GCC-3.4.6源代码学习笔记(63)
4.3.1.7.7. 具有 C++ 链接性的 C++ 语言成分
4.3.1.7.7.1. bad_alloc
current_lang_name 表示程序所用的语言,现在它被更新为表示 C++ 语言的标识符。它确定了标识符的链接性。例如, C++ 的标识符需要其名字被修饰,而 C 的标识符是不需要的。
cxx_init_decl_processing (continue)
3080 /* Now, C++. */
3081 current_lang_name = lang_name_cplusplus;
3082
3083 {
3084 tree bad_alloc_id;
3085 tree bad_alloc_type_node;
3086 tree bad_alloc_decl;
3087 tree newtype, deltype;
3088 tree ptr_ftype_sizetype;
3089
3090 push_namespace (std_identifier);
3091 bad_alloc_id = get_identifier ("bad_alloc");
3092 bad_alloc_type_node = make_aggr_type (RECORD_TYPE);
3093 TYPE_CONTEXT (bad_alloc_type_node) = current_namespace ;
3094 bad_alloc_decl
3095 = create_implicit_typedef (bad_alloc_id, bad_alloc_type_node);
3096 DECL_CONTEXT (bad_alloc_decl) = current_namespace ;
3097 TYPE_STUB_DECL (bad_alloc_type_node) = bad_alloc_decl;
3098 pop_namespace ();
对于 C++ ,在 std 名字空间提供了一个非常重要的操作符 new ,它是 C 语言中 malloc 的替代者。这个操作符的标准行为是,如果没有内存能够分配,将抛出异常 std::bad_alloc 。因而,下面类型 bad_alloc 将被创建,不过这里它只是一个占位符,因为这里只给出了空的类型定义,不是真正的定义。以后如果用户通过包含头文件 <new> ,使用了 bad_alloc (比如,调用了 new 操作符), bad_alloc 的真正定义将被解析以产生最终正确的节点;而如果没有地方使用 bad_alloc ,这个伪定义就会留在那里。
859 tree
860 make_aggr_type (enum tree_code code) in lex.c
861 {
862 tree t = cxx_make_type (code);
863
864 if (IS_AGGR_TYPE_CODE (code))
865 SET_IS_AGGR_TYPE (t, 1);
866
867 return t;
868 }
注意由 make_aggr_type 创建的聚集类型( class/struct/union )没有任何域。它只是一个空对象的定义。
808 tree
809 cxx_make_type (enum tree_code code) in lex.c
810 {
811 tree t = make_node (code);
812
813 /* Create lang_type structure. */
814 if (IS_AGGR_TYPE_CODE (code)
815 || code == BOUND_TEMPLATE_TEMPLATE_PARM)
816 {
817 struct lang_type *pi;
818
819 pi = ggc_alloc_cleared (sizeof (struct lang_type));
820
821 TYPE_LANG_SPECIFIC (t) = pi;
822 pi->u.c.h.is_lang_type_class = 1;
823
824 #ifdef GATHER_STATISTICS
825 tree_node_counts [(int)lang_type] += 1;
826 tree_node_sizes [(int)lang_type] += sizeof (struct lang_type);
827 #endif
828 }
829
830 /* Set up some flags that give proper default behavior. */
831 if (IS_AGGR_TYPE_CODE (code))
832 {
833 SET_CLASSTYPE_INTERFACE_UNKNOWN_X (t, interface_unknown );
834 CLASSTYPE_INTERFACE_ONLY (t) = interface_only ;
835
836 /* Make sure this is laid out, for ease of use later. In the
837 presence of parse errors, the normal was of assuring this
838 might not ever get executed, so we lay it out *immediately*. */
839 build_pointer_type (t);
840 }
841 else
842 /* We use TYPE_ALIAS_SET for the CLASSTYPE_MARKED bits. But,
843 TYPE_ALIAS_SET is initialized to -1 by default, so we must
844 clear it here. */
845 TYPE_ALIAS_SET (t) = 0;
846
847 /* We need to allocate a TYPE_BINFO even for TEMPLATE_TYPE_PARMs
848 since they can be virtual base types, and we then need a
849 canonical binfo for them. Ideally, this would be done lazily for
850 all types. */
851 if (IS_AGGR_TYPE_CODE (code) || code == TEMPLATE_TYPE_PARM
852 || code == BOUND_TEMPLATE_TEMPLATE_PARM
853 || code == TYPENAME_TYPE)
854 TYPE_BINFO (t) = make_binfo (size_zero_node, t, NULL_TREE, NULL_TREE);
855
856 return t;
857 }
对于支持面向对象编程的语言,聚集类型(例如, C++ 的 struct/class/union )必须有一个方法来记录,它与它所派生的子类,及所继承的父类的关系。这就是类型中的 binfo 节点。这里正如我们之前所提及的,这里创建的 binfo 节点也是空的。
