Java基础学习第二十六天——网络编程总结
| 文档版本 | 开发工具 | 测试平台 | 工程名字 | 日期 | 作者 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1.0 | 2016.04.03 | lutianfei | none |
第十二章网络编程
网络编程概述
- 就是用来实现网络互连的不同计算机上运行的程序间可以进行数据交换。
网络模型
- 计算机网络之间以何种规则进行通信,就是网络模型研究问题。
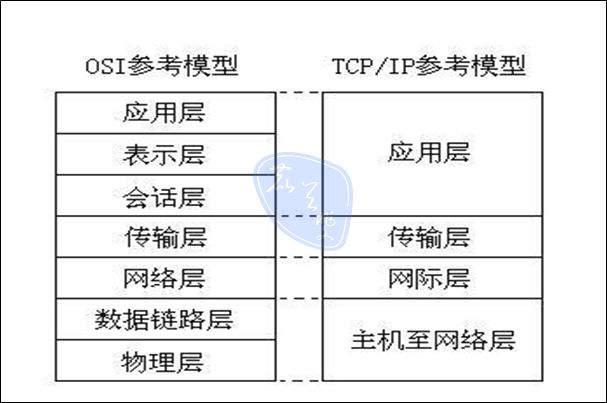
网络模型一般是指
- OSI(Open System Interconnection开放系统互连)参考模型
- TCP/IP参考模型
网络模型7层概述
1 .
物理层:主要定义物理设备标准,如网线的接口类型、光纤的接口类型、各种传输介质的传输速率等。它的主要作用是传输比特流。这一层的数据叫做比特。2 .
数据链路层:主要将从物理层接收的数据进行MAC地址(网卡的地址)的封装与解封装。常把这一层的数据叫做帧。在这一层工作的设备是交换机,数据通过交换机来传输。3 .
网络层:主要将从下层接收到的数据进行IP地址的封装与解封装。在这一层工作的设备是路由器,常把这一层的数据叫做数据包。4 .
传输层:定义了一些传输数据的协议和端口号。 主要是将从下层接收的数据进行分段和传输,到达目的地址后再进行重组。常常把这一层数据叫做段。TCP:传输控制协议,传输效率低,可靠性强,用于传输可靠性要求高,数据量大的数据。UDP:用户数据包协议,与TCP特性恰恰相反,用于传输可靠性要求不高,数据量小的数据。
- 如QQ聊天数据就是通过这种方式传输的。
5 .
会话层:通过传输层建立数据传输的通路。主要在你的系统之间发起会话或者接受会话请求(设备之间需要互相认识可以是IP也可以是MAC或者是主机名)。6 .
表示层:主要是进行对接收的数据进行解释、加密与解密、压缩与解压缩等(把计算机能够识别的东西转换成人能够能识别的东西(如图片、声音等)。7 .
应用层: 主要是一些终端的应用,比如说FTP(各种文件下载),WEB(IE浏览),QQ之类的(可以把它理解成我们在电脑屏幕上可以看到的东西.就是终端应用)。
网络通信三要素
- IP地址:InetAddress
- 网络中设备的标识,不易记忆,可用主机名
- 端口号
- 用于标识进程的逻辑地址,不同进程的标识
- 传输协议
- 通讯的规则
- 常见协议:TCP,UDP
网络通信模型
- 第一个条件:我要先找到你 (IP)
- 第二个条件:你得有接收数据的地方 耳朵 (端口)
- 第三个条件:我跟你说话,你能接收到,咱按什么方式接收啊,我说英文你懂吗,说韩文你懂吗,不懂是吧,所以我还是说中文把.(协议)
IP地址
要想让网络中的计算机能够互相通信,必须为每台计算机指定一个标识号,通过这个标识号来指定要接受数据的计算机和识别发送的计算机,在TCP/IP协议中,这个标识号就是IP地址。
如何获取和操作IP地址呢?
