论C++STL源码中关于堆算法的那些事
关于堆,我们肯定熟知的就是它排序的时间复杂度在几个排序算法里面算是比较靠上的O(nlogn)经常会拿来和快速排序和归并排序讨论,而且它还有个优点是它的空间复杂度为O(1), 但是STL中没有给我们提供像vector, deque, stack, queue之类的数据结构供我们使用,但在C++STL中却提供了一些列的算法,让我们依旧可以使用堆,比如make_heap(), push_heap(), pop_heap(), sort_heap()。今天就来论论这几个算法,在介绍上述算法之前先引入两个关于堆的算法,上述四个算法本质上都使用引入的两个算法。
一、关于堆的两个算法
1. 堆的插入算法
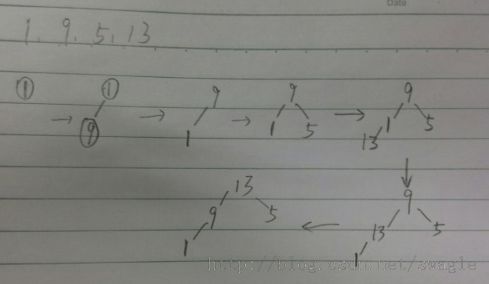
下面先看个例子,一个数组a[]={1,9,5,13},建一个最大堆,下图为过程:
从图中可以看出没插入一个元素,调整后都是一个最大堆,而且是插入到最后一个上(假设数组是可以动态增长的),这样是从下往上进行调整(percolate up),这样的调整算法叫插入法, 下面来看看插入法的代码实现:
void insert_heap(int a[], int i){
while(i>0){
int j=(i-1)/2;
if(a[i] < a[j]){
swap(a[i], a[j]);
i=j;
}
else break;
}
}
2. 堆的筛选法
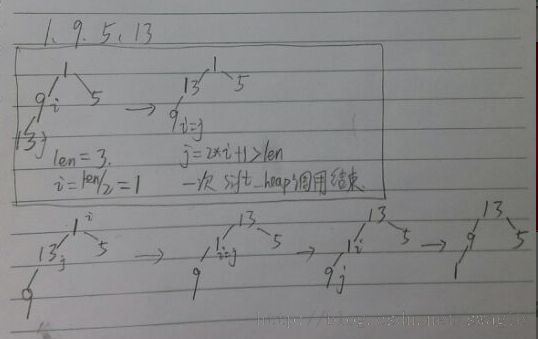
我们还是来先看两个用堆排序的例子
例:a[]={1, 9, 5, 13}, 排序过程如下图
像这样一次自上而下的调整过程,叫做筛选法, 算法实现:
void sift_heap(int a[], int i){
// j 是 i 的左孩子
int j=2*i+1;
int n = strlen(a);
while(j<n){
if(j<n-1 && a[j]<a[j+1]) ++j;
if(a[i]<a[j]){
swap(a[i],a[j]);
i=j;
j=2*i+1;
}
else
break;
}
}
void build_heap(int a[], int n){
int i=n/2;
//循环完后,就建立了一个最大堆
for(; i>=0; ++i){
sift_heap(a, i);
}
}
二、STL算法中的xxxx_heap算法
stl中的关于堆的算法都是在vector上实现的,并且实现的最大堆,且最大的元素位于数组的第一个位置。
1. push_heap
首先来看看STL中的该算法的实现,该算法实现在stl_heap.h文件中,再此函数被调用的时候,新元素已经插入到底部容器的最尾端。
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class Compare>
inline void push_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last){
__push_heap_aux(first, last, distance_type(first), value_type(first));
}
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class Distance, class T>
inline void __push_heap_aux(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, Distance*, T*) {
__push_heap(first, Distance((last - first) - 1), Distance(0), T(*(last - 1)));
}
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class Distance, class T>
void __push_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, Distance holeIndex, Distance topIndex, T value) {
Distance parent = (holeIndex - 1) / 2;
while (holeIndex > topIndex && *(first + parent) < value) {
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + parent);
holeIndex = parent;
parent = (holeIndex - 1) / 2;
}
*(first + holeIndex) = value;
} 可以看到push_heap算法最终调用的是__push_heap,算法内部都用的是迭代器,first是指向堆顶的迭代器,holeIndex指的新插入元素位置距离堆顶的距离,first+topIndex是该堆顶的位置,topIndex是距离, value是新插入的元素的值。
可以看出__push_heap就是我们介绍的第一种堆算法----插入法。
2. __adjust_heap
在详细介绍pop_heap, sort_heap, make_heap三个算法前先来介绍另一个算法__adjust_heap,__adjust_heap函数定义如下:
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class Distance, class T>
void __adjust_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, Distance holeIndex, Distance len, T value) {
Distance topIndex = holeIndex;
Distance secondChild = 2 * holeIndex + 2; //得到右孩子节点
while (secondChild < len) {
if (*(first + secondChild) < *(first + (secondChild - 1))) //选择左右孩子中的较大节点
secondChild--;
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + secondChild);
holeIndex = secondChild;
secondChild = 2 * (secondChild + 1);
}
if (secondChild == len) {
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + (secondChild - 1));
holeIndex = secondChild - 1;
}
//此时没有满足整个堆的性质,需要再从下往上调整一次
__push_heap(first, holeIndex, topIndex, value);
} 通过将该算法和介绍的第二个算法相比,可知这个算法就是筛选法。
3. pop_heap
pop_heap算法并不是将堆顶元素删除,而只是将其移到堆的最后,然后调整堆的时候按照len=len-1, 来进行调整,调整后之前最大的元素放在了容器的最后,可以用back()得到。
函数定义如下
template <class RandomAccessIterator>
inline void pop_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last) {
__pop_heap_aux(first, last, value_type(first));
}
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class T>
inline void __pop_heap_aux(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, T*) {
__pop_heap(first, last - 1, last - 1, T(*(last - 1)), distance_type(first));
}
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class T, class Distance>