同样注意到,这个伪 bad_alloc 节点没有真正被加入到名字空间,而是它的上下文设置为该名字空间。这是因为这个类型还没有定义好,还不能用。
4.3.1.7.7.2. Binfo 及 basetype 的细节
在 C++ 中,非虚继承总是具有以下的布局,例如, X 继承自 Y ,而 Y 继承自 Z 。
<!-- /* Font Definitions */ @font-face {font-family:宋体; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-alt:SimSun; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} @font-face {font-family:"/@宋体"; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} /* Style Definitions */ p.MsoNormal, li.MsoNormal, div.MsoNormal {mso-style-parent:""; margin:0cm; margin-bottom:.0001pt; text-align:justify; text-justify:inter-ideograph; mso-pagination:none; font-size:10.5pt; mso-bidi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-font-family:宋体; mso-font-kerning:1.0pt;} /* Page Definitions */ @page {mso-page-border-surround-header:no; mso-page-border-surround-footer:no;} @page Section1 {size:612.0pt 792.0pt; margin:72.0pt 90.0pt 72.0pt 90.0pt; mso-header-margin:36.0pt; mso-footer-margin:36.0pt; mso-paper-source:0;} div.Section1 {page:Section1;} -->
图 39 :非虚继承的布局
而对于虚继承 ,例如 X 继承自 Y ,而 Y 虚拟继承自 Z 。这个布局看上去就像:
 <!-- /* Font Definitions */ @font-face {font-family:宋体; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-alt:SimSun; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} @font-face {font-family:"/@宋体"; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} /* Style Definitions */ p.MsoNormal, li.MsoNormal, div.MsoNormal {mso-style-parent:""; margin:0cm; margin-bottom:.0001pt; text-align:justify; text-justify:inter-ideograph; mso-pagination:none; font-size:10.5pt; mso-bidi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-font-family:宋体; mso-font-kerning:1.0pt;} /* Page Definitions */ @page {mso-page-border-surround-header:no; mso-page-border-surround-footer:no;} @page Section1 {size:612.0pt 792.0pt; margin:72.0pt 90.0pt 72.0pt 90.0pt; mso-header-margin:36.0pt; mso-footer-margin:36.0pt; mso-paper-source:0;} div.Section1 {page:Section1;} -->
<!-- /* Font Definitions */ @font-face {font-family:宋体; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-alt:SimSun; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} @font-face {font-family:"/@宋体"; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} /* Style Definitions */ p.MsoNormal, li.MsoNormal, div.MsoNormal {mso-style-parent:""; margin:0cm; margin-bottom:.0001pt; text-align:justify; text-justify:inter-ideograph; mso-pagination:none; font-size:10.5pt; mso-bidi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-font-family:宋体; mso-font-kerning:1.0pt;} /* Page Definitions */ @page {mso-page-border-surround-header:no; mso-page-border-surround-footer:no;} @page Section1 {size:612.0pt 792.0pt; margin:72.0pt 90.0pt 72.0pt 90.0pt; mso-header-margin:36.0pt; mso-footer-margin:36.0pt; mso-paper-source:0;} div.Section1 {page:Section1;} -->
图 40 :虚拟继承的布局
basetype 表示一个数据类型在另一个类型的继承链中的特定的一次使用。每个这样的 basetype 的使用,都有它所拥有的 binfo 对象来描述。 binfo 对象是一个 TREE_VEC 节点。继承由对给定的类型所分配的 binfo 节点来表示。例如,给定类型 X 和 Y , Y 被 X 继承,那么 3 个 binfo 节点将被分配:一个描述 X 的 binfo 属性,类似的一个描述 Y 的 binfo 属性,而最后一个描述 Y 作为 X 基类的 binfo 的属性。这样,给定一个 class X 的指针,通过查看 X 的 binfo 的 basetypes ,可以得到作为 X basetype 的 Y 的 binfo 的指针。
