STL系列之九 探索hash_set
Title: STL系列之九 探索hash_set
Author: MoreWindows
Blog: http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows
E-mail: [email protected]
KeyWord: C++ STL set hash_set 哈希表 链地址法
本文将着重探索hash_set比set快速高效的原因,阅读本文前,推荐先阅读本文的姊妹篇《STL系列之六 set与hash_set》
一.hash_set之基石——哈希表
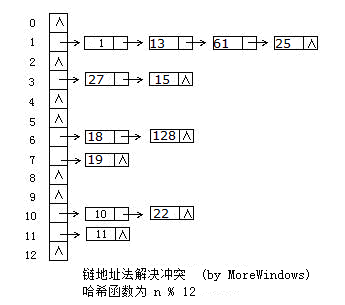
hash_set的底层数据结构是哈希表,因此要深入了解hash_set,必须先分析哈希表。哈希表是根据关键码值(Key-Value)而直接进行访问的数据结构,它用哈希函数处理数据得到关键码值,关键码值对应表中一个特定位置再由应该位置来访问记录,这样可以在时间复杂性度为O(1)内访问到数据。但是很有可能出现多个数据经哈希函数处理后得到同一个关键码——这就产生了冲突,解决冲突的方法也有很多,各大数据结构教材及考研辅导书上都会介绍大把方法。这里采用最方便最有效的一种——链地址法,当有冲突发生时将具同一关键码的数据组成一个链表。下图展示了链地址法的使用:
二.简化版的hash_table
按照上面的分析和图示,并参考《编程珠玑》第15章中哈希表的实现,不难写出一个简单的哈希表,我们称之为简化版hash_table。该哈希表由一个指针数组组成,数组中每个元素都是链表的表头指针,程序分为hash_table.h,hash_table.cpp和main.cpp。
1.hash_table.h
- #pragma once
- #define NULL 0
- //简化版hash_table
- //by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows )
- struct Node
- {
- int val;
- Node *next;
- Node(int n)
- {
- this->val = n;
- this->next = NULL;
- }
- };
- class hash_table
- {
- public:
- hash_table(const int ntablesize);
- ~hash_table();
- bool insert(int n);
- void insert(int *pFirst, int *pLast);
- bool find(int n);
- int size();
- int HashFun(int n);
- public:
- int m_nTableSize;
- int m_nTableDataCount;
- Node** m_ppTable;
- };
2.hash_table.cpp
- //简化版hash_table
- //by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows )
- #include "hash_table.h"
- #include <malloc.h>
- #include <memory.h>
- hash_table::hash_table(const int ntablesize)
- {
- m_nTableSize = ntablesize;
- m_ppTable = (Node**)malloc(sizeof(Node*) * m_nTableSize);
- if (m_ppTable == NULL)
- return ;
- m_nTableDataCount = 0;
- memset(m_ppTable, 0, sizeof(Node*) * m_nTableSize);
- }
- hash_table::~hash_table()
- {
- free(m_ppTable);
- m_ppTable = NULL;
- m_nTableDataCount = 0;
- m_nTableSize = 0;
- }
- int inline hash_table::HashFun(int n)
- {
- return (n ^ 0xdeadbeef) % m_nTableSize;
- }
- int hash_table::size()
- {
- return m_nTableDataCount;
- }
- bool hash_table::insert(int n)
- {
- int key = HashFun(n);
- //在该链表中查找该数是否已经存在
- for (Node *p = m_ppTable[key]; p != NULL; p = p->next)
- if (p->val == n)
- return true;
- //在链表的头部插入
- Node *pNode = new Node(n);
- if (pNode == NULL)
- return false;
- pNode->next = m_ppTable[key];
- m_ppTable[key] = pNode;
- m_nTableDataCount++;
- return true;
- }
- bool hash_table::find(int n)
- {
- int key = HashFun(n);
