数据结构:2-3树
声明:本文为学习 数据结构与算法分析(第三版) Clifford A.Shaffer 著 的学习笔记,代码有参考该书的示例代码。
2-3树
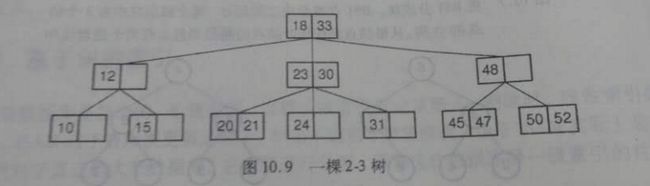
2-3 树的形状定义如下:
- 一个结点包含一个或两个关键码。
- 每个内部结点有两个子结点(如果它包含一个关键码)或者三个子结点(如果它包含两个关键码),它因此得名 2-3 树。
- 所有叶结点都在树结构的同一层,因此树的高度总是平衡的。
2-3 树保持了类似于BST 的检索树的特征。
为了维持这些形状特征和检索特征,在结点插入、删除时需要采取特别的操作。2-3 树有这样一个优点,它能以相对较低的代价保持树高度的平衡。
一棵二叉树
2-3 树结点的实现
首先定义2-3树的结点:
template<typename Key, typename E>
class Tree_23Node
{
protected:
Key lkey, rkey;
E lit, rit;
public:
static Key emptyKey;
static void setEmptyKey(const Key& key)
{
emptyKey = key;
}
Tree_23Node() { lkey = rkey = emptyKey; }
virtual ~Tree_23Node() {}
virtual Key leftKey() const { return lkey; }
virtual Key rightKey() const { return rkey; }
virtual E leftValue() const { return lit; }
virtual E rightValue() const { return rit; }
virtual Tree_23Node* leftChild() const { return nullptr; }
virtual Tree_23Node* rightChild() const { return nullptr; }
virtual Tree_23Node* midChild() const { return nullptr; }
virtual void setLeafChild( Tree_23Node* ) {}
virtual void setMidChild( Tree_23Node* ) {}
virtual void setRightChild( Tree_23Node* ) {}
virtual void setLeft(const Key& k, const E& it = nullptr) { lkey = k, lit = it; }
virtual void setRight(const Key& k, const E& it = nullptr) { rkey = k, rit = it; }
//------------------------------------
virtual Tree_23Node<Key, E>* add(Tree_23Node<Key, E>* root) = 0;
virtual bool isLeaf() const = 0;
};
template<typename Key, typename E>
Key Tree_23Node<Key, E>::emptyKey = reinterpret_cast< Key >(0);
这里做的有点复杂了。但是因为叶子结点是没有孩子结点的指针的,所以再分别定义内部结点和叶子结点。
2-3 树结点的插入
在 2-3 树中,比较难的是,2-3 树的插入。
2-3 树的插入,有时候是需要叶结点的分裂。
2-3 树的插入是把记录插入到叶结点,然后再一层层提升。
首先应该是完成2-3 树的结点的插入,叶子结点的插入如下:
Tree_23Node<Key, E>* add(Tree_23Node<Key, E>* root)
{
if(rkey == emptyKey)
{
if(root->leftKey() >= lkey)
{
rkey = root->leftKey(), rit = root->leftValue();
}
else
{
rkey = lkey, rit = lit;
lkey = root->leftKey(), lit = root->leftValue();
}
delete root;
return this;
}
else if( root->leftKey() < lkey) //Add left
{
root->setMidChild(new LeafNode(rkey, rit));
rkey = lkey, rit = lit;
lkey = root->leftKey(), lit = root->leftValue();
root->setLeft(rkey, rit);
rkey = emptyKey;
root->setLeafChild(this);
return root;
}
else if( root->leftKey() < rkey) //Add center
{
root->setMidChild(new LeafNode(rkey, rit));
root->setLeafChild(this);
rkey = emptyKey;
return root;
}
else //add right
{
root->setLeafChild(this);
root->setMidChild(new LeafNode(root->leftKey(), root->leftValue() ));
root->setLeft(rkey, rit);
rkey = emptyKey;
return root;
}
}返回的是提升的结点。如果没有结点提升,则返回该结点的 this 指针。
内部结点的 add 差不多,只是要记得处理孩子指针的指向:
Tree_23Node<Key, E>* add(Tree_23Node<Key, E>* root)
{
if(rkey == emptyKey )
{
if( root->leftKey() >= lkey)
{
rkey = root->leftKey(), rit = root->leftValue();
mchild = root->leftChild(), rchild = root->midChild();
}
else
{
rkey = lkey, rit = lit;
lkey = root->leftKey(), lit = root->leftValue();
rchild = mchild;
lchild = root->leftChild(), mchild = root->midChild();
}
delete root;
return this;
}
else if(root->leftKey() < lkey) //add left