 <!-- /* Font Definitions */ @font-face {font-family:宋体; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-alt:SimSun; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} @font-face {font-family:黑体; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-alt:SimHei; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:1 135135232 16 0 262144 0;} @font-face {font-family:"/@宋体"; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} @font-face {font-family:"/@黑体"; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:1 135135232 16 0 262144 0;} /* Style Definitions */ p.MsoNormal, li.MsoNormal, div.MsoNormal {mso-style-parent:""; margin:0cm; margin-bottom:.0001pt; text-align:justify; text-justify:inter-ideograph; mso-pagination:none; font-size:10.5pt; mso-bidi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-font-family:宋体; mso-font-kerning:1.0pt;} h6 {mso-style-next:Normal; margin-top:12.0pt; margin-right:0cm; margin-bottom:3.2pt; margin-left:0cm; text-align:justify; text-justify:inter-ideograph; line-height:133%; mso-pagination:lines-together; page-break-after:avoid; mso-outline-level:6; font-size:12.0pt; font-family:Arial; mso-fareast-font-family:黑体; mso-bidi-font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-font-kerning:1.0pt;} a:link, span.MsoHyperlink {color:blue; text-decoration:underline; text-underline:single;} a:visited, span.MsoHyperlinkFollowed {color:purple; text-decoration:underline; text-underline:single;} /* Page Definitions */ @page {mso-page-border-surround-header:no; mso-page-border-surround-footer:no;} @page Section1 {size:612.0pt 792.0pt; margin:72.0pt 90.0pt 72.0pt 90.0pt; mso-header-margin:36.0pt; mso-footer-margin:36.0pt; mso-paper-source:0;} div.Section1 {page:Section1;} /* List Definitions */ @list l0 {mso-list-id:628780947; mso-list-template-ids:-1270293672;} @list l0:level1 {mso-level-start-at:4; mso-level-tab-stop:21.25pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:21.25pt; text-indent:-21.25pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt;} @list l0:level2 {mso-level-start-at:3; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/."; mso-level-tab-stop:19.85pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:1.0cm; text-indent:-1.0cm; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-ansi-font-weight:bold; mso-ansi-font-style:normal;} @list l0:level3 {mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/."; mso-level-tab-stop:1.0cm; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:1.0cm; text-indent:-1.0cm; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt;} @list l0:level4 {mso-level-start-at:7; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/."; mso-level-tab-stop:35.45pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:35.45pt; text-indent:-35.45pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman";} @list l0:level5 {mso-level-start-at:7; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/.%5/."; mso-level-tab-stop:42.55pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:42.55pt; text-indent:-42.55pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman";} @list l0:level6 {mso-level-start-at:2; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/.