JPA 初探—配置及逆向工程增删改查案例
JPA全称Java Persistence API,即Java持久化API,它为Java开发人员提供了一种对象/关系映射工具来管理Java应用中的关系数据,结合其他ORM的使用(如Hibernate),能达到简化开发流程的目的,使开发者能够专注于实现自己的业务逻辑上。目前比较成熟的 JPA 框架主要包括 Jboss 的 Hibernate EntityManager、Oracle 捐献给 Eclipse 社区的 EclipseLink、Apache 的 OpenJPA 等。本文中使用EclipseLink Jpa配置实现
一、创建新数据库连接
在MyEclipse中,点击Window—>Open Perspective,选择MyEclipse Database Explorer,创建一个新的数据库连接,如图所示,本文所用是MySQL数据库。
二、创建一个示例项目
1、右击项目—>MyEclipse—>Add Jpa Capabilities,添加EclipseLink,点击下一步,如图:
2、选择刚刚创建的数据库连接,如图所示:
3、点击完成后,会自动默认在src的META-INF中生成persistence.xml持久化文件(路径不需要修改),且persistence.xml内容如下。其中,<class></class>中内容是后面通过JPA逆向工程自动添加进的实体类,此处可暂时忽略。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <persistence version="2.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd"> <persistence-unit name="springjersyjpa" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL"> <provider> org.eclipse.persistence.jpa.PersistenceProvider </provider> <class>com.spring.jersy.jpa.hibernate.model.Country</class> <class>com.spring.jersy.jpa.hibernate.model.Province</class> <class>com.spring.jersy.jpa.hibernate.model.User</class> <properties> <property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.user" value="root" /> <property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.password" value="root" /> <property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test" /> <property name="eclipselink.ddl-generation" value="create-tables" /> <property name="eclipselink.persistence-context.flush-mode" value="COMMIT" /> </properties> </persistence-unit> </persistence>
三、JPA逆向工程
MyEclipse提供了JPA逆向工程,能够将数据库中的表、字段等信息自动生成实体类并注解一一对应。具体流程如下:
1、进入MyEclipse Database Explorer,打开刚刚创建的“com.jdbc.mysql.Driver”连接,选择测试数据库“test”。
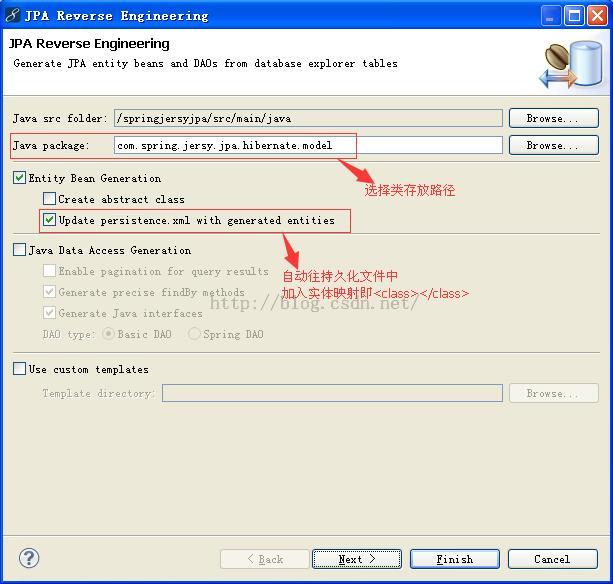
2、选择要逆向生成的表,右击选择“JPA Reverse Engineering”。弹出如图:
3、生成的实体类如下所示:
package com.spring.jersy.jpa.hibernate.model; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; import javax.persistence.CascadeType; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.FetchType; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import static javax.persistence.GenerationType.IDENTITY; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.OneToMany; import javax.persistence.Table; /** * Country entity. @author MyEclipse Persistence Tools */ @Entity @Table(name = "country", catalog = "test") public class Country implements java.io.Serializable { // Fields private Integer cid; private String cname; private Set<Province> provinces = new HashSet<Province>(0); // Constructors /** default constructor */ public Country() { } /** minimal constructor */ public Country(String cname) { this.cname = cname; } /** full constructor */ public Country(String cname, Set<Province> provinces) { this.cname = cname; this.provinces = provinces; } // Property accessors @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = IDENTITY) @Column(name = "cId", unique = true, nullable = false) public Integer getCid() { return this.cid; } public void setCid(Integer cid) { this.cid = cid; } @Column(name = "cName", nullable = false, length = 32) public String getCname() { return this.cname; } public void setCname(String cname) { this.cname = cname; } @OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "country") public Set<Province> getProvinces() { return this.provinces; } public void setProvinces(Set<Province> provinces) { this.provinces = provinces; } }package com.spring.jersy.jpa.hibernate.model; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.FetchType; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import static javax.persistence.GenerationType.IDENTITY; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.JoinColumn; import javax.persistence.ManyToOne; import