GCC后端及汇编发布(6)
3.3. 构建识别树
3.3.3. 创建识别树
对于每个指令描述模式(正如我们看到有 3 个类型的模式在使用—— define_insn , define_split 及 define_peephole2 。但是它们被分别处理,因此有 3 种树对应这 3 个类型的模式),将构建形如 图 13 的树。为了从这些树,以高效、方便的方式,产生 insn-recog.c ,我们需要把这些树合并成一棵大的树。这正是 merge_trees . 的目的。对于所有的描述, merge_trees 应该构建一棵如下的树。
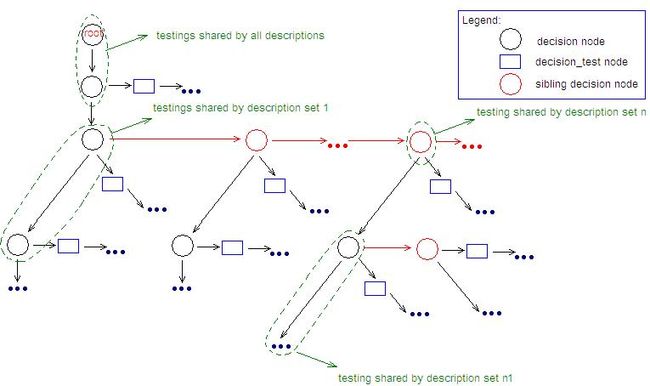
图 14 : 由 merge_trees 创建的描述树
图 14 的树(目标树)从指令的第一棵描述树,通过加入其它描述树,生长起来。对于这些树,它们将与目标树,从根节点开始,进行比较。在那些目标树中的节点不同于描述树节点的位置,该描述树节点将被作为目标树节点的兄弟节点加入。而如果目标树节点被发现与描述树节点相同,就进入这两棵树的下一级节点(在这两棵树中,深度由 decision 节点的 position 域,以我们在上面看到的方式,来显示),然后重复比较,合并或深入的步骤。
显然,每个指令与目标树的某个叶子匹配,注意到叶子与指令是一一对应的。从根节点到特定的叶子,其路径代表了用于选择该指令的条件测试。
1397 static void
1398 merge_trees (struct decision_head *oldh, struct decision_head *addh) in genrecog.c
1399 {
1400 struct decision *next, *add;
1401
1402 if (addh->first == 0)
1403 return ;
1404 if (oldh->first == 0)
1405 {
1406 *oldh = *addh;
1407 return ;
1408 }
1409
1410 /* Trying to merge bits at different positions isn't possible. */
1411 if (strcmp (oldh->first->position, addh->first->position))
1412 abort ();
1413
1414 for (add = addh->first; add ; add = next)
1415 {
1416 struct decision *old, *insert_before = NULL;
1417
1418 next = add->next;
1419
1420 /* The semantics of pattern matching state that the tests are
1421 done in the order given in the MD file so that if an insn
1422 matches two patterns, the first one will be used. However,
1423 i n practice, most, if not all, patterns are unambiguous so
1424 that their order is independent. In that case, we can merge
1425 identical tests and group all similar modes and codes together.
1426
1427 Scan starting from the end of OLDH until we reach a point
1428 where we reach the head of the list or where we pass a
1429 pattern that could also be true if NEW is true. If we find
1430 an identical pattern, we can merge them. Also, record the
1431 last node that tests the same code and mode and the last one
1432 that tests just the same mode.