%5/.%6/."; mso-level-tab-stop:49.6pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:49.6pt; text-indent:-49.6pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt;} @list l0:level7 {mso-level-start-at:7; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/.%5/.%6/.%7/."; mso-level-tab-stop:2.0cm; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:2.0cm; text-indent:-2.0cm; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt;} @list l0:level8 {mso-level-start-at:2; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/.%5/.%6/.%7/.%8/."; mso-level-tab-stop:63.8pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:63.8pt; text-indent:-63.8pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt;} @list l0:level9 {mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/.%5/.%6/.%7/.%8/.%9/."; mso-level-tab-stop:70.9pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:70.9pt; text-indent:-70.9pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt; mso-bidi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-ansi-font-weight:bold;} ol {margin-bottom:0cm;} ul {margin-bottom:0cm;} -->
<!-- /* Font Definitions */ @font-face {font-family:宋体; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-alt:SimSun; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} @font-face {font-family:黑体; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-alt:SimHei; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:1 135135232 16 0 262144 0;} @font-face {font-family:"/@宋体"; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} @font-face {font-family:"/@黑体"; panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1; mso-font-charset:134; mso-generic-font-family:auto; mso-font-pitch:variable; mso-font-signature:1 135135232 16 0 262144 0;} /* Style Definitions */ p.MsoNormal, li.MsoNormal, div.MsoNormal {mso-style-parent:""; margin:0cm; margin-bottom:.0001pt; text-align:justify; text-justify:inter-ideograph; mso-pagination:none; font-size:10.5pt; mso-bidi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-fareast-font-family:宋体; mso-font-kerning:1.0pt;} h6 {mso-style-next:Normal; margin-top:12.0pt; margin-right:0cm; margin-bottom:3.2pt; margin-left:0cm; text-align:justify; text-justify:inter-ideograph; line-height:133%; mso-pagination:lines-together; page-break-after:avoid; mso-outline-level:6; font-size:12.0pt; font-family:Arial; mso-fareast-font-family:黑体; mso-bidi-font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-font-kerning:1.0pt;} a:link, span.MsoHyperlink {color:blue; text-decoration:underline; text-underline:single;} a:visited, span.MsoHyperlinkFollowed {color:purple; text-decoration:underline; text-underline:single;} /* Page Definitions */ @page {mso-page-border-surround-header:no; mso-page-border-surround-footer:no;} @page Section1 {size:612.0pt 792.0pt; margin:72.0pt 90.0pt 72.0pt 90.0pt; mso-header-margin:36.0pt; mso-footer-margin:36.0pt; mso-paper-source:0;} div.Section1 {page:Section1;} /* List Definitions */ @list l0 {mso-list-id:628780947; mso-list-template-ids:-1270293672;} @list l0:level1 {mso-level-start-at:4; mso-level-tab-stop:21.25pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:21.25pt; text-indent:-21.25pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt;} @list