- 为了方便我们对IP地址的获取和操作,java提供了一个类
InetAddress。
- 为了方便我们对IP地址的获取和操作,java提供了一个类
所谓IP地址就是给每个连接在Internet上的主机分配的一个32bit地址。按照TCP/IP规定,IP地址用二进制来表示,每个IP地址长32bit,比特换算成字节,就是4个字节。IP地址的这种表示法叫做“
点分十进制表示法”,这显然比1和0容易记忆得多。
IP地址的组成
IP地址 =
网络号码+主机地址A类IP地址: 第一段号码为网络号码,剩下的三段号码为本地计算机的号码B类IP地址:前二段号码为网络号码,剩下的二段号码为本地计算机的号码C类IP地址:前三段号码为网络号码,剩下的一段号码为本地计算机的号码特殊地址:
- 127.0.0.1
回环地址,可用于测试本机的网络是否有问题。
- eg : ping 127.0.0.1
- xxx.xxx.xxx.0 网络地址
- xxx.xxx.xxx.255 广播地址
- 127.0.0.1
InetAddress类的使用
- 没有构造方法,那么如何使类提供的功能呢?
- 要掌握的方法
- 获取任意主机:getByName
- 主机名:getHostName
- 主机Ip地址:getHostAddress
端口号
- 物理端口 网卡口
- 逻辑端口 我们指的就是逻辑端口
- A:每个网络程序都会至少有一个逻辑端口
- B:用于标识进程的逻辑地址,不同进程的标识
- C:有效端口:0~65535,其中0~1024系统使用或保留端口。
- 通过360可以查看端口号
协议UDP和TCP
UDP
- 将数据源和目的封装成数据包中,不需要建立连接;每个数据报的大小在限制在64k;因无连接,是不可靠协议;不需要建立连接,速度快
- 举例:
- 聊天留言,在线视频,视频会议,发短信,邮局包裹。
TCP
- 建立连接,形成传输数据的通道;在连接中进行大数据量传输;通过三次握手完成连接,是可靠协议;必须建立连接,效率会稍低
- 举例:
- 下载,打电话,QQ聊天(你在线吗,在线,就回应下,就开始聊天了)
Socket编程
- 又称
网络编程,套接字编程 - Socket套接字:
- 网络上具有唯一标识的
IP地址和端口号组合在一起才能构成唯一能识别的标识符套接字。
- 网络上具有唯一标识的
- Socket原理机制:
- 通信的两端都有Socket。
- 网络通信其实就是Socket间的通信。
- 数据在两个Socket间通过IO传输。
UDP传输过程
DatagramSocket与DatagramPacket- 建立发送端,接收端。
- 建立数据包。
- 调用Socket的发送接收方法。
- 关闭Socket。
- 发送端与接收端是两个独立的运行程序。
UDP传输-发送端思路
- 1:建立udp的socket服务
- 2:将要发送的数据封装成数据包
- 3:通过udp的socket服务,将数据包发送出
4:关闭资源
UDP传输-发送端代码
/* * UDP协议发送数据: * A:创建发送端Socket对象 * B:创建数据,并把数据打包 * C:调用Socket对象的发送方法发送数据包 * D:释放资源 */
public class SendDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建发送端Socket对象
// DatagramSocket()
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
// 创建数据,并把数据打包
// DatagramPacket(byte[] buf, int length, InetAddress address, int port)
// 创建数据
byte[] bys = "hello,udp,我来了".getBytes();
// 长度
int length = bys.length;
// IP地址对象
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.92");
// 端口
int port = 10086;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, length, address, port);
// 调用Socket对象的发送方法发送数据包
// public void send(DatagramPacket p)
ds.send(dp);
// 释放资源
ds.close();
}
}UDP传输-接收端思路
- 1:建立udp的socket服务.
- 2:通过receive方法接收数据
- 3:将收到的数据存储到数据包对象中
- 4:通过数据包对象的功能来完成对接收到数据进行解析.
