XML解析
<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">XML解析是JAVA中重要的技术之一。下面主要以一个小例子来呈现出JAVA中对XML文档的解析方式,此处以DOM(Document Object Model)解析技术为例。</span>
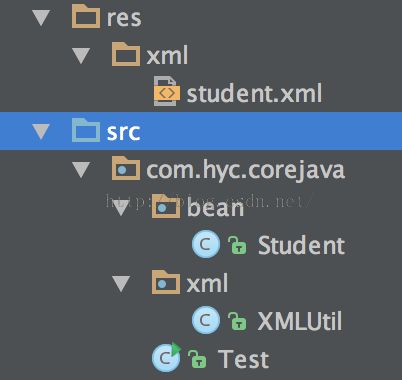
首先新建一个java项目,取名为corejava。此处例子是为了解析xml文档,那么就要建一个xml标准文档:在corejava目录下新建一个文件夹,取名为res,再在res目录下新建一个文件夹,取名为xml,再在文件夹xml目录下新建一个xml文档,并取名为student.xml。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<students>
<student>
<name>LiLei</name>
<age>23</age>
</student>
<student>
<name>HanMei</name>
<age>22</age>
</student>
</students>
然后在src目录下新建包与java文件,具体如下所示:
其中,Student文件内容如下所示:
package com.hyc.corejava.bean;
/**
* Created by huashuncai on 15/9/16.
*/
public class Student {
public static final String XML_TAG = "student";
public static final String XML_NAME_TAG = "name";
public static final String XML_AGE_TAG = "age";
private String name;
private String age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, String age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
XMLUtil、Test的文件内容具体如下所示:
package com.hyc.corejava.xml;
import com.hyc.corejava.bean.Student;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by huashuncai on 15/9/16.
*/
public class XMLUtil {
/**
* XML文档的根元素
*
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
public static Element getRootFrom(String fileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = null;
Document document = null;
try {
builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
document = builder.parse(file);
return document.getDocumentElement();
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 从文件中取出学生列表
*
* @param fileName
* @return
* @see XMLUtil#getRootFrom(String)
*/
public static List<Student> getStudentListfrom(String fileName) {
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
Element root = getRootFrom(fileName);
NodeList elements = null;
if (root != null) {
elements = root.getElementsByTagName(Student.XML_TAG);
Student stu = null;
Node node = null;
for (int i = 0; i < elements.getLength(); i++) {
stu = new Student();
node = elements.item(i);
NodeList childElements = node.getChildNodes();
for (int j = 0; j < childElements.getLength(); j++) {
node = childElements.item(j);
if (node instanceof Element) {
if (((Element) node).getTagName().equals(Student.XML_NAME_TAG)) {
stu.setName(node.getTextContent());
} else if (((Element) node).getTagName().equals(Student.XML_AGE_TAG)) {
stu.setAge(node.getTextContent());
}
}
}
studentList.add(stu);
}
return studentList;
}
return null;
}
}
package com.hyc.corejava;
import com.hyc.corejava.bean.Student;
import com.hyc.corejava.xml.XMLUtil;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by huashuncai on 15/9/16.
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("res/xml/student.xml");
List<Student> studentList = XMLUtil.getStudentListfrom(file.getAbsolutePath());
if (studentList != null && studentList.size() != 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < studentList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("Name:" + studentList.get(i).getName() + "\tAge:" + studentList.get(i).getAge());
}
}
}
}
亲测成功!