l0:level2 {mso-level-start-at:3; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/."; mso-level-tab-stop:19.85pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:1.0cm; text-indent:-1.0cm; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-ansi-font-weight:bold; mso-ansi-font-style:normal;} @list l0:level3 {mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/."; mso-level-tab-stop:1.0cm; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:1.0cm; text-indent:-1.0cm; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt;} @list l0:level4 {mso-level-start-at:7; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/."; mso-level-tab-stop:35.45pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:35.45pt; text-indent:-35.45pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman";} @list l0:level5 {mso-level-start-at:7; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/.%5/."; mso-level-tab-stop:42.55pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:42.55pt; text-indent:-42.55pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman";} @list l0:level6 {mso-level-start-at:2; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/.%5/.%6/."; mso-level-tab-stop:49.6pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:49.6pt; text-indent:-49.6pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt;} @list l0:level7 {mso-level-start-at:7; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/.%5/.%6/.%7/."; mso-level-tab-stop:2.0cm; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:2.0cm; text-indent:-2.0cm; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt;} @list l0:level8 {mso-level-start-at:2; mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/.%5/.%6/.%7/.%8/."; mso-level-tab-stop:63.8pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:63.8pt; text-indent:-63.8pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt;} @list l0:level9 {mso-level-text:"%1/.%2/.%3/.%4/.%5/.%6/.%7/.%8/.%9/."; mso-level-tab-stop:70.9pt; mso-level-number-position:left; margin-left:70.9pt; text-indent:-70.9pt; mso-ansi-font-size:12.0pt; mso-bidi-font-size:12.0pt; font-family:"Times New Roman"; mso-ansi-font-weight:bold;} ol {margin-bottom:0cm;} ul {margin-bottom:0cm;} -->
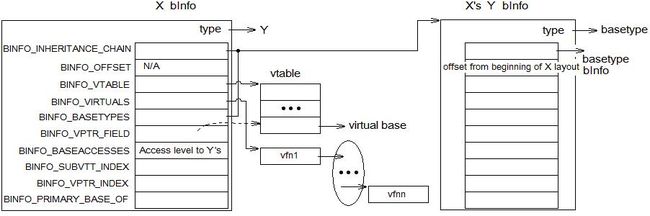
图 41 : binfo 间的关系
对于 C++ 作为一个 TREE_VEC , binfo 的内容如下(由 [] 所包括的内容是访问对应域的宏):
Pos 0 : [BINFO_INHERITANCE_CHAIN ] 用于建立代表继承链的槽。例如,如果 X 派生自 Y ,而 Y 派生自 Z ,那么这个域可以用于将 X 的 binfo 节点链接到 X 中的 Y 的 binfo 节点,来表示 X 到 Y 的继承。同样, X 中的 Y 的 binfo 节点的这个槽,可以指向由 Y 所继承的 Z (在 X 的继承等级中)。在这个形式中,可以通过使用 binfo 节点本身,来表示及遍历具体的继承(而不是使用新内存来指向这些 binfo 节点)。由依赖语言的前端对这个信息进行必要的维护。
Pos 1 : [BINFO_OFFSET ] basetype 在包含其类型中的偏移。这个域保存了从完整对象的基址到该对象中代表该基类的那部分对象的基址的偏移。除非是多继承,这个值永远是 0 。
Pos 2 : [BINFO_VTABLE ] 属于这个 basetype 的虚函数表。虚函数表提供了一个运行时方法分发的机制。虚函数表的表项是依赖于语言的。
Pos 3 : [BINFO_VIRTUALS ] 虚函数表中的虚函数。它是一个 tree_list ,用作一个初始的、近似物,为这个 basetype 构建虚函数表。
Pos 4 : [BINFO_BASETYPES ] 被这个 basetype 所继承的直接 basetypes 的 binfos 构成的 vector 。如果这个 basetype 描述的是派生类 C 中的类型 D ,并且如果 D 的 basetypes 是 E 和 F ,那么这个 vector 包含了被 C 继承的 E 和 F 的 binfo 。