5:可以对资源进行关闭
UDP传输-接收端代码
/* * UDP协议接收数据: * A:创建接收端Socket对象 * B:创建一个数据包(接收容器) * C:调用Socket对象的接收方法接收数据 * D:解析数据包,并显示在控制台 * E:释放资源 */
public class ReceiveDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建接收端Socket对象
// DatagramSocket(int port)
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10086);
// 创建一个数据包(接收容器)
// DatagramPacket(byte[] buf, int length)
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int length = bys.length;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, length);
// 调用Socket对象的接收方法接收数据
// public void receive(DatagramPacket p)
ds.receive(dp); // 阻塞式
// 解析数据包,并显示在控制台
// 获取对方的ip
// public InetAddress getAddress()
InetAddress address = dp.getAddress();
String ip = address.getHostAddress();
// public byte[] getData():获取数据缓冲区
// public int getLength():获取数据的实际长度
byte[] bys2 = dp.getData();
int len = dp.getLength();
String s = new String(bys2, 0, len);
System.out.println(ip + "传递的数据是:" + s);
// 释放资源
ds.close();
}
}- 优化后代码
/* * 多次启动接收端: * java.net.BindException: Address already in use: Cannot bind * 端口被占用。 */
public class ReceiveDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建接收端的Socket对象
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(12345);
// 创建一个包裹
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length);
// 接收数据
ds.receive(dp);
// 解析数据
String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
String s = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength());
System.out.println("from " + ip + " data is : " + s);
// 释放资源
ds.close();
}
}
public class SendDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建发送端的Socket对象
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
// 创建数据并打包
byte[] bys = "helloworld".getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length,
InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.92"), 12345);
// 发送数据
ds.send(dp);
// 释放资源
ds.close();
}
}UDP案例
- 从键盘录入数据进行发送,如果输入的是886那么客户端就结束输入数据。
/* * 多次启动接收端: * java.net.BindException: Address already in use: Cannot bind * 端口被占用。 */
public class ReceiveDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建接收端的Socket对象
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(12345);
while (true) {
// 创建一个包裹
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length);
// 接收数据
ds.receive(dp);
// 解析数据
String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
String s = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength());
System.out.println("from " + ip + " data is : " + s);
}
// 释放资源
// 接收端应该一直开着等待接收数据,是不需要关闭
// ds.close();
}
}
/* * 数据来自于键盘录入 * 键盘录入数据要自己控制录入结束。 */
public class SendDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建发送端的Socket对象
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
// 封装键盘录入数据
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
if ("886".equals(line)) {
break;
}
// 创建数据并打包
byte[] bys = line.getBytes();
// DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length,
// InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.92"), 12345);
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length,InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.255"), 12345);
// 发送数据
ds.send(dp);
}
// 释放资源
ds.close();
}
}- 把刚才发送和接收程序分别用线程进行封装,完成一个UDP的聊天程序。
/* * 通过多线程改进刚才的聊天程序,这样我就可以实现在一个窗口发送和接收数据了 */
public class ChatRoom {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket dsSend = new DatagramSocket();
DatagramSocket dsReceive = new DatagramSocket(12306);
SendThread st = new SendThread(dsSend);
ReceiveThread rt = new ReceiveThread(dsReceive);
Thread t1 = new Thread(st);
Thread t2 = new Thread(rt);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
public class ReceiveThread implements Runnable {
private DatagramSocket ds;
public ReceiveThread(DatagramSocket ds) {
this.ds = ds;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
// 创建一个包裹
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length);
// 接收数据
ds.receive(dp);
// 解析数据
String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
String s = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength());
System.out.println("from " + ip + " data is : " + s);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class SendThread implements Runnable {
private DatagramSocket ds;
public SendThread(DatagramSocket ds) {
this.ds = ds;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 封装键盘录入数据
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
System.in));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
if ("886".equals(line)) {
break;
}
// 创建数据并打包
byte[] bys = line.getBytes();
// DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length,
// InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.92"), 12345);
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length,
InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.255"), 12306);
// 发送数据
ds.send(dp);
}