1433
1434 If we have no match, place NEW after the closest match we found. */
1435
1436 for (old = oldh->last; old; old = old->prev)
1437 {
1438 if (nodes_identical (old, add))
1439 {
1440 merge_accept_insn (old, add);
1441 merge_trees (&old->success, &add->success);
1442 goto merged_nodes;
1443 }
1444
1445 if (maybe_both_true (old, add, 0))
1446 break ;
1447
1448 /* Insert the nodes in DT test type order, which is roughly
1449 how expensive/important the test is. Given that the tests
1450 are also ordered within the list, examining the first is
1451 sufficient. */
1452 if ((int) add->tests->type < (int) old->tests->type)
1453 insert_before = old;
1454 }
1455
1456 if (insert_before == NULL)
1457 {
1458 add->next = NULL;
1459 add->prev = oldh->last;
1460 oldh->last->next = add;
1461 oldh->last = add;
1462 }
1463 else
1464 {
1465 if ((add->prev = insert_before->prev) != NULL)
1466 add->prev->next = add;
1467 else
1468 oldh->first = add;
1469 add->next = insert_before;
1470 insert_before->prev = add;
1471 }
1472
1473 merged_nodes: ;
1474 }
1475 }
这是一个非常复杂的过程,让我们一步一步来。在 main 中的调用点,我们看到该函数的第一个参数 oldh 指向我们例子的 recog_tree ,而第二个参数 addh 指向 图 13 所示的树。首先,它将检查以下的节点。
图 15 : merge_tree 函数,图 1
在 1438 行,函数 nodes_identical 将检查上面的 decision 节点,来确定它们是否是相同的对象。而现在在 1436 行 oldh 的 prev 域,及在 1418 行 addh 的 next 域,都是 null 。
1317 static int
1318 nodes_identical (struct decision *d1, struct decision *d2) in genrecog.c
1319 {
1320 struct decision_test *t1, *t2;
1321
1322 for (t1 = d1->tests, t2 = d2->tests; t1 && t2; t1 = t1->next, t2 = t2->next)
1323 {
1324 if (t1->type != t2->type)
1325 return 0;
1326 if (! nodes_identical_1 (t1, t2))
1327 return 0;
1328 }
1329
1330 /* For success, they should now both be null. */
1331 if (t1 != t2)
1332 return 0;
1333
1334 /* Check that their subnodes are at the same position, as any one set
1335 of sibling decisions must be at the same position. Allowing this
1336 requires complications to find_afterward and when change_state is
1337 invoked. */
1338 if (d1->success.first
1339 && d2->success.first
1340 && strcmp (d1->success.first->position, d2->success.first->position))
1341 return 0;
1342
1343 return 1;
1344 }
上面,在 1326 行,在比较了类型之后, nodes_identical_1 进一步检查内容是否匹配。接着在 1338 行,要完全相同,跟随它们的节点的 position 也必须是相同的。显然我们例子中所关注的节点是相同的。
给定两个声明完全相同的节点,在 1440 行的函数 merge_accept_insn 拷贝这两个指令的接受状态。下面的 DT_accept_insn 表示一旦通过这个 decision_test ,对应的指令被匹配。即,这个 decision_test 节点是匹配这个指令的最后一个测试。
1353 static void
1354 merge_accept_insn (struct decision *oldd, struct decision *addd) in genrecog.c
1355 {
1356 struct decision_test *old, *add;
1357
1358 for (old = oldd->tests; old; old = old->next)
1359 if (old->type == DT_accept_insn)
1360 break ;
1361 if (old == NULL)
1362 return ;
1363
1364 for (add = addd->tests; add; add = add->next)
1365 if (add->type == DT_accept_insn)
1366 break ;
1367 if (add == NULL)
1368 return ;
1369
1370 /* If one node is for a normal insn and the second is for the base
1371 insn with clobbers stripped off, the second node should be ignored. */
1372
1373 if (old->u.insn.num_clobbers_to_add == 0
1374 && add->u.insn.num_clobbers_to_add > 0)
1375 {
1376 /* Nothing to do here. */
1377 }
1378 else if (old->u.insn.num_clobbers_to_add > 0
1379 && add->u.insn.num_clobbers_to_add == 0)
1380 {
1381 /* In this case, replace OLD with ADD. */
1382 old->u.insn = add->u.insn;
1383 }
1384 else
1385 {
1386 message_with_line (add->u.insn.lineno, "`%s' matches `%s'",
1387 get_insn_name (add->u.insn.code_number),
1388 get_insn_name (old->u.insn.code_number));
1389 message_with_line (old->u.insn.lineno, "previous definition of `%s'",
1390 get_insn_name (old->u.insn.code_number));
1391 error_count ++;
1392 }
1393 }
上面的 num_clobbers_to_add ,在 make_insn_sequence 中,设置为 PARALLEL 对象中元素数目的记录。如果它们在是否带 clobber 上不相同,那么这个冲突是由 make_insn_sequence 造成的,我们可以丢掉带有 clobber 的版本。如果这两个节点不能通过 clobber 来区分,我们在机器描述文件中找到了一个二义性错误。这个机制用于筛选更有效率的指令。
对于两个相同的节点,那样 merge_trees 沿着链,递归入下一个节点。我们可以看到,对于这两个链,接着的节点也是相同的,直到来到以下节点。
图 16 : merge_tree 函数,图 2
对于这两个节点, nodes_identical 在 DT_Code 类型的 decision_test 的子节点处返回 0 。然后函数 maybe_both_true 将被调用。这个函数把描述树的节点与目标树的兄弟节点比较,如果任一兄弟节点匹配这个节点就返回 1 ,如果没有找到这样的兄弟节点就返回 0 ,不确定则返回 -1 。
1202 static int
1203 maybe_both_true (struct decision *d1, struct decision *d2, in genrecog.c
1204 int toplevel)
1205 {
1206 struct decision *p1, *p2;
1207 int cmp;
1208
1209 /* Don't compare strings on the different positions in insn. Doing so
1210 is incorrect and results in false matches from constructs like
1211
1212 [(set (subreg:HI (match_operand:SI "register_operand" "r") 0)
1213 (subreg:HI (match_operand:SI "register_operand" "r") 0))]
1214 vs
1215 [(set (match_operand:HI "register_operand" "r")
1216 (match_operand:HI "register_operand" "r"))]
1217
1218 If we are presented with such, we are recursing through the remainder
1219 of a node's success nodes (from the loop at the end of this function).
