A* Pathfinding Project (Unity A*寻路插件) 使用教程
Unity4.6 后续版本都已经内置了寻路AI了,之前的文章有介绍
Unity3d 寻路功能 介绍及项目演示
然而两年来项目中一直使用的是 A* Pathfinding 这个插件的,所以抽时间来写下这个插件的简单使用。
根据游戏的类型,使用到的插件功能可能会不一样,我这里只介绍最简单的,也是使用的最多的简单寻路。复杂的如跟随、动态,都有对应的例子来学习。
我也一直都没有去看……
转自http://blog.csdn.net/huutu http://www.thisisgame.com.cn
下面是动态图,借助 A* 插件,编写很少的代码就可以做到寻路。
1、创建场景
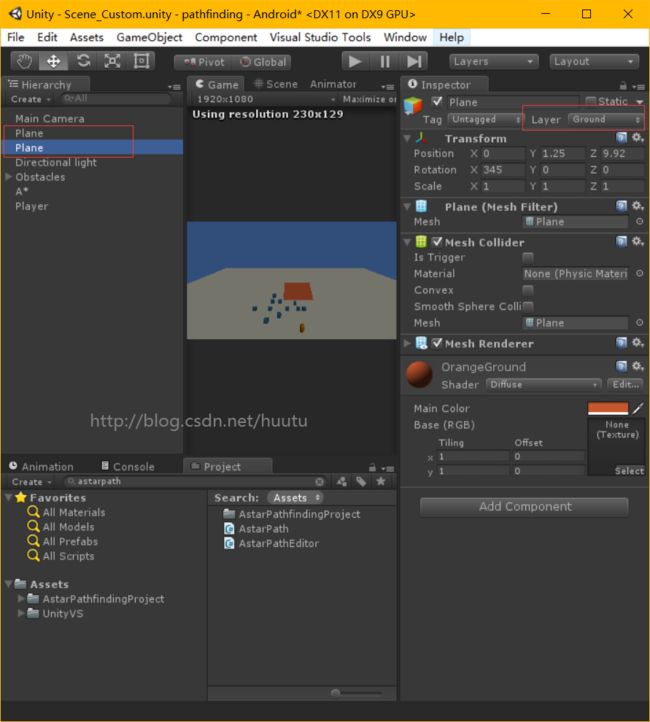
在场景中添加一些Cube 作为障碍物 Obstacles,添加一个 Capsule 作为Player,然后添加一个Plane 作为地面,再添加一个Plane,作为斜坡测试。
在创建一个GameObject,改名为 A* ,添加A Star Path (Path finder) 组件。
2、编辑场景,指定障碍物
A* 插件中,是根据 Layer 来判断障碍物的,所以我们要把 作为障碍物的 Cubes 都设置到 Obstacle 这一个Layer。
然后给我们的地板,设置Layer 为 Ground ,两块地板都是
转自http://blog.csdn.net/huutu http://www.thisisgame.com.cn
3、生成寻路网格
选中 A* ,在Inspector 中,展开 。查看下面的面板。
如图中,
黑色箭头所指是宽高,这里的宽高,是指格子的数量。这里用到的就是 A* 的格子寻路。
调整宽高,覆盖整个Plane。
红色箭头所指,是左上、右上、左下、右下、中心 四个点,选中其中一个点,就可以调整这个点的位置。
选中中心,点击蓝色箭头所指的 Snap Size,会根据中心的位置来自动对齐。
继续设置。
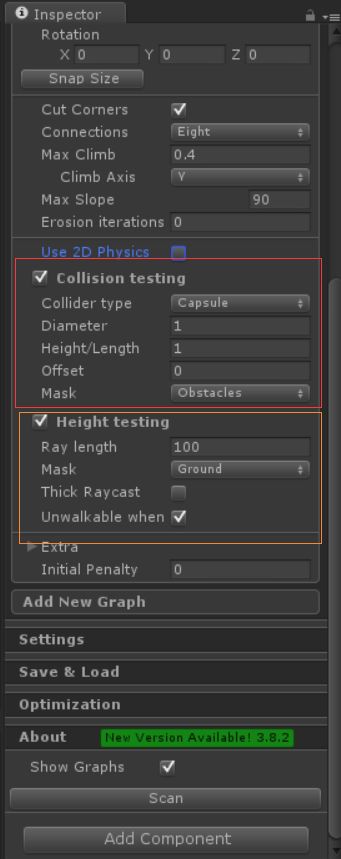
红框中的Collision Testing,是生成 禁止通过 格子的。
因为我们的 Cubes 是障碍物,所以在 Mask 中选择 Cubes 所在的Layer - Obstacles。
黄色框中的Height Testing 是用来 让寻路节点 与 Ground 进行检测的,比如要爬坡的时候就需要检测高度。
设置完成后,点击Scan,就会生成寻路网格。
转自http://blog.csdn.net/huutu http://www.thisisgame.com.cn
4、编写寻路 AI 代码
生成寻路网格之后,我们在代码中就可以使用 A* 来进行寻路了。
首先在 Player 这个 Capsule 上添加Seeker 组件。
然后新建脚本 AStarPlayer.cs 作为测试代码。
在代码中,首先我们从 屏幕发射射线,来定位目标位置。
然后使用 Seeker 来开始生成最短路径。
Seeker生成路径成功后,会把每一个节点的位置保存在 List中。
我们按照顺序读取 List 中的位置,位移Player 到对应的位置,就完成了寻路。
下面是完整代码:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using Pathfinding;
public class AStarPlayer : MonoBehaviour
{
//目标位置;
Vector3 targetPosition;
Seeker seeker;
CharacterController characterController;
//计算出来的路线;
Path path;
//移动速度;
float playerMoveSpeed = 10f;
//当前点
int currentWayPoint = 0;
bool stopMove = true;
//Player中心点;
float playerCenterY = 1.0f;
// Use this for initialization
void Start ()
{
seeker = GetComponent<Seeker>();
playerCenterY = transform.localPosition.y;
}
//寻路结束;
public void OnPathComplete(Path p)
{
Debug.Log("OnPathComplete error = "+p.error);
if (!p.error)
{
currentWayPoint = 0;
path = p;
stopMove = false;
}
for (int index = 0; index < path.vectorPath.Count; index++)
{
Debug.Log("path.vectorPath["+index+"]="+path.vectorPath[index]);
}
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update ()
{
if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0))
{
RaycastHit hit;
if (!Physics.Raycast(Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition), out hit, 100))
{
return;
}
if (!hit.transform)
{
return;
}
targetPosition = hit.point;// new Vector3(hit.point.x, transform.localPosition.y, hit.point.z);
Debug.Log("targetPosition=" + targetPosition);
seeker.StartPath(transform.position, targetPosition,OnPathComplete);
}
}
void FixedUpdate()
{
if (path == null || stopMove)
{
return;
}
//根据Player当前位置和 下一个寻路点的位置,计算方向;
Vector3 currentWayPointV = new Vector3(path.vectorPath[currentWayPoint].x, path.vectorPath[currentWayPoint].y + playerCenterY, path.vectorPath[currentWayPoint].z);
Vector3 dir = (currentWayPointV - transform.position).normalized;