javax.persistence.Table; /** * Province entity. @author MyEclipse Persistence Tools */ @Entity @Table(name = "province", catalog = "test") public class Province implements java.io.Serializable { // Fields private Short id; private Country country; private String proName; // Constructors /** default constructor */ public Province() { } /** full constructor */ public Province(Country country, String proName) { this.country = country; this.proName = proName; } // Property accessors @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = IDENTITY) @Column(name = "id", unique = true, nullable = false) public Short getId() { return this.id; } public void setId(Short id) { this.id = id; } @ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY) @JoinColumn(name = "cId", nullable = false) public Country getCountry() { return this.country; } public void setCountry(Country country) { this.country = country; } @Column(name = "proName", nullable = false, length = 32) public String getProName() { return this.proName; } public void setProName(String proName) { this.proName = proName; } }
四、JPA测试
JPA与Hibernate很相似,Hibernate依赖SessionFactory—>Session,JPA依赖EntityManagerFactory—>EntityManager实现各种操作。测试案例如下:
package com.spring.jersy.jpa.hibernate.test; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import javax.persistence.Query; import com.spring.jersy.jpa.hibernate.model.Country; public class JpaTest { private static EntityManagerFactory entityFactory = Persistence .createEntityManagerFactory("springjersyjpa"); public static void main(String agrs[]) { queryProvinceInnerJoinCountry(); } /** * 内连接多表关联查询 */ public static void queryProvinceInnerJoinCountry() { EntityManager em = entityFactory.createEntityManager(); // JPA中JPQL查询,必须为每个table定义别名 //字段名要和实体类中属性相对应 String jql = "select p.proName,c.cname from Province p inner join p.country c "; Query query = em.createQuery(jql); List<Object> list = query.getResultList(); for (Iterator iterator = list.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) { Object[] obj = (Object[]) iterator.next(); System.out.println(obj[0]+" "+obj[1]); } em.close(); entityFactory.close(); } /** * 查询所有国家 */ public static void findCountryAll() { EntityManager em = entityFactory.createEntityManager(); // JPA中JPQL查询,必须为每个table定义别名 //字段名要和实体类中属性相对应 Query query = em.createQuery("select c.cId, c.cname from Country c "); List<Object> list = query.getResultList(); for (Iterator iterator = list.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) { Object[] obj = (Object[]) iterator.next(); System.out.println(obj[1]); } em.close(); entityFactory.close(); } /** * 根据国家编号查询国家名称 * * @param id */ public static void queryCountryBycId(Integer id) { EntityManager em = entityFactory.createEntityManager(); // JPA中JPQL查询,必须为每个table定义别名 //字段名要和实体类中属性相对应 Query query = em .createQuery("select c.cname from Country c where c.cId = :id", String.class); String name = (String) query.setParameter("id", id).getSingleResult(); System.out.println(name); em.close(); entityFactory.close(); } /** * 修改信息 */ public static void updateCountry() { EntityManager em = entityFactory.createEntityManager(); //打开事务 em.getTransaction().begin(); Country country = em.find(Country.class, 2); country.setCname("英国"); em.persist(country); //事务提交 em.getTransaction().commit(); em.close(); entityFactory.close(); } /** * 添加信息 */ public static void saveCountry() { EntityManager em = entityFactory.createEntityManager(); em.getTransaction().begin(); Country country = new Country(); country.setCname("中国"); em.persist(country); em.getTransaction().commit(); em.close(); entityFactory.close(); } }JPA支持JQL SQL语法,与Hibernate的HQL语法很近,但是也有很多不同的地方,如:JQL中实体类代表相应的表时,必须取别名(alias)等。