1220 Skip forward until we come to a position that matches.
1221
1222 Due to the way position strings are constructed, we know that iterating
1223 forward from the lexically lower position (e.g. "00") will run into
1224 the lexically higher position (e.g. "1") and not the other way around.
1225 This saves a bit of effort. */
1226
1227 cmp = strcmp (d1->position, d2->position);
1228 if (cmp != 0)
1229 {
1230 if (toplevel)
1231 abort ();
1232
1233 /* If the d2->position was lexically lower, swap. */
1234 if (cmp > 0)
1235 p1 = d1, d1 = d2, d2 = p1;
1236
1237 if (d1->success.first == 0)
1238 return 1;
1239 for (p1 = d1->success.first; p1; p1 = p1->next)
1240 if (maybe_both_true (p1, d2, 0))
1241 return 1;
1242
1243 return 0;
1244 }
1245
1246 /* Test the current level. */
1247 cmp = maybe_both_true_1 (d1->tests, d2->tests);
1248 if (cmp >= 0)
1249 return cmp;
1250
1251 /* We can't prove that D1 and D2 cannot both be true. If we are only
1252 to check the top level, return 1. Otherwise, see if we can prove
1253 that all choices in both successors are mutually exclusive. If
1254 either does not have any successors, we can't prove they can't both
1255 be true. */
1256
1257 if (toplevel || d1->success.first == 0 || d2->success.first == 0)
1258 return 1;
1259
1260 for (p1 = d1->success.first; p1; p1 = p1->next)
1261 for (p2 = d2->success.first; p2; p2 = p2->next)
1262 if (maybe_both_true (p1, p2, 0))
1263 return 1;
1264
1265 return 0;
1266 }
然后 merge_trees 开始处理 position(‘10’) 的节点。对于这些节点,在 1227 行的测试将可通过。它们具有相同的位置。接着函数 maybe_both_true_1 测试属于这两个节点的 decision_test ,来确保这些测试集是相同的。如果匹配,它将返回 1 ,可能匹配则返回 -1 ,不匹配则返回 0 。
1168 static int
1169 maybe_both_true_1 (struct decision_test *d1, struct decision_test *d2) in genrecog.c
1170 {
1171 struct decision_test *t1, *t2;
1172
1173 /* A match_operand with no predicate can match anything. Recognize
1174 this by the existence of alone DT_accept_op test. */
1175 if (d1->type == DT_accept_op || d2->type == DT_accept_op)
1176 return 1;
1177
1178 /* Eliminate pairs of tests while they can exactly match. */
1179 while (d1 && d2 && d1->type == d2->type)
1180 {
1181 if (maybe_both_true_2 (d1, d2) == 0)
1182 return 0;
1183 d1 = d1->next, d2 = d2->next;
1184 }
1185
1186 /* After that, consider all pairs. */
1187 for (t1 = d1; t1 ; t1 = t1->next)
1188 for (t2 = d2; t2 ; t2 = t2->next)
1189 if (maybe_both_true_2 (t1, t2) == 0)
1190 return 0;
1191
1192 return -1;
1193 }
maybe_both_true_2 处理测试集中的具体测试。如果两个测试是相同的,它返回 1 ;如果不同,则返回 0 ;如果不能证明它们是相同的,就返回 -1 。
1058 static int
1059 maybe_both_true_2 (struct decision_test *d1, struct decision_test *d2) in genrecog.c
1060 {
1061 if (d1->type == d2->type)
1062 {
1063 switch (d1->type)
1064 {
1065 case DT_mode:
1066 return d1->u.mode == d2->u.mode;
1067
1068 case DT_code:
1069 return d1->u.code == d2->u.code;
1070
1071 case DT_veclen:
1072 return d1->u.veclen == d2->u.veclen;
1073
1074 case DT_elt_zero_int:
1075 case DT_elt_one_int:
1076 case DT_elt_zero_wide:
1077 case DT_elt_zero_wide_safe:
1078 return d1->u.intval == d2->u.intval;
1079
