(Caffe)基本类Blob,Layer,Net(一)
Caffe中,Blob,Layer,Net,Solver是最为核心的类,以下介绍这几个类,Solver将在下一节介绍。
1 Blob
1.1 简介
Blob是:1.对待处理数据带一层封装,用于在Caffe中通信传递。
2.也为CPU和GPU间提供同步能力
3.数学上,是一个N维的C风格的存储数组
总的来说,Caffe使用Blob来交流数据,其是Caffe中标准的数组与统一的内存接口,它是多功能的,在不同的应用场景具有不同的含义,如可以是:batches of images, model parameters, and derivatives for optimization等。
1.2 源代码
/**
* @brief A wrapper around SyncedMemory holders serving as the basic
* computational unit through which Layer%s, Net%s, and Solver%s
* interact.
*
* TODO(dox): more thorough description.
*/
template <typename Dtype>
class Blob {
public:
Blob()
: data_(), diff_(), count_(0), capacity_(0) {}
/// @brief Deprecated; use <code>Blob(const vector<int>& shape)</code>.
explicit Blob(const int num, const int channels, const int height,
const int width);
explicit Blob(const vector<int>& shape);
.....
protected:
shared_ptr<SyncedMemory> data_;
shared_ptr<SyncedMemory> diff_;
shared_ptr<SyncedMemory> shape_data_;
vector<int> shape_;
int count_;
int capacity_;
DISABLE_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(Blob);
}; // class Blob
注:此处只保留了构造函数与成员变量。
说明:
- Blob在实现上是对SyncedMemory(见1.4部分)进行了一层封装。
- shape_为blob维度,见1.3部分
- data_为原始数据
- diff_为梯度信息
- count为该blob的总容量(即数据的size),函数count(x,y)(或count(x))返回某个切片[x,y]([x,end])内容量,本质上就是shape[x]*shape[x+1]*....*shape[y]的值
1.3 Blob的shape
由源代码中可以注意到Blob有个成员变量:vector<ini> shape_
其作用:
- 对于图像数据,shape可以定义为4维的数组(Num, Channels, Height, Width)或(n, k, h, w),所以Blob数据维度为n*k*h*w,Blob是row-major保存的,因此在(n, k, h, w)位置的值物理位置为((n * K + k) * H + h) * W + w。其中Number是数据的batch size,对于256张图片为一个training batch的ImageNet来说n = 256;Channel是特征维度,如RGB图像k = 3
- 对于全连接网络,使用2D blobs (shape (N, D)),然后调用InnerProductLayer
- 对于参数,维度根据该层的类型和配置来确定。对于有3个输入96个输出的卷积层,Filter核 11 x 11,则blob为96 x 3 x 11 x 11. 对于全连接层,1000个输出,1024个输入,则blob为1000 x 1024.
1.4 SyncedMemory
由1.2知,Blob本质是对SyncedMemory的再封装。其核心代码如下:
/**
* @brief Manages memory allocation and synchronization between the host (CPU)
* and device (GPU).
*
* TODO(dox): more thorough description.
*/
class SyncedMemory {
public:
...
const void* cpu_data();
const void* gpu_data();
void* mutable_cpu_data();
void* mutable_gpu_data();
...
private:
...
void* cpu_ptr_;
void* gpu_ptr_;
...
