Object
Java中的Object是所有类的父类,是“万类之源”
Class Object
java.lang.Object
public class Object
Class Object is the root of the class hierarchy. Every class has Object as a superclass. All objects, including arrays, implement the methods of this class.
我们把jdk安装路径目录下的src.rar文件解压,可以看到Object.java:
(为了页面大小,删除了大量的注释,读者自行查看)
仔细观察上面的各方法,很快就知道哪些方法可以被子类所继承,被finally,private修饰的方法已经被"写死"在父类中,子类不能继承修改,而static方法不具有多态特性。(java中除了被private,static,private修饰的方法是前期绑定,其他的方法都是后期绑定,这是题外话,这属于多态方面的知识)
查阅API文档,Object类中定义的方法: http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/index.html
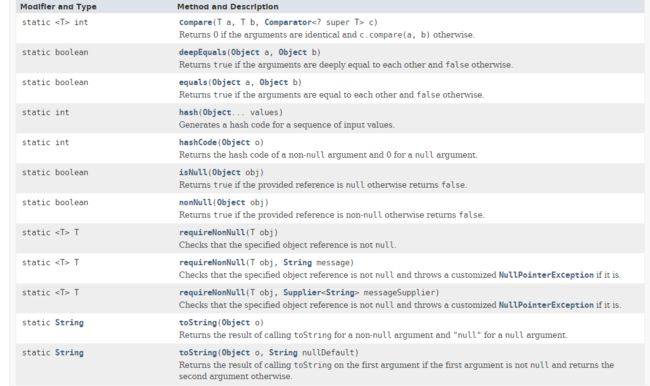
其中可以被子类继承的方法是: clone , equals , finalize , getClass , hashCode , notify , notifyAll , toString , wait , wait , wait
具体的各个方法可以查阅API文档去了解。
执行结果:

指出该方法可能抛出异常,则对这种异常,一定要进行捕获处理(对于把异常抛给调用者,但是最终还是被处理),上面重写了clone方法,并用public修饰,为了在Test类中可以调用。然后在Test类中捕获可能发生的异常,引用m是从n clone而来,所以equals为true,而且hashCode也相等,接着在栈里创建了Name引用p,n赋值给p,也就是两者指向同一堆内存,比较p,n的hashCode,是相同的!p,m的hashCode也是相同的!脑海里应该自然的浮现四块内存区域:栈中:m,n,p 堆中:new出的Name对象 m,p,n指针指向Name对象
这里说明的是,hashCode并不是实际的物理地址!
getClass()返回的是当前运行的类对象
关于toString()方法,这里不再赘述,学习java的朋友,这个方法都应该很熟悉。
上面简单的介绍,也是自己一个小小的总结,关于深入的了解Object类,可以参考其他书籍,如果错误之处,请读者指正!
Class Object
java.lang.Object
public class Object
Class Object is the root of the class hierarchy. Every class has Object as a superclass. All objects, including arrays, implement the methods of this class.
我们把jdk安装路径目录下的src.rar文件解压,可以看到Object.java:
(为了页面大小,删除了大量的注释,读者自行查看)
点击(此处)折叠或打开
- public class Object {
-
- private static native void registerNatives();
- static {
- registerNatives();
- }
-
- public boolean equals(Object obj) {
- return (this == obj);
- }
-
- protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
-
- public String toString() {
- return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
- }
-
- public final native void notify();
-
- public final native void notifyAll();
-
- public final native void wait(long timeout) throws InterruptedException;
-
- public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos) throws InterruptedException {
- if (timeout < 0) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
- }
-
- if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException(
- "nanosecond timeout value out of range");
- }
-
- if (nanos >= 500000 || (nanos != 0 && timeout == 0)) {
- timeout++;
- }
-
- wait(timeout);
- }
-
- public final void wait() throws InterruptedException {
- wait(0);
- }
-
- protected void finalize() throws Throwable { }
- }
仔细观察上面的各方法,很快就知道哪些方法可以被子类所继承,被finally,private修饰的方法已经被"写死"在父类中,子类不能继承修改,而static方法不具有多态特性。(java中除了被private,static,private修饰的方法是前期绑定,其他的方法都是后期绑定,这是题外话,这属于多态方面的知识)
查阅API文档,Object类中定义的方法: http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/index.html

其中可以被子类继承的方法是: clone , equals , finalize , getClass , hashCode , notify , notifyAll , toString , wait , wait , wait
具体的各个方法可以查阅API文档去了解。
点击(此处)折叠或打开
- public class Name implements Cloneable {
-
- private String firstName,lastName;
- public Name(String firstName,String lastName){
-
- this.firstName = firstName;
- this.lastName = lastName;
- }
- public String getFirstName(){
- return firstName;
- }
- public String getLastName(){
- return lastName;
- }
- public String toString(){
-
- return firstName + " " + lastName;
- }
-
- public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
- return (Name)super.clone();
- }
-
- public boolean equals(Object obj){
-
- if(obj instanceof Name){
-
- Name name = (Name)obj;
- return (firstName.equals(firstName))&&(lastName.equals(lastName));
- }
- return super.equals(obj);
- }
- public int hashCode(){
-
- return firstName.hashCode();
- }
- }
-
- public class Test{
-
- public static void main(String[] args){
- Name n = new Name("diy","os");
- try{
- Name m =(Name)n.clone();
- String ss = m.getFirstName() + m.getLastName();
- System.out.println(ss);
- System.out.println(m.equals(n));
- System.out.println(n.equals(m));
- System.out.println("m.hashCode:" + m.hashCode() + " " + "n.hashCode:" + n.hashCode());
-
- Name p = n;
- System.out.println("n.hashCode:" + n.hashCode() + " " + "p.hashCode:" + p.hashCode());
- System.out.println("p.hashCode" + p.hashCode() + " " + "m.hashCode" + m.hashCode());
- System.out.println(n.getClass());
- }catch(CloneNotSupportedException e){
-
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
-
- }
- }

指出该方法可能抛出异常,则对这种异常,一定要进行捕获处理(对于把异常抛给调用者,但是最终还是被处理),上面重写了clone方法,并用public修饰,为了在Test类中可以调用。然后在Test类中捕获可能发生的异常,引用m是从n clone而来,所以equals为true,而且hashCode也相等,接着在栈里创建了Name引用p,n赋值给p,也就是两者指向同一堆内存,比较p,n的hashCode,是相同的!p,m的hashCode也是相同的!脑海里应该自然的浮现四块内存区域:栈中:m,n,p 堆中:new出的Name对象 m,p,n指针指向Name对象
这里说明的是,hashCode并不是实际的物理地址!
getClass()返回的是当前运行的类对象
关于toString()方法,这里不再赘述,学习java的朋友,这个方法都应该很熟悉。
上面简单的介绍,也是自己一个小小的总结,关于深入的了解Object类,可以参考其他书籍,如果错误之处,请读者指正!