//计算这一帧要朝着 dir方向 移动多少距离;
dir *= playerMoveSpeed * Time.fixedDeltaTime;
//计算加上这一帧的位移,是不是会超过下一个节点;
float offset = Vector3.Distance(transform.localPosition, currentWayPointV);
if (offset < 0.1f)
{
transform.localPosition = currentWayPointV;
currentWayPoint++;
if (currentWayPoint == path.vectorPath.Count)
{
stopMove = true;
currentWayPoint = 0;
path = null;
}
}
else
{
if (dir.magnitude > offset)
{
Vector3 tmpV3 = dir * (offset / dir.magnitude);
dir = tmpV3;
currentWayPoint++;
if (currentWayPoint == path.vectorPath.Count)
{
stopMove = true;
currentWayPoint = 0;
path = null;
}
}
transform.localPosition += dir;
}
}
}
至此简单的寻路了。
在A* 的Example 中,有很多个例子。
最简单的寻路脚本写法是 直接继承 AIPath 。
下面新建一个 脚本 PlayerAI.cs 继承 AIPath 来作为测试
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using Pathfinding.RVO;
namespace Pathfinding
{
[RequireComponent(typeof(Seeker))]
[RequireComponent(typeof(CharacterController))]
public class PlayerAI : AIPath
{
/** Minimum velocity for moving */
public float sleepVelocity = 0.4F;
/** Speed relative to velocity with which to play animations */
public float animationSpeed = 0.2F;
/** Effect which will be instantiated when end of path is reached.
* \see OnTargetReached */
public GameObject endOfPathEffect;
public new void Start()
{
//Call Start in base script (AIPath)
base.Start();
}
/** Point for the last spawn of #endOfPathEffect */
protected Vector3 lastTarget;
public override void OnTargetReached()
{
if (endOfPathEffect != null && Vector3.Distance(tr.position, lastTarget) > 1)
{
GameObject.Instantiate(endOfPathEffect, tr.position, tr.rotation);
lastTarget = tr.position;
}
}
public override Vector3 GetFeetPosition()
{
return tr.position;
}
protected new void Update()
{
if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0))
{
RaycastHit hit;
if (!Physics.Raycast(Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition), out hit, 100))
{
return;
}
if (!hit.transform)
{
return;
}
target.localPosition = hit.point;
}
//Get velocity in world-space
Vector3 velocity;
if (canMove)
{
//Calculate desired velocity
Vector3 dir = CalculateVelocity(GetFeetPosition());
//Rotate towards targetDirection (filled in by CalculateVelocity)
RotateTowards(targetDirection);
dir.y = 0;
if (dir.sqrMagnitude > sleepVelocity * sleepVelocity)
{
//If the velocity is large enough, move
}
else
{
//Otherwise, just stand still (this ensures gravity is applied)
dir = Vector3.zero;
}
if (this.rvoController != null)
{
rvoController.Move(dir);
velocity = rvoController.velocity;
}
else
if (navController != null)
{
#if FALSE
navController.SimpleMove (GetFeetPosition(), dir);
#endif
velocity = Vector3.zero;
}
else if (controller != null)
{
controller.SimpleMove(dir);
velocity = controller.velocity;
}
else
{
Debug.LogWarning("No NavmeshController or CharacterController attached to GameObject");
velocity = Vector3.zero;
}
}
else
{
velocity = Vector3.zero;
}
}
}
}
代码量少,但是不如自己写的直观。
两种不同的脚本都可以实现寻路效果。
示例项目打包下载:
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hsm6YNi