}; // class SyncedMemory Blob同时保存了
data_和
diff_,其类型为SyncedMemory的指针。
对于data_(diff_相同),其实际值要么存储在CPU(cpu_ptr_)要么存储在GPU(gpu_ptr_),有两种方式访问CPU数据(GPU相同):
1)常量方式,void* cpu_data(),其不改变cpu_ptr_指向存储区域的值。
2)可变方式,void* mutable_cpu_data(),其可改变cpu_ptr_指向存储区值。
以mutable_cpu_data()为例
void* SyncedMemory::mutable_cpu_data() {
to_cpu();
head_ = HEAD_AT_CPU;
return cpu_ptr_;
}
inline void SyncedMemory::to_cpu() {
switch (head_) {
case UNINITIALIZED:
CaffeMallocHost(&cpu_ptr_, size_, &cpu_malloc_use_cuda_);
caffe_memset(size_, 0, cpu_ptr_);
head_ = HEAD_AT_CPU;
own_cpu_data_ = true;
break;
case HEAD_AT_GPU:
#ifndef CPU_ONLY
if (cpu_ptr_ == NULL) {
CaffeMallocHost(&cpu_ptr_, size_, &cpu_malloc_use_cuda_);
own_cpu_data_ = true;
}
caffe_gpu_memcpy(size_, gpu_ptr_, cpu_ptr_);
head_ = SYNCED;
#else
NO_GPU;
#endif
break;
case HEAD_AT_CPU:
case SYNCED:
break;
}
}
说明:
- 经验上来说,如果不需要改变其值,则使用常量调用的方式,并且,不要在你对象中保存其指针。为何要这样设计呢,因为这样涉及能够隐藏CPU到GPU的同步细节,以及减少数据传递从而提高效率,当你调用它们的时候,SyncedMem会决定何时去复制数据,通常情况是仅当gnu或cpu修改后有复制操作,引用1官方文档中有一个例子说明何时进行复制操作。
- 调用mutable_cpu_data()可以让head转移到cpu上
- 第一次调用mutable_cpu_data()是UNINITIALIZED将执行9到14行,将为cpu_ptr_分配host内存
- 若head从gpu转移到cpu,将把数据从gpu复制到cpu中
2 Layer
2.1简介
Layer是Caffe的基础以及基本计算单元。Caffe十分强调网络的层次性,可以说,一个网络的大部分功能都是以Layer的形式去展开的,如convolute,pooling,loss等等。
在创建一个Caffe模型的时候,也是以Layer为基础进行的,需按照src/caffe/proto/caffe.proto中定义的网络及参数格式定义网络 prototxt文件(需了解google protocol buffer)
2.2 Layer与Blob的关系
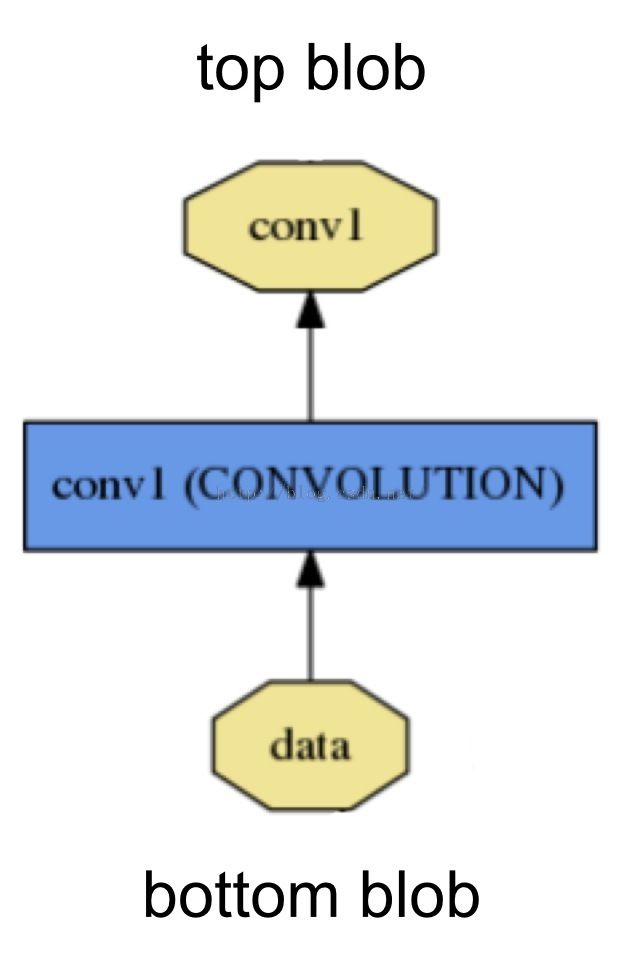
如图,名为conv1的Layer 的输入是名为data的bottom blob,其输出是名为conv1的top blob。
其protobuff定义如下,一个layer有一个到多个的top和bottom,其对应于blob
layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
....
}
2.3源代码
/**
* Layer%s must implement a Forward function, in which they take their input
* (bottom) Blob%s (if any) and compute their output Blob%s (if any).