1080 default :
1081 break ;
1082 }
1083 }
1084
1085 /* If either has a predicate that we know something about, set
1086 things up so that D1 is the one that always has a known
1087 predicate. Then see if they have any codes in common. */
1088
1089 if (d1->type == DT_pred || d2->type == DT_pred)
1090 {
1091 if (d2->type == DT_pred)
1092 {
1093 struct decision_test *tmp;
1094 tmp = d1, d1 = d2, d2 = tmp;
1095 }
1096
1097 /* If D2 tests a mode, see if it matches D1. */
1098 if (d1->u.pred.mode != VOIDmode)
1099 {
1100 if (d2->type == DT_mode)
1101 {
1102 if (d1->u.pred.mode != d2->u.mode
1103 /* The mode of an address_operand predicate is the
1104 mode of the memory, not the operand. It can only
1105 be used for testing the predicate, so we must
1106 ignore it here. */
1107 && strcmp (d1->u.pred.name, "address_operand") != 0)
1108 return 0;
1109 }
1110 /* Don't check two predicate modes here, because if both predicates
1111 accept CONST_INT, then both can still be true even if the modes
1112 are different. If they don't accept CONST_INT, there will be a
1113 separate DT_mode that will make maybe_both_true_1 return 0. */
1114 }
1115
1116 if (d1->u.pred.index >= 0)
1117 {
1118 /* If D2 tests a code, see if it is in the list of valid
1119 codes for D1's predicate. */
1120 if (d2->type == DT_code)
1121 {
1122 const RTX_CODE *c = &preds [d1->u.pred.index].codes[0];
1123 while (*c != 0)
1124 {
1125 if (*c == d2->u.code)
1126 break ;
1127 ++c;
1128 }
1129 if (*c == 0)
1130 return 0;
1131 }
1132
1133 /* Otherwise see if the predicates have any codes in common. */
1134 else if (d2->type == DT_pred && d2->u.pred.index >= 0)
1135 {
1136 const RTX_CODE *c1 = &preds [d1->u.pred.index].codes[0];
1137 int common = 0;
1138
1139 while (*c1 != 0 && !common)
1140 {
1141 const RTX_CODE *c2 = &preds [d2->u.pred.index].codes[0];
1142 while (*c2 != 0 && !common)
1143 {
1144 common = (*c1 == *c2);
1145 ++c2;
1146 }
1147 ++c1;
1148 }
1149
1150 if (!common)
1151 return 0;
1152 }
1153 }
1154 }
1155
1156 /* Tests vs veclen may be known when strict equality is involved. */
1157 if (d1->type == DT_veclen && d2->type == DT_veclen_ge)
1158 return d1->u.veclen >= d2->u.veclen;
1159 if (d1->type == DT_veclen_ge && d2->type == DT_veclen)
1160 return d2->u.veclen >= d1->u.veclen;
1161
1162 return -1;
1163 }
对于这里感兴趣的节点, maybe_both_true_2 将对第二个子节点返回 0 ,它进而使得在 1182 行的 maybe_both_true_1 返回 0 。接着函数 maybe_both_true 在 1249 行也返回 0 。
那么回到 merge_trees ,在 1445 行,因为 maybe_both_true 返回 0 。在 1452 行的代码执行在两个相等的类型上。那么在 1456 行, insert_before 当前是 null 。在执行了 1456 行的 IF 块之后,我们可以得到如下的节点。两个位置是“ 10 ”的节点被链接为兄弟节点。
图 17 : merge_tree 函数,图 3
从这个图中,我们可以看到,向 recog_tree 加入了一个分枝。看到事实上从 addh 剥除了公共的部分,对 recog_tree 的根节点,它们不可到达。
main (continued)
2662 if (error_count )
2663 return FATAL_EXIT_CODE;
2664
2665 puts ("/n/n");
2666
2667 process_tree (&recog_tree, RECOG);
2668 process_tree (&split_tree, SPLIT);
2669 process_tree (&peephole2_tree, PEEPHOLE2);
2670
2671 fflush (stdout);
2672 return (ferror (stdout) != 0 ? FATAL_EXIT_CODE : SUCCESS_EXIT_CODE);
2673 }