- for (Node *pNode = m_ppTable[key]; pNode != NULL; pNode = pNode->next)
- if (pNode->val == n)
- return true;
- return false;
- }
- void hash_table::insert(int *pFirst, int *pLast)
- {
- for (int *p = pFirst; p != pLast; p++)
- this->insert(*p);
- }
3.main.cpp
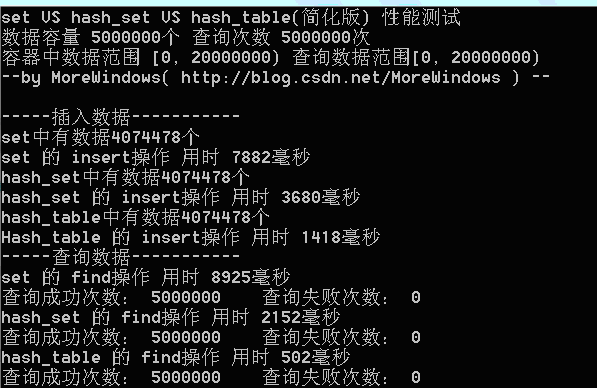
在main.cpp中,对set、hash_set、简化版hash_table作一个性能测试,测试环境为Win7+VS2008的Release设置(下同)。
- //测试set,hash_set及简化版hash_table
- // by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows )
- #include <set>
- #include <hash_set>
- #include "hash_table.h"
- #include <iostream>
- #include <ctime>
- #include <cstdio>
- #include <cstdlib>
- using namespace std;
- using namespace stdext; //hash_set
- void PrintfContainerElapseTime(char *pszContainerName, char *pszOperator, long lElapsetime)
- {
- printf("%s 的 %s操作 用时 %d毫秒\n", pszContainerName, pszOperator, lElapsetime);
- }
- // MAXN个数据 MAXQUERY次查询
- const int MAXN = 5000000, MAXQUERY = 5000000;
- int a[MAXN], query[MAXQUERY];
- int main()
- {
- printf("set VS hash_set VS hash_table(简化版) 性能测试\n");
- printf("数据容量 %d个 查询次数 %d次\n", MAXN, MAXQUERY);
- const int MAXNUM = MAXN * 4;
- const int MAXQUERYNUM = MAXN * 4;
- printf("容器中数据范围 [0, %d) 查询数据范围[0, %d)\n", MAXNUM, MAXQUERYNUM);
- printf("--by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows ) --\n\n");
- //随机生成在[0, MAXNUM)范围内的MAXN个数
- int i;
- srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
- for (i = 0; i < MAXN; ++i)
- a[i] = (rand() * rand()) % MAXNUM;
- //随机生成在[0, MAXQUERYNUM)范围内的MAXQUERY个数
- srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
- for (i = 0; i < MAXQUERY; ++i)
- query[i] = (rand() * rand()) % MAXQUERYNUM;
- set<int> nset;
- hash_set<int> nhashset;
- hash_table nhashtable(MAXN + 123);
- clock_t clockBegin, clockEnd;
- //insert
- printf("-----插入数据-----------\n");
- clockBegin = clock();
- nset.insert(a, a + MAXN);
- clockEnd = clock();
- printf("set中有数据%d个\n", nset.size());
- PrintfContainerElapseTime("set", "insert", clockEnd - clockBegin);
- clockBegin = clock();
- nhashset.insert(a, a + MAXN);
- clockEnd = clock();
- printf("hash_set中有数据%d个\n", nhashset.size());
- PrintfContainerElapseTime("hash_set", "insert", clockEnd - clockBegin);
- clockBegin = clock();
- for (i = 0; i < MAXN; i++)
- nhashtable.insert(a[i]);
- clockEnd = clock();
- printf("hash_table中有数据%d个\n", nhashtable.size());