* They may also implement a Backward function, in which they compute the error
* gradients with respect to their input Blob%s, given the error gradients with
* their output Blob%s.
*/
template <typename Dtype>
class Layer {
public:
/**
* You should not implement your own constructor. Any set up code should go
* to SetUp(), where the dimensions of the bottom blobs are provided to the
* layer.
*/
explicit Layer(const LayerParameter& param)
: layer_param_(param), is_shared_(false) {
...
}
virtual ~Layer() {}
/**
* @brief Implements common layer setup functionality.
* @param bottom the preshaped input blobs
* @param top
* the allocated but unshaped output blobs, to be shaped by Reshape
*/
void SetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
...
}
...
/**
* @brief Given the bottom blobs, compute the top blobs and the loss.
* \return The total loss from the layer.
*
* The Forward wrapper calls the relevant device wrapper function
* (Forward_cpu or Forward_gpu) to compute the top blob values given the
* bottom blobs. If the layer has any non-zero loss_weights, the wrapper
* then computes and returns the loss.
*
* Your layer should implement Forward_cpu and (optionally) Forward_gpu.
*/
inline Dtype Forward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
/**
* @brief Given the top blob error gradients, compute the bottom blob error
* gradients.
*
* @param top
* the output blobs, whose diff fields store the gradient of the error
* with respect to themselves
* @param propagate_down
* a vector with equal length to bottom, with each index indicating
* whether to propagate the error gradients down to the bottom blob at
* the corresponding index
* @param bottom
* the input blobs, whose diff fields will store the gradient of the error
* with respect to themselves after Backward is run
*
* The Backward wrapper calls the relevant device wrapper function
* (Backward_cpu or Backward_gpu) to compute the bottom blob diffs given the
* top blob diffs.
*
* Your layer should implement Backward_cpu and (optionally) Backward_gpu.
*/
inline void Backward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
...
protected:
/** The protobuf that stores the layer parameters */
LayerParameter layer_param_;
/** The phase: TRAIN or TEST */
Phase phase_;
/** The vector that stores the learnable parameters as a set of blobs. */
vector<shared_ptr<Blob<Dtype> > > blobs_;
/** Vector indicating whether to compute the diff of each param blob. */
vector<bool> param_propagate_down_;
/** The vector that indicates whether each top blob has a non-zero weight in
* the objective function. */
vector<Dtype> loss_;
virtual void Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) = 0;
virtual void Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
// LOG(WARNING) << "Using CPU code as backup.";
return Forward_cpu(bottom, top);
}
virtual void Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) = 0;
virtual void Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
// LOG(WARNING) << "Using CPU code as backup.";
Backward_cpu(top, propagate_down, bottom);
}
...
}; // class Layer 说明:每一层定义了三种操作
Setup:Layer的初始化
Forward:前向传导计算,根据bottom计算top,调用了Forward_cpu(必须实现)和Forward_gpu(可选,若未实现,则调用cpu的)
Backward:反向传导计算,根据top计算bottom的梯度,其他同上
2.4派生类分类
在Layer的派生类中,主要可以分为Vision Layers
- Vision Layers
Vison 层主要用于处理视觉图像相关的层,以图像作为输入,产生其他的图像。其主要特点是具有空间结构。
