Python time时间模块学习
time包
time包的基础类型是struct_time。
time.sleep() 让程序 延时,以秒为单位。
time.time() 返回时间戳,浮点型。
time.strptime(string, format)
用法 ,将字符串转换成 struct_time,返回时间结构struct_time
time_struct = time.strptime('2014-10-10 22:22:12',"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
time.strftime(format,struct_time)
用法,struct_time将转换成 字符串, 返回字符串。
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d",struct_time)
如果是将当前时间转化成字符串 用 time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.localtime())
time.mktime(time_struct)
用法,时间结构到时间戳,返回浮点形式的 时间戳。
time.gmtime(time_stamp)
用法,将时间戳,转化成时间结构,返回时间结构。
time.localtime()time.gmtime(1812950932)
用法,将时间戳,转化成时间结构,返回时间结构。
gmtime()和loaltime() 都是将 时间戳 转换成 时间结构 ,不同之处是 gmtime 转化成 格林威治时间, localtime 转换出来的是当地时间,比如我们就是北京时间。 所以一般time.localtime() 括号里都不加参数,默认就是取得当前的时间戳,转换成当前时间。
time.localtime()
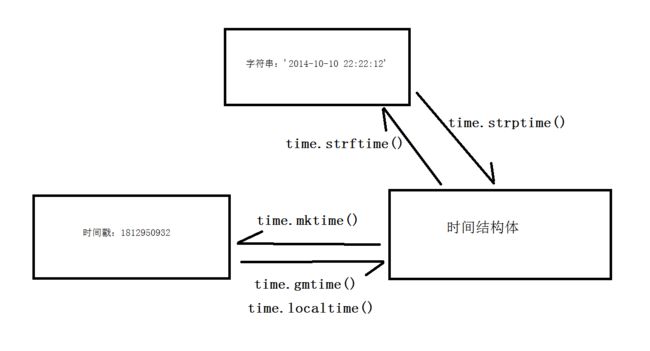
总结
字符串 到 time_struct 用 time.strptime()
time_struct 到 字符串 用 time.strftime()
时间戳 到 time_struct 用 time.gmtime(time_stamp) 或者 time.localtime(time_stamp) time_stamp可以省略
time_struct 到 时间戳 用 time.mktime(time_struct)
可以看到 字符串 和 时间戳之间 没有 直接转换的关系 ,可以通过 时间结构 来作为 过渡。
简图:
虽然 time.ctime() 也是 将 时间戳 转化为 字符串,但是不能用 格式化字符 来定制,用处有限。如
time.ctime(1212950932) 的 返回结果 是 Mon Jun 9 02:48:52 2008 。
time.asctime(time_struct) 也是将 时间结构体 ,转化成 字符串,通ctime一样,生成的字符串格式,不能定制。如
time.asctime(time_struct) 的返回结果是 Mon Jun 14 05:28:52 2027。
数据库中的类型如果是datetime,用timetuple()方法可以转化为time_struct类型。如
kaifu_date.timetuple()
时间偏移
new_date = oldDate + datetime.timedelta(seconds=-1)
表示一天前的 字符串
now = datetime.datetime.now()
now = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.localtime())
yesterday = now - datetime.timedelta(days=1)
print time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d",yesterday.timetuple())
MySQL 中取出来的时间类型 转换 到 时间戳
time.mktime(update_time.timetuple())