- PrintfContainerElapseTime("Hash_table", "insert", clockEnd - clockBegin);
- //find
- printf("-----查询数据-----------\n");
- int nFindSucceedCount, nFindFailedCount;
- nFindSucceedCount = nFindFailedCount = 0;
- clockBegin = clock();
- for (i = 0; i < MAXQUERY; ++i)
- if (nset.find(query[i]) != nset.end())
- ++nFindSucceedCount;
- else
- ++nFindFailedCount;
- clockEnd = clock();
- PrintfContainerElapseTime("set", "find", clockEnd - clockBegin);
- printf("查询成功次数: %d 查询失败次数: %d\n", nFindSucceedCount, nFindFailedCount);
- nFindSucceedCount = nFindFailedCount = 0;
- clockBegin = clock();
- for (i = 0; i < MAXQUERY; ++i)
- if (nhashset.find(query[i]) != nhashset.end())
- ++nFindSucceedCount;
- else
- ++nFindFailedCount;
- clockEnd = clock();
- PrintfContainerElapseTime("hash_set", "find", clockEnd - clockBegin);
- printf("查询成功次数: %d 查询失败次数: %d\n", nFindSucceedCount, nFindFailedCount);
- nFindSucceedCount = nFindFailedCount = 0;
- clockBegin = clock();
- for (i = 0; i < MAXQUERY; ++i)
- if (nhashtable.find(query[i]))
- ++nFindSucceedCount;
- else
- ++nFindFailedCount;
- clockEnd = clock();
- PrintfContainerElapseTime("hash_table", "find", clockEnd - clockBegin);
- printf("查询成功次数: %d 查询失败次数: %d\n", nFindSucceedCount, nFindFailedCount);
- return 0;
- }
在数据量为500万时测试结果如下:
从程序运行结果可以发现,我们自己实现的hash_table(简化版)在插入和查找的效率要远高于set。为了进一步分析,最好能统计hash_table中的各个链表的长度情况,这样可以有效的了解平均每次查找要访问多少个数据。写出统计hash_table各链表长度的函数如下:
- // by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows )
- void StatisticHashTable(hash_table &ht)
- {
- const int MAXLISTLINE = 100;
- int i, a[MAXLISTLINE], nExtendListNum;
- nExtendListNum = 0;
- memset(a, 0, sizeof(a[0]) * MAXLISTLINE);
- for (i = 0; i < ht.m_nTableSize; i++)
- {
- int sum = 0;
- for (Node *p = ht.m_ppTable[i]; p != NULL; p = p->next)
- ++sum;
- if (sum >= MAXLISTLINE)
- nExtendListNum++;
- else
- a[sum]++;
- }
- printf("hash_table中链表长度统计:\n");
- for (i = 0; i < MAXLISTLINE; i++)
- if (a[i] > 0)
- {
- printf(" 长度为%d的链表有%d个 这些链表中数据占总数据的%.2lf%%\n", i, a[i], (a[i] * i * 100.0) / ht.size());
- }
- printf(" 长度超过%d的链表有%d个\n", MAXLISTLINE, nExtendListNum);
- }
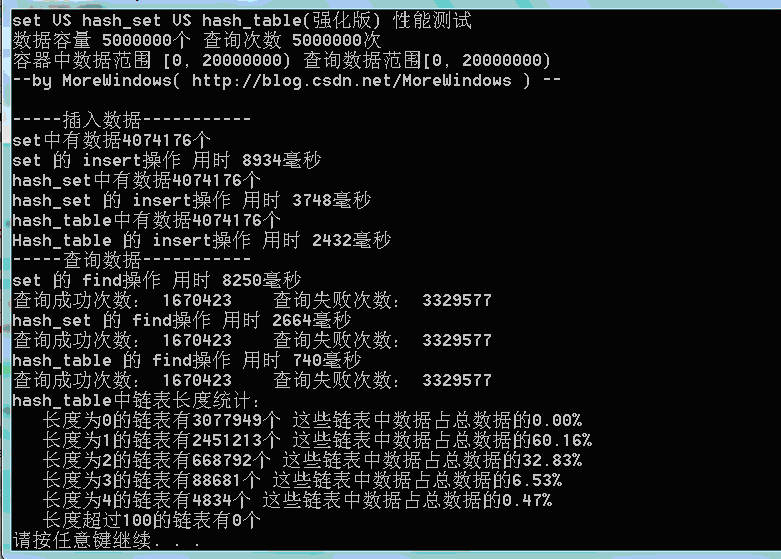
用此段代码得到链表长度的统计结果:
可以发现在hash_table中最长的链表也只有5个元素,长度为1和长度为2的链表中的数据占全部数据的89%以上。因此绝大数查询将仅仅访问哈希表1次到2次。这样的查询效率当然会比set(内部使用红黑树——类似于二叉平衡树)高的多。有了这个图示,无疑已经可以证明hash_set会比set快速高效了。但hash_set还可以动态的增加表的大小,因此我们再实现一个表大小可增加的hash_table。
三.强化版hash_table