包含Convolution(conv_layer.hpp)、Pooling(pooling_layer.hpp)、Local Response Normalization(LRN)(lrn_layer.hpp)、im2col等,注:老版本的Caffe有头文件include/caffe/vision_layers.hpp,新版本中用include/caffe/layer/conv_layer.hpp等取代
- Loss Layers
这些层产生loss,如Softmax(SoftmaxWithLoss)、Sum-of-Squares / Euclidean(EuclideanLoss)、Hinge / Margin(HingeLoss)、Sigmoid Cross-Entropy(SigmoidCrossEntropyLoss)、Infogain(InfogainLoss)、Accuracy and Top-k等
- Activation / Neuron Layers
元素级别的运算,运算均为同址计算(in-place computation,返回值覆盖原值而占用新的内存)。如:ReLU / Rectified-Linear and Leaky-ReLU(ReLU)、Sigmoid(Sigmoid)、TanH / Hyperbolic Tangent(TanH)、Absolute Value(AbsVal)、Power(Power)、BNLL(BNLL)等
- Data Layers
网络的最底层,主要实现数据格式的转换,如:Database(Data)、In-Memory(MemoryData)、HDF5 Input(HDF5Data)、HDF5 Output(HDF5Output)、Images(ImageData)、Windows(WindowData)、Dummy(DummyData)等
- Common Layers
Caffe提供了单个层与多个层的连接。如:Inner Product(InnerProduct)、Splitting(Split)、Flattening(Flatten)、Reshape(Reshape)、Concatenation(Concat)、Slicing(Slice)、Elementwise(Eltwise)、Argmax(ArgMax)、Softmax(Softmax)、Mean-Variance Normalization(MVN)等
注,括号内为Layer Type,没有括号暂缺信息,详细咱见引用2
3 Net
3.1简介
一个Net由多个Layer组成。一个典型的网络从data layer(从磁盘中载入数据)出发到loss layer结束。如图是一个简单的逻辑回归分类器。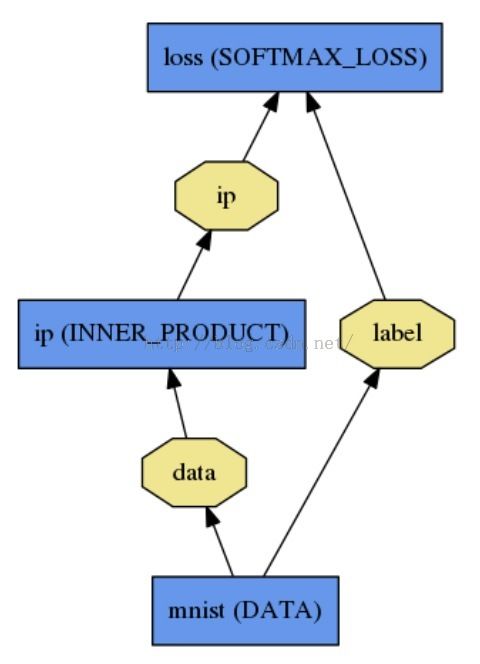
name: "LogReg"
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
data_param {
source: "input_leveldb"
batch_size: 64
}
}
layer {
name: "ip"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "data"
top: "ip"
inner_product_param {
num_output: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "ip"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
}
3.2源代码
/**
* @brief Connects Layer%s together into a directed acyclic graph (DAG)
* specified by a NetParameter.
*
* TODO(dox): more thorough description.
*/
template <typename Dtype>
class Net {
public:
...
/// @brief Initialize a network with a NetParameter.
void Init(const NetParameter& param);
...
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& Forward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>* > & bottom,
Dtype* loss = NULL);
...
/**
* The network backward should take no input and output, since it solely
* computes the gradient w.r.t the parameters, and the data has already been
* provided during the forward pass.
*/
void Backward();
...
Dtype ForwardBackward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>* > & bottom) {
Dtype loss;
Forward(bottom, &loss);
Backward();
return loss;
}
...
protected:
...
/// @brief The network name
string name_;
/// @brief The phase: TRAIN or TEST
Phase phase_;
/// @brief Individual layers in the net
vector<shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> > > layers_;
/// @brief the blobs storing intermediate results between the layer.
vector<shared_ptr<Blob<Dtype> > > blobs_;
vector<vector<Blob<Dtype>*> > bottom_vecs_;
vector<vector<Blob<Dtype>*> > top_vecs_;
...
/// The root net that actually holds the shared layers in data parallelism
const Net* const root_net_;
};
} // namespace caffe
说明:
- Init中,通过创建blob和layer搭建了整个网络框架,以及调用各层的SetUp函数。
- blobs_存放这每一层产生的blobls的中间结果,bottom_vecs_存放每一层的bottom blobs,top_vecs_存放每一层的top blobs
参考文献:
[1].http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/tutorial/net_layer_blob.html
[2].http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/tutorial/layers.html
[3].https://yufeigan.github.io
[4].https://www.zhihu.com/question/27982282