorSet(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); 23 XMVECTOR u = XMVectorSet(1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 0.0f); 24 XMVECTOR v = XMVectorSet(-2.0f, 1.0f, -3.0f, 0.0f); 25 XMVECTOR w = XMVectorSet(0.707f, 0.707f, 0.0f, 0.0f); 26 27 XMVECTOR a = u + v; 28 XMVECTOR b = u - v; 29 XMVECTOR c = 10.0f * u; 30 XMVECTOR L = XMVector3Length(u); 31 XMVECTOR d = XMVector3Normalize(u); 32 XMVECTOR s = XMVector3Dot(u, v); 33 XMVECTOR e = XMVector3Cross(u, v); 34 35 XMVECTOR projW; 36 XMVECTOR perpW; 37 XMVector3ComponentsFromNormal(&projW, &perpW, w, n); 38 39 bool equal = XMVector3Equal(projW + perpW, w) != 0; 40 bool notEqual = XMVector3NotEqual(projW + perpW, w) != 0; 41 XMVECTOR angelVec = XMVector3AngleBetweenVectors(projW, perpW); 42 float angleRadians = XMVectorGetX(angelVec); 43 float angleDegrees = XMConvertToDegrees(angleRadians); 44 45 cout << "u = " << u << endl; 46 cout << "v = " << v << endl; 47 cout << "w = " << w << endl; 48 cout << "n = " << n << endl; 49 cout << "a = u + v = " << a << endl; 50 cout << "b = u - v = " << b << endl; 51 cout << "c = 10 * u = " << c << endl; 52 cout << "d = u / ||u|| = " << d << endl; 53 cout << "e = u x v = " << e << endl; 54 cout << "L = ||u|| = " << L << endl; 55 cout << "s = u.v = " << s << endl; 56 cout << "projW = " << projW << endl; 57 cout << "perpW = " << perpW << endl; 58 cout << "projW + perpW == w = " << equal << endl; 59 cout << "projW + perpW != w = " << notEqual << endl; 60 cout << "angle = " << angleDegrees << endl; 61 62 return 0; 63 }
3.
1 #include <windows.h> // for FLOAT definition 2 #include <xnamath.h> 3 #include <iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 cout.precision(8); 9 10 // Check support for SSE2 (Pentium4, AMD K8, and above). 11 if( !XMVerifyCPUSupport() ) 12 { 13 cout << "xna math not supported" << endl; 14 return 0; 15 } 16 17 XMVECTOR u = XMVectorSet(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f); 18 XMVECTOR n = XMVector3Normalize(u); 19 20 float LU = XMVectorGetX(XMVector3Length(n)); 21 22 // Mathematically, the length should be 1. Is it numerically? 23 cout << LU << endl; 24 if( LU == 1.0f ) 25 cout << "Length 1" << endl; 26 else 27 cout << "Length not 1" << endl; 28 29 // Raising 1 to any power should still be 1. Is it? 30 float powLU = powf(LU, 1.0e6f); 31 cout << "LU^(10^6) = " << powLU << endl; 32 }