首先来看看VS2008中hash_set是如何实现动态的增加表的大小,hash_set是在hash_set.h中声明的,在hash_set.h中可以发现hash_set是继承_Hash类的,hash_set本身并没有太多的代码,只是对_Hash作了进一步的封装,这种做法在STL中非常常见,如stack栈和queue单向队列都是以deque双向队列作底层数据结构再加一层封装。
_Hash类的定义和实现都在xhash.h类中,微软对_Hash类的第一句注释如下——
hash table -- list with vector of iterators for quick access。
哈哈,这句话说的非常明白。这说明_Hash实际上就是由vector和list组成哈希表。再阅读下代码可以发现_Hash类增加空间由_Grow()函数完成,当空间不足时就倍增,并且表中原有数据都要重新计算hash值以确定新的位置。
知道了_Hash类是如何运作的,下面就来考虑如何实现强化版的hash_table。当然有二个地方还可以改进:
1._Hash类使用的list为双向链表,但在在哈希表中使用普通的单链表就可以了。因此使用STL中的vector再加入《STL系列之八 slist单链表》一文中的slist来实现强化版的hash_table。
2.在空间分配上使用了一个近似于倍增的素数表,最开始取第一个素数,当空间不足时就使用下一个素数。经过实际测试这种效果要比倍增法高效一些。
在这二个改进之上的强化版的hash_table代码如下:
- //使用vector< slist<T> >为容器的hash_table
- // by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows )
- template< class T, class container = vector<slist<T>> >
- class hash_table
- {
- public:
- hash_table();
- hash_table(const int ntablesize);
- ~hash_table();
- void clear();
- bool insert(T &n);
- void insert(T *pFirst, T *pLast);
- bool erase(T &n);
- void resize(int nNewTableSize);
- bool find(T &n);
- int size();
- int HashFun(T &n);
- private:
- static int findNextPrime(int curPrime);
- public:
- int m_nDataCount;
- int m_nTableSize;
- container m_Table;
- static const unsigned int m_primes[50];
- };
- //素数表
- template< class T, class container>
- const unsigned int hash_table<T, container>::m_primes[50] = {
- 53, 97, 193, 389, 769, 1453, 3079, 6151, 1289, 24593, 49157, 98317,
- 196613, 393241, 786433, 1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917,
- 25165843, 50331653, 100663319, 201326611, -1
- };
- template< class T, class container>
- int inline hash_table<T, container>::HashFun(T &n)
- {
- return (n ^ 0xdeadbeef) % m_nTableSize;
- }
- template< class T, class container>
- hash_table<T, container>::hash_table()
- {
- m_nDataCount = 0;
- m_nTableSize = m_primes[0];
- m_Table.resize(m_nTableSize);
- }
- template< class T, class container>
- hash_table<T, container>::hash_table(const int ntablesize)
- {
- m_nDataCount = 0;
- m_nTableSize = ntablesize;
- m_Table.resize(m_nTableSize);
- }
- template< class T, class container>
- hash_table<T, container>::~hash_table()
- {
- clear();
- }
- template< class T, class container>
- void hash_table<T, container>::clear()
- {
- for (int i = 0; i < m_nTableSize; i++)
- m_Table[i].clear();
- m_nDataCount = 0;
- }
- template< class T, class container>