Pos 5 : [BINFO_VPTR_FIELD ] 一个描述虚基类的 binfo 记录,即,该节点设置了标识 TREE_VIA_VIRTUAL ,这个域帮助定位虚基类。其确切的内容是依赖于语言的。在 C++ 前端,这个域是一个 INTEGER_CST ,它给出了相对于虚函数表的偏移,在这个位置上可以找到虚基类。
Pos 6 : [BINFO_BASEACCESSES ] 表示该 binfo 到其基类的访问权限。其值有 access_public_node , access_proected_node 或 access_private_node 。如果这个数组不存在,则暗示 public 的访问权限。
Pos 7 : [BINFO_SUBVTT_INDEX ] 这个子对象的子虚表表在虚表表( VTT )中所对应的索引。如果没有子虚表表( subVTT ),则为 NULL_TREE 。
一个类如果有虚基类,就要求一个 VTT 。它包含了:
1 – 用于该类的完整对象的主虚指针。
2 – 每个需要 VTT 的,直接的非虚基类的次级 VTT 。
3 – 用于每个具有虚基类或在虚继承路径上的,直接或间接基类的,次级虚指针。
4 – 直接或间接虚基类的次级 VTT 。
次级 VTT 看上去类似于完整对象的 VTT ,但没有第 4 部分。
Pos 8 : [BINFO_VPTR_INDEX ] VTT 中的索引,在该位置可以找到该子对象的虚指针( vptr )。如果中 VTT 中没有次级虚指针,则是 NULL_TREE 。这是上面 Pos 7 所提及的主虚指针。
Pos 9 : [BINFO_PRIMARY_BASE_OF ] 主基类的 binfo 节点。对于虚基类,它的内容与 BINFO_INHERITANCE_CHAIN 不相同,因为一个虚基类有时虽然不是一个直接基类但仍然可以是主基类。
make_binfo 是构建 binfo 最基本的函数。为出现在程序中,通常的类准备 binfo 的函数,则是 xref_basetypes ,在需要新的 binfo 时,它将调用 make_binfo 。
771 tree
772 make_binfo (tree offset, tree binfo, tree vtable, tree virtuals) in cp/tree.c
773 {
774 tree new_binfo = make_tree_vec (BINFO_LANG_ELTS);
775 tree type;
776
777 if (TREE_CODE (binfo) == TREE_VEC)
778 {
779 type = BINFO_TYPE (binfo);
780 BINFO_DEPENDENT_BASE_P(new_binfo)=BINFO_DEPENDENT_BASE_P(binfo);
781 }
782 else
783 {
784 type = binfo;
785 binfo = NULL_TREE;
786 BINFO_DEPENDENT_BASE_P (new_binfo) = 1;
787 }
788
789 TREE_TYPE (new_binfo) = TYPE_MAIN_VARIANT (type);
790 BINFO_OFFSET (new_binfo) = offset;
791 BINFO_VTABLE (new_binfo) = vtable;
792 BINFO_VIRTUALS (new_binfo) = virtuals;
793
794 if (binfo && !BINFO_DEPENDENT_BASE_P (binfo)
795 && BINFO_BASETYPES (binfo) != NULL_TREE)
796 {
797 BINFO_BASETYPES (new_binfo) = copy_node (BINFO_BASETYPES (binfo));
798 /* We do not need to copy the accesses, as they are read only. */
799 BINFO_BASEACCESSES (new_binfo) = BINFO_BASEACCESSES (binfo);
800 }
801 return new_binfo;
802 }
在 786 行, BINFO_DEPENDENT_BASE_P 标记该 binfo 是一个有依赖的基类,不应该在继承链中对其进行查找。例子有这里的 bad_alloc_type_node ,模板类型参数,及 typename 声明类型。在创建完 bad_alloc_type_node 后,这还不算结束。记得在 C++ 中,当使用 S 时你是不需要写 struct S ,可以直接用 S 。这通过函数 create_implicit_typedef 来创建一个 TYPE_DECL ,效果就好像用户写了 typedef struct S S 。
930 tree
931 create_implicit_typedef (tree name, tree type) in decl.c
932 {
933 tree decl;
934
935 decl = build_decl (TYPE_DECL, name, type);
936 DECL_ARTIFICIAL (decl) = 1;
937 /* There are other implicit type declarations, like the one *within*
938 a class that allows you to write `S::S'. We must distinguish
939 amongst these. */
940 SET_DECL_IMPLICIT_TYPEDEF_P (decl);
941 TYPE_NAME (type) = decl;
942
943 return decl;
944 }
另外,在前端, class/struct 均被构建成 RECORD_TYPE (这也是为什么有些 C++ 教程声称 struct 和 class 没有本质区别的原因),因此 make_aggr_type 中 864 行的 IS_AGGR_TYPE_CODE 对 RECORD_TYPE 和 UNION_TYPE 返回 true 。
4.3.1.7.7.2. new 和 delete 操作符
虽然你可以在自己的程序里使用异常 bad_alloc ,但最初它的出现是伴随操作符 new 和 new[] 。这也是标准的定义。那么需要将 bad_alloc 和这 2 个操作符绑定起来。在 初始化操作符数据 一节,操作符的标识符节点被创建,但相应的声明节点还没有。因此在 3100 行, new 和 new[] 都被构建为类型 void* f(size_t) 。
cxx_init_decl_processing (continue)
3100 ptr_ftype_sizetype
3101 = build_function_type (ptr_type_node,
3102 tree_cons (NULL_TREE,
3103 size_type_node,
3104 void_list_node));
3105 newtype = build_exception_variant
3106 (ptr_ftype_sizetype, add_exception_specifier