// 释放资源
ds.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}TCP传输
- Socket和ServerSocket
- 建立客户端和服务器端
- 建立连接后,通过Socket中的IO流进行数据的传输
- 关闭socket
- 同样,客户端与服务器端是两个独立的应用程序。
TCP传输-客户端思路
- 1:建立客户端的Socket服务,并明确要连接的服务器。
- 2:如果连接建立成功,就表明已经建立了数据传输的通道。就可以在该通道通过IO进行数据的读取和写入。该通道称为
Socket流,Socket流中既有读取流,也有写入流。 - 3:通过Socket对象的方法,可以获取这两个流。
- 4:通过流的对象可以对数据进行传输
5:如果传输数据完毕,关闭资源
TCP传输-客户端代码
/* * 连接被拒绝。TCP协议一定要先开服务器。 * java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused: connect */
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建发送端的Socket对象
// Socket(InetAddress address, int port)
// Socket(String host, int port)
// Socket s = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.92"), 8888);
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.12.92", 8888);
// 获取输出流,写数据
// public OutputStream getOutputStream()
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
os.write("hello,tcp,我来了".getBytes());
// 释放资源
s.close();
}
}TCP传输-服务器端思路
- 1:建立服务器端的
socket服务,需要一个端口 - 2:服务端没有直接流的操作,而是通过
accept方法获取客户端对象,再通过获取到的客户端对象的流和客户端进行通信。 - 3:通过客户端的获取流对象的方法,读取数据或者写入数据
4:如果服务完成,需要关闭客户端,然后关闭服务器,但是,一般会关闭客户端,不会关闭服务器,因为服务端是一直提供服务的。
TCP传输-服务器端代码
/* * TCP协议接收数据: * A:创建接收端的Socket对象 * B:监听客户端连接。返回一个对应的Socket对象 * C:获取输入流,读取数据显示在控制台 * D:释放资源 */
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建接收端的Socket对象
// ServerSocket(int port)
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
// 监听客户端连接。返回一个对应的Socket对象
// public Socket accept()
Socket s = ss.accept(); // 侦听并接受到此套接字的连接。此方法在连接传入之前一直阻塞。
// 获取输入流,读取数据显示在控制台
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len = is.read(bys); // 阻塞式方法
String str = new String(bys, 0, len);
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip + "---" + str);
// 释放资源
s.close();
// ss.close(); //这个不应该关闭
}
}
TCP传输案例
- 服务器给客户端反馈
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建服务器Socket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9999);
// 监听客户端的连接
Socket s = ss.accept(); // 阻塞
// 获取输入流
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len = is.read(bys); // 阻塞
String server = new String(bys, 0, len);
System.out.println("server:" + server);
// 获取输出流
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
os.write("数据已经收到".getBytes());
// 释放资源
s.close();
// ss.close();
}
}
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建客户端Socket对象
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.12.92", 9999);
// 获取输出流
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
os.write("今天天气很好,适合睡觉".getBytes());
// 获取输入流
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len = is.read(bys);// 阻塞
String client = new String(bys, 0, len);
System.out.println("client:" + client);
// 释放资源
s.close();
}
}- 客户端键盘录入,服务器输出到控制台
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建服务器Socket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(22222);
// 监听客户端连接
Socket s = ss.accept();
// 包装通道内容的流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
s.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
// br.close();
s.close();
// ss.close();
}
}
/* * 客户端键盘录入,服务器输出到控制台 */
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建客户端Socket对象
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.12.92", 22222);
// 键盘录入数据
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// 把通道内的流给包装一下
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
s.getOutputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// 键盘录入数据要自定义结束标记
if ("886".equals(line)) {
break;
}
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
// 释放资源
// bw.close();
// br.close();
s.close();
}
}- 客户端键盘录入,服务器输出文本文件
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建服务器Socket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(23456);
// 监听客户端连接
Socket s = ss.accept();
// 封装通道内的数据
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
s.getInputStream()));
// 封装文本文件
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("a.txt"));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
// br.close();
s.close();
// ss.close();
}
}- 客户端文本文件,服务器输出到控制台
/* * 客户端文本文件,服务器输出到控制台 */
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建Socket对象
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.12.92", 34567);
// 封装文本文件
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(
"InetAddressDemo.java"));
// 封装通道内的流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
s.getOutputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
br.close();
s.close();
}
}
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建服务器Socket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(34567);
// 监听客户端连接
Socket s = ss.accept();
// 封装通道内的流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
s.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
s.close();
}
}TCP传输容易出现的问题
- 客户端连接上服务端,两端都在等待,没有任何数据传输。
- 通过例程分析:
- 因为read方法或者readLine方法是阻塞式。
- 解决办法:
- 自定义结束标记