inline void __pop_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, RandomAccessIterator result, T value, Distance*) {
*result = *first;
__adjust_heap(first, Distance(0), Distance(last - first), value);
} 可以看出pop_heap最后调用的是__adjust_heap。
4. sort_heap
sort_heap就是对堆进行排序。 从pop_heap得之,它每次可获得heap中键值最大的元素,如果持续对整个heap做pop_heap操作,每次将操作范围从后向前缩减一个元素,当整个程序执行完毕时,数组就是按照从大到小的顺序递增,下面是实际代码:
template <class RandomAccessIterator>
void sort_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last) {
while (last - first > 1) pop_heap(first, last--);
}
5. make_heap
make_heap用来将一段现有的数据转化为一个heap,下面是具体实现:
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class Compare>
inline void make_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, Compare comp) {
__make_heap(first, last, comp, value_type(first), distance_type(first));
}
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class Compare, class T, class Distance>
void __make_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, Compare comp, T*, Distance*) {
if (last - first < 2) return; // 长度为0或1,就返回;
Distance len = last - first;
//找到第一个调整的节点
Distance parent = (len - 2)/2;
while (true) {
__adjust_heap(first, parent, len, T(*(first + parent)), comp);
if (parent == 0) return;
parent--;
}
} 可以看见,该算法是从len/2开始调整,一直到parent为0,这就是我在上面第一部分的筛选法时候举的例子。
注: 以上所列出的STL算法均为SGI STL并且,列出的均为不能只能排序规则的一组。
三、STL中堆的应用
虽然stl中没有提供堆这个数据结构,但是priority queue的内部确是由堆来实现的。priority queue允许用户以任何次序将任何元素推入容器内,但取出的时候一定是从优先权最高的元素开始取。binary heap正好具有这样的特性。为了平衡各个操作的时间复杂度和实现的复杂度,binary heap适合作为priority queue的底层机制。下面贴一个priority_queue的完整实现代码,请注意在几个构造函数中都使用了make_heap算法,在push函数中使用了push_heap算法,在pop中使用了pop_heap算法:
#ifndef __STL_LIMITED_DEFAULT_TEMPLATES
template <class T, class Sequence = vector<T>,
class Compare = less<typename Sequence::value_type> >
#else
template <class T, class Sequence, class Compare>
#endif
class priority_queue {
public:
typedef typename Sequence::value_type value_type;
typedef typename Sequence::size_type size_type;
typedef typename Sequence::reference reference;
typedef typename Sequence::const_reference const_reference;
protected:
Sequence c;
Compare comp;
public:
priority_queue() : c() {}
explicit priority_queue(const Compare& x) : c(), comp(x) {}
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const Compare& x)
: c(first, last), comp(x) { make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp); }
template <class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
: c(first, last) { make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp); }
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
priority_queue(const value_type* first, const value_type* last,
const Compare& x) : c(first, last), comp(x) {
make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
}
priority_queue(const value_type* first, const value_type* last)
: c(first, last) { make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp); }
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
bool empty() const { return c.empty(); }
size_type size() const { return c.size(); }
const_reference top() const { return c.front(); }
void push(const value_type& x) {
__STL_TRY {
c.push_back(x);
push_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
}
__STL_UNWIND(c.clear());
}
void pop() {
__STL_TRY {
pop_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
c.pop_back();
}
__STL_UNWIND(c.clear());
}
};
// no equality is provided
__STL_END_NAMESPACE
#endif /* __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_QUEUE_H */
如果你觉得本篇对你有收获,请帮顶。
另外,我本人开通了微信公众号--分享技术之美,我会不定期的分享一些我学习的东西.
另外,我本人开通了微信公众号--分享技术之美,我会不定期的分享一些我学习的东西.
你可以搜索公众号:
swalge
或者扫描下方二维码关注我
(转载文章请注明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/swagle/article/details/24330605 )