{
decltype(root) center = new IntalNode(lkey, lit, root, this);
lkey = rkey, lit = rit;
rkey = emptyKey;
lchild = mchild, mchild = rchild, rchild = nullptr;
return center;
}
else if(root->leftKey() < rkey)
{
//add center
decltype(root) right = new IntalNode(rkey, rit, root->midChild(), rchild);
rkey = emptyKey;
mchild = root->leftChild();
rchild = nullptr;
root->setLeafChild(this), root->setMidChild(right);
return root;
}
else
{
//add right
decltype(root) center = new IntalNode(rkey, rit, this, root);
rkey = emptyKey;
rchild = nullptr;
return center;
}
}*在书中,结点的实现并没有分开叶子结点和内部结点,这里分开实现结点,所以add 的方法也要分别实现。(其实代码还是有点臃肿了)
2-3树的实现
结点的定义好了,那么树的实现也容易多了。
树依然继承字典的接口(具体看前面的博客)。
这里展示一下树的插入辅助函数
Tree_23Node<Key, E>* insertHelp(Tree_23Node<Key, E>* root, const Key& k, const E& it)
{
if(root == nullptr ) return new LeafNode<Key, E>(k, it);
if(root->isLeaf())
{
return root->add( new IntalNode<Key, E>(k, it));
}
else if(k < root->leftKey() )
{
auto temp = insertHelp(root->leftChild(), k, it);
if(temp!=root->leftChild() )
return root->add(temp);
return root;
}
else if(root->rightKey()==root->emptyKey || k < root->rightKey() )
{
auto temp = insertHelp(root->midChild(), k, it);
if(temp != root->midChild() )
return root->add(temp);
return root;
}
else
{
auto temp = insertHelp(root->rightChild(), k, it);
if(temp != root->rightChild() )
return root->add(temp);
return root;
}
}由于2-3树是树高平衡的,而且每一个内部结点至少有2个子结点,从而知道树的最大深度是 logn 。
//———————–我是分割线——————————
后来写2-3树的删除操作时,才发现,前面的代码写得实在是复杂了。但是,就这样先,博客也不改了。
2-3树的删除
为什么要把删除和插入分开呢?
因为书上是没有2-3树的删除的,笔者自己查阅资料学习的。
非常感谢这位博客的博主 2-3 树 (第四篇) - angGoGo world
内部结点的删除
2-3树的删除分为内部结点、叶子结点的删除。结点删除后会导致树的结构不平衡,不足以维持2-3树的基本形状,所以有时候还要修复树。
先看看内部结点的删除。
回忆一下堆的删除,寻找inorder successor,在叶结点中找一个结点替代要删除的值,然后再删除叶结点。
这里同理,也就是说,还是先找一个值和内部结点替换,然后再删除叶子结点。
如下:
53 / \ 34 60 / \ / \ 2 48,50 56 70
删除34的话,那么就把48放到34 的位置,然后删除48。
所以结果是:
53 / \ 48 60 / \ / \ 2 50 56 70
如果<48,50>结点中只有<48> 的话,那么树就会变得不平衡,需要修复,这里为了讨论方便,暂时不讨论复杂的情况
叶子结点的删除
叶子结点的删除很容易,只要把值删掉就可以了,然后需要注意的细节就是删除左键值对时,记得用右键值对填在左键值对上
53 / \ 34 60 / \ / \ 2 48,50 56 70
这颗树删除掉48 ,则变为:
53 / \ 34 60 / \ / \ 2 50 56 70
树的修复
假如有树:
53 / \ 34 60 / \ / \ 2,18 50 56 70
如果上面那棵树再删除50的话,树就变为:
53 / \ 34 60 / \ / \ 2,18 <> 56 70
有一个结点为空,这不符合2-3树的特征,那么就需要进行修复。
修复的步骤如下 :
- 看兄弟结点是否有值可借,如果有则把父结点中合适的值拉下来,从兄弟结点中借一个值作为父结点的值
- 如果没有值可借,那么就把父结点拉下来合并
- 回到 1 步骤,处理父结点,知道树的形状符合2-3树
有点难理解,看例子。
向兄弟借值
以上为例,把34拉下到右子树的位置,然后把18的值推上去。
那么修复后,树应该是:
53 / \ 18 60 / \ / \ 2 34 56 70
同理,当结点左右关键值时,处理也是一样的:
53,78 / | \ 10,20 60 98
删除60时,结果是:
20,78 / | \ 10 53 98
合并父结点
以下面这棵树为例,当删除34结点时
53 / \ 18 60 / \ / \ 2 34 56 70
变为:
53 / \ 18 60 / \ / \ 2 <> 56 70
由于兄弟结点没有值可以借,那么就需要合并父结点:
53 / \ <> 60 / \ / \ 2,18 <> 56 70
此时处理《2,18》的父结点。按照顺序,没有兄弟结点可借,那么继续合并父结点:
53,60 / | \ 2,18 56 70
此时树的形状就符合2-3树的特征了。
注意在合并父结点的时候,记得处理孩子结点。如上,当合并 53,60时,应该合并把53 的左子树的孩子赋给53的左子树。
删除的代码如下:
virtual Tree_23Node* deleteKey(const Key& k)
{
if(lkey !=k && rkey != k)
return nullptr;
if(isLeaf())//if is LeafNode
{
if(lkey == k)
{
rightToLeft();
}
rkey = emptyKey;
return this;
}
else
{
//if is IntalNode