- bool hash_table<T, container>::insert(T &n)
- {
- int key = HashFun(n);
- if (!m_Table[key].find(n))
- {
- m_nDataCount++;
- m_Table[key].push_front(n);
- if (m_nDataCount >= m_nTableSize)
- resize(findNextPrime(m_nTableSize));
- }
- return true;
- }
- template< class T, class container>
- bool hash_table<T, container>::erase(T &n)
- {
- int key = HashFun(n);
- if (m_Table[key].remove(n))
- {
- m_nDataCount--;
- return true;
- }
- else
- {
- return false;
- }
- }
- template< class T, class container>
- void hash_table<T, container>::insert(T *pFirst, T *pLast)
- {
- for (T *p = pFirst; p != pLast; p++)
- this->insert(*p);
- }
- template< class T, class container>
- void hash_table<T, container>::resize(int nNewTableSize)
- {
- if (nNewTableSize <= m_nTableSize)
- return;
- int nOldTableSize = m_nTableSize;
- m_nTableSize = nNewTableSize;
- container tempTable(m_nTableSize); //创建一个更大的表
- for (int i = 0; i < nOldTableSize; i++)//将原表中数据重新插入到新表中
- {
- Node<T> *cur = m_Table[i].m_head;
- while (cur != NULL)
- {
- int key = HashFun(cur->val);
- Node<T> *pNext = cur->next;
- cur->next = tempTable[key].m_head;
- tempTable[key].m_head = cur;
- cur = pNext;
- }
- m_Table[i].m_head = NULL;
- }
- m_Table.swap(tempTable);
- }
- template< class T, class container>
- int hash_table<T, container>::size()
- {
- return m_nDataCount;
- }
- template< class T, class container>
- bool hash_table<T, container>::find(T &n)
- {
- int key = HashFun(n);
- return m_Table[key].find(n);
- }
- //在素数表中找到比当前数大的最小数
- template< class T, class container>
- int hash_table<T, container>::findNextPrime(int curPrime)
- {
- unsigned int *pStart = (unsigned int *)m_primes;
- while (*pStart <= curPrime)
- ++pStart;
- return *pStart;
- }
下面再对set、hash_set、强化版hash_table的性能测试:
测试结果一(数据量500万):
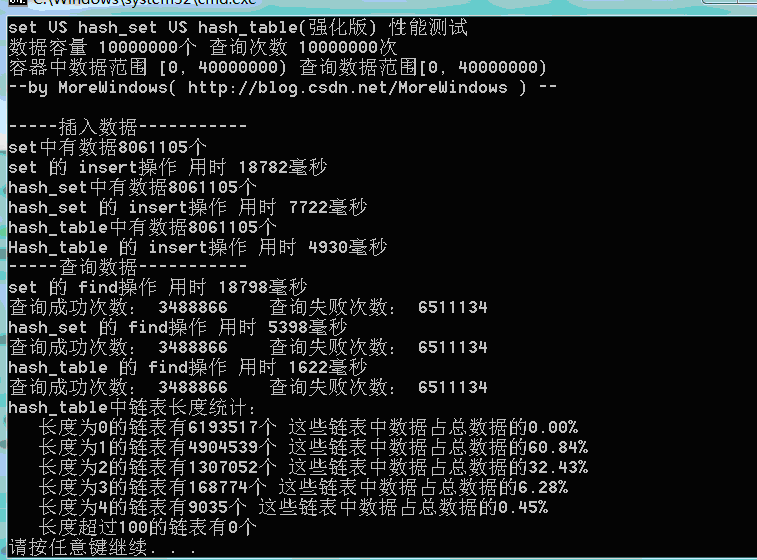
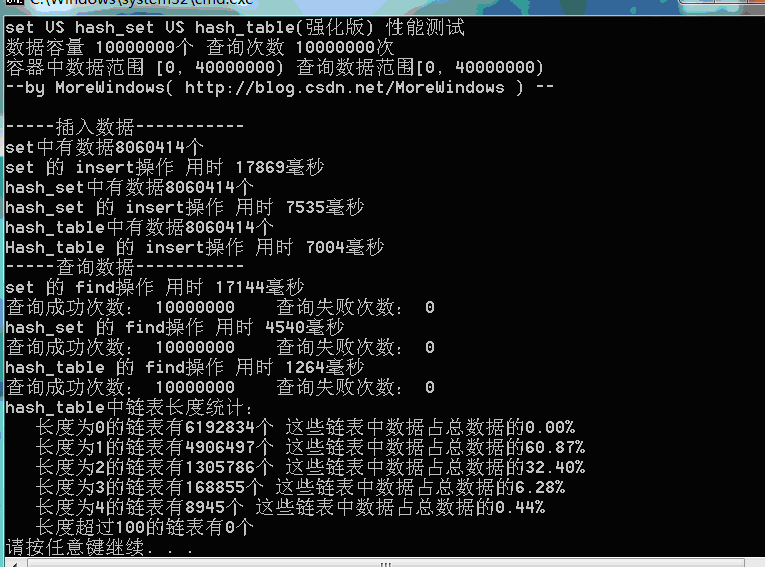
测试结果二(数据量1千万):
测试结果三(数据量1千万):
可以看出,由于强化版hash_table的哈希表在增加表空间大小时会花费额外的一些时间,所以插入数据的用时与STL提供的hash_set用时相差不多了。但查找还是比hash_set要快的一些。
四.结语
从简化版到强化版的hash_table,我们不仅知道了hash_set底层数据结构——哈希表的运作机制,还知道了如何实现大小动态变化的哈希表。达到了本文让读者了解hash_set快速高效的原因。当然本文所给hash_table距真正的hash_set还有不小的距离,有兴趣的读者可以进一步改进。
此外,本文所示范的哈希表也与最近流行的NoSql数据库颇有渊源, NoSql数据库也是通过Key-Value方式来访问数据的(访问数据的方式上非常类似哈希表),其查找效率与传统的数据库相比也正如本文中hast_set与set的比较。正因为NoSql数据库在基础数据结构上的天然优势,所以它完全可以支持海量数据的查询修改且对操作性能要求很高场合如微博等。
zz from:http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/7330323