3107 (NULL_TREE, bad_alloc_type_node, -1));
3108 deltype = build_exception_variant (void_ftype_ptr, empty_except_spec);
3109 push_cp_library_fn (NEW_EXPR, newtype);
3110 push_cp_library_fn (VEC_NEW_EXPR, newtype);
3111 global_delete_fndecl = push_cp_library_fn (DELETE_EXPR, deltype);
3112 push_cp_library_fn (VEC_DELETE_EXPR, deltype);
3113 }
不过类型 void* f(size_t) 并不确切,正确的应该是 void* f(size_t) throw bad_alloc 。这个变体由函数 build_exception_variant 构建。因为函数可以抛出多于一种的异常, build_exception_variant 的第二个参数需要是一个 tree_list 的形式。这个 tree_list 由 add_exception_specifier 准备。
1277 tree
1278 add_exception_specifier (tree list, tree spec, int complain) in typeck2.c
1279 {
1280 bool ok;
1281 tree core = spec;
1282 bool is_ptr;
1283 int diag_type = -1; /* none */
1284
1285 if (spec == error_mark_node)
1286 return list;
1287
1288 my_friendly_assert (spec && (!list || TREE_VALUE (list)), 19990317);
1289
1290 /* [except.spec] 1, type in an exception specifier shall not be
1291 incomplete, or pointer or ref to incomplete other than pointer
1292 to cv void. */
1293 is_ptr = TREE_CODE (core) == POINTER_TYPE;
1294 if (is_ptr || TREE_CODE (core) == REFERENCE_TYPE)
1295 core = TREE_TYPE (core);
1296 if (complain < 0)
1297 ok = true;
1298 else if (VOID_TYPE_P (core))
1299 ok = is_ptr;
1300 else if (TREE_CODE (core) == TEMPLATE_TYPE_PARM)
1301 ok = true;
1302 else if (processing_template_decl)
1303 ok = true;
1304 else
1305 {
1306 ok = true;
1307 /* 15.4/1 says that types in an exception specifier must be complete,
1308 but it seems more reasonable to only require this on definitions
1309 and calls. So just give a pedwarn at this point; we will give an
1310 error later if we hit one of those two cases. */
1311 if (!COMPLETE_TYPE_P (complete_type (core)))
1312 diag_type = 2; /* pedwarn */
1313 }
1314
1315 if (ok)
1316 {
1317 tree probe;
1318
1319 for (probe = list; probe; probe = TREE_CHAIN (probe))
1320 if (same_type_p (TREE_VALUE (probe), spec))
1321 break ;
1322 if (!probe)
1323 list = tree_cons (NULL_TREE, spec, list);
1324 }
1325 else
1326 diag_type = 0; /* error */
1327
1328 if (diag_type >= 0 && complain)
1329 cxx_incomplete_type_diagnostic (NULL_TREE, core, diag_type);
1330
1331 return list;
1332 }
下面的 push_cp_library_fn 则构建这个库函数的声明节点,并将其加入 std 名字空间。这里的库函数具有 C++ 链接性的。
3370 static tree
3371 push_cp_library_fn (enum tree_code operator_code, tree type) in decl.c
3372 {
3373 tree fn = build_cp_library_fn (ansi_opname (operator_code),
3374 operator_code,
3375 type);
3376 pushdecl (fn);
3377 return fn;
3378 }
其中 ansi_opname 为操作符提取其标识符。
868 #define ansi_opname (CODE) / in cp-tree.h
869 (operator_name_info [(int) (CODE)].identifier)
3327 static tree
3328 build_cp_library_fn (tree name, enum tree_code operator_code, tree type) in decl.c
3329 {
3330 tree fn = build_library_fn_1 (name, operator_code, type);
3331 TREE_NOTHROW (fn) = TYPE_NOTHROW_P (type);
3332 DECL_CONTEXT (fn) = FROB_CONTEXT (current_namespace);
3333 SET_DECL_LANGUAGE (fn, lang_cplusplus);
3334 set_mangled_name_for_decl (fn);
3335 return fn;
3336 }
上面的 set_mangled_name_for_decl 将为函数创建修饰名,并且将其设置入 DECL_ASSEMBLER_NAME 。然后这个创建的 FUNCTION_DECL 通过 pushdecl 加入当前名字空间,过程参见 把 FUNCTION_DECL加入当前名字空间 。