Tree_23Node* temp = nullptr;
if( lkey == k)
{
temp = findMin(midChild());
lkey = temp->leftKey();
lit = temp->leftValue();
}
else
{
temp = findMin(rightChild());
rkey = temp->leftKey();
rit = temp->leftValue();
}
return temp->deleteKey(temp->leftKey());
}
}修复树的代码如下:
virtual void fixed(Tree_23Node* parent)
{
if(parent == nullptr)
return;
else if(parent->leftChild() == this)
{
auto mid = parent->midChild();
//midChild borrow to leftChild
if(mid->rightKey() == emptyKey)
{
//合并上下结点
mid->setRight(mid->leftKey(), mid->leftValue());
mid->setRightChild( mid->midChild() );
mid->setMidChild( mid->leftChild() );
mid->setLeft(parent->leftKey(), parent->leftValue() );
if(leftChild() != nullptr)
{
mid->setLeftChild( leftChild() );
}
else
mid->setLeftChild( midChild() );
delete parent->leftChild();
parent->rightToLeft();
}
else
{
//代替
setLeft(parent->leftKey(), parent->leftValue());
if(midChild() != nullptr)
setLeftChild(midChild());
setMidChild(mid->leftChild());
parent->setLeft(mid->leftKey(), mid->leftValue());
mid->rightToLeft();
}
return;
}
else if(parent->midChild() == this)
{
//先向左借
if(parent->leftChild()->rightKey() != emptyKey)
{
auto left = parent->leftChild();
setLeft(parent->leftKey(), parent->leftValue());
if(leftChild() != nullptr)
setMidChild(leftChild());
setLeftChild(left->rightChild());
parent->setLeft(left->rightKey(), left->rightValue());
left->setRight(emptyKey, left->rightValue());
left->setRightChild(nullptr);
}
else if(parent->rightChild()!=nullptr && parent->rightChild()->rightKey() != emptyKey)
{
//向右借
auto right = parent->rightChild();
setLeft(parent->rightKey(), parent->rightValue());
if(midChild() != nullptr)
setLeftChild(midChild());
setMidChild(right->leftChild());
parent->setRight(right->leftKey(), right->leftValue());
right->rightToLeft();
}
else
{
//合并、向左边合并
auto left = parent->leftChild();
left->setRight(parent->leftKey(), parent->leftValue() );
if(leftChild() != nullptr)
left->setRightChild( leftChild() );
else
left->setRightChild( midChild() );
delete parent->midChild();
parent->setMidChild( parent->rightChild() );
parent->setLeft( parent->rightKey(), parent->rightValue() );
parent->setRight(emptyKey, parent->rightValue() );
parent->setRightChild(nullptr);
}
}
else if(parent->rightChild() == this)
{
auto mid = parent->midChild();
if(mid->rightKey() == emptyKey)
{
//合并
mid->setRight(parent->rightKey(), parent->rightValue() );
if( leftChild() != nullptr )
mid->setRightChild( leftChild() );
else
mid->setRightChild( midChild() );
parent->setRight(emptyKey, parent->rightValue());
delete parent->rightChild();
parent->setRightChild(nullptr);
}
else
{
//借结点
setLeft(parent->rightKey(), parent->rightValue());
if(leftChild() != nullptr)
setMidChild(leftChild());
setLeftChild(mid->rightChild());
parent->setRight(mid->rightKey(), mid->rightValue());
mid->setRight(emptyKey, mid->rightValue());
mid->setRightChild(nullptr);
}
return ;
}
}当然,如果延续本文的写法,那么在修复树的时候,需要额外的查找来找到当前结点的父结点。
一个比较好的方法是,在结点中保存父结点的指针。这是用空间换时间的一个好方法。
其他代码可以在github上找到:
xiaosa233
–END–