- 使用shutdownInput,shutdownOutput方法。
- 客户端文本文件,服务器输出文本文件
/* * 问题:按照我们正常的思路加入反馈信息,结果却没反应。为什么呢? * 读取文本文件是可以以null作为结束信息的,但是呢,通道内是不能这样结束信息的。 * 所以,服务器根本就不知道你结束了。而你还想服务器给你反馈。所以,就相互等待了。 * * 如何解决呢? * A:再多写一条数据,告诉服务器,读取到这条数据说明我就结束,你也结束吧。 * 这样做可以解决问题,但是不好。 * B:Socket对象提供了一种解决方案 * public void shutdownOutput() */
public class UploadClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建客户端Socket对象
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.12.92", 11111);
// 封装文本文件
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(
"InetAddressDemo.java"));
// 封装通道内流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
s.getOutputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { // 阻塞
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
//Socket提供了一个终止,它会通知服务器你别等了,我没有数据过来了
s.shutdownOutput();
// 接收反馈
BufferedReader brClient = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
s.getInputStream()));
String client = brClient.readLine(); // 阻塞
System.out.println(client);
// 释放资源
br.close();
s.close();
}
}
public class UploadServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建服务器端的Socket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(11111);
// 监听客户端连接
Socket s = ss.accept();// 阻塞
// 封装通道内的流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
s.getInputStream()));
// 封装文本文件
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("Copy.java"));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { // 阻塞
// if("over".equals(line)){
// break;
// }
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
// 给出反馈
BufferedWriter bwServer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
s.getOutputStream()));
bwServer.write("文件上传成功");
bwServer.newLine();
bwServer.flush();
// 释放资源
bw.close();
s.close();
}
}- 上传图片案例
public class UploadServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建服务器Socket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(19191);
// 监听客户端连接
Socket s = ss.accept();
// 封装通道内流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(s.getInputStream());
// 封装图片文件
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("mn.jpg"));
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) {
bos.write(bys, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
// 给一个反馈
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
os.write("图片上传成功".getBytes());
bos.close();
s.close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建客户端Socket对象
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.12.92", 19191);
// 封装图片文件
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(
"林青霞.jpg"));
// 封装通道内的流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) {
bos.write(bys, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
s.shutdownOutput();
// 读取反馈
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bys2 = new byte[1024];
int len2 = is.read(bys2);
String client = new String(bys2, 0, len2);
System.out.println(client);
// 释放资源
bis.close();
s.close();
}
}- 服务器的代码用线程进行封装,这样可以模拟一个同时接收多人上传文件的服务器。(用循环也可以但是效率低,是单线程的程序)
public class UploadClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建客户端Socket对象
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.12.92", 11111);
// 封装文本文件
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(
// "InetAddressDemo.java"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(
"ReceiveDemo.java"));
// 封装通道内流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
s.getOutputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { // 阻塞
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
// Socket提供了一个终止,它会通知服务器你别等了,我没有数据过来了
s.shutdownOutput();
// 接收反馈
BufferedReader brClient = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
s.getInputStream()));
String client = brClient.readLine(); // 阻塞
System.out.println(client);
// 释放资源
br.close();
s.close();
}
}
public class UserThread implements Runnable {
private Socket s;
public UserThread(Socket s) {
this.s = s;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 封装通道内的流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
s.getInputStream()));
// 封装文本文件
// BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new
// FileWriter("Copy.java"));
// 为了防止名称冲突
String newName = System.currentTimeMillis() + ".java";
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(newName));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { // 阻塞
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
// 给出反馈
BufferedWriter bwServer = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));
bwServer.write("文件上传成功");
bwServer.newLine();
bwServer.flush();
// 释放资源
bw.close();
s.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class UploadServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建服务器Socket对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(11111);
while (true) {
Socket s = ss.accept();
new Thread(new UserThread(s)).start();
}
}
}