linux进程间通信-----信号总结
相关文章:
linux信号的阻塞和未决
linux中sleep详解实例
废话不说,先把所有的信号列出来(注意里面没有32, 33信号),敲命令 kill -l
还有一个命令 man 7 signal 来查看信号的默认行为
后32个信号表示实时信号,是可靠信号,这保证了发送的多个实时信号都被接收;
实时信号都支持排队,都是可靠信号;非实时信号都不支持排队,都是不可靠信号;
#include <signal.h> typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int); sighandler_t signal(int signum, sighandler_t handler);signal是注册信号的函数,当注册了该信号的行为后,那么进程收到该信号会执行设置好的行为;
参数handler还可以指定两个特殊的值; SIG_IGN是屏蔽该信号;SIG_DFL是恢复默认行为,SIGINT的默认行为是进程退出;
#include <sys/types.h> #include <signal.h> int kill(pid_t pid, int sig);发送信号的函数,可以向进程ID为pid的进程发送sig信号;也可以向自身发送信号;
实例1:进程注册了SIGINT和SIGQUIT信号的处理函数;
SIGINT的值为2,SIGQUIT的值为3;按下Ctrl+c产生SIGINT信号,按下Ctrl+\产生SIGQUIT信号;
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: int_quit_signal.cpp
> Author:
> Mail:
> Created Time: 2015年12月16日 星期三 21时48分22秒
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <signal.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
void handler(int num)
{
cout << "\nrecvive the signal is " << num << endl;
if(num == SIGQUIT){
cout << "recevie the exit signal..." << endl;
exit(0);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//注册中断信号SIGINT
signal(SIGINT, handler);
signal(SIGQUIT, handler);
cout << "main process is waiting for the signal of SIGINT and SIGQUIT..." << endl;
while(1){
pause();
}
cout << "main process exit.." << endl;
exit(0);
}
实例2:进程执行的前10秒是屏蔽了SIGINT信号,所以当产生SIGINT信号的时候进程不处理直接忽略;10秒过后就恢复默认行为,当产生SIGINT信号的时候进程直接退出;
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: int_quit_signal.cpp
> Author:
> Mail:
> Created Time: 2015年12月16日 星期三 21时48分22秒
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <signal.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//注册中断信号SIGINT
signal(SIGINT, SIG_IGN);
cout << "main process is sleeping(10s)...." << endl;
sleep(10);
cout << "\nthe signal has the default action and waiting the SIGITN to quit..." << endl;
signal(SIGINT, SIG_DFL);
sleep(100);
cout << "main process exit.." << endl;
exit(0);
}

实例3:在这个例子中要使用kill来发送信号;程序的内容是,在父进程中注册SIGINT信号的信号处理函数,在子进程中每个2秒钟就向父进程发送一个SIGINT信号;
关于子进程中的每2秒发送一个信号,可以简单的使用while循环加上slepp(2)来实现;我这里使用alarm函数来实现,
该函数设置一个闹钟延迟发送信号告诉linux内核n秒中以后,发送SIGALRM信号;所以我在子进程安装对SIGALRM的信号处理函数,并在该信号处理函数中再调用alarm函数;
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: int_quit_signal.cpp
> Author:
> Mail:
> Created Time: 2015年12月16日 星期三 21时48分22秒
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <signal.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
void handler(int num)
{
cout << "parent recvive the signal is " << num << endl;
if(num == SIGQUIT){
cout << "parent receive the signal of quit.." << endl;
exit(0);
}
}
void child_handler(int num)
{
cout << "child receive the signal is " << num << endl;
if(num == SIGQUIT){
cout << "child receive the signal of quit.." << endl;
exit(0);
}
kill(getppid(), SIGINT);//向父进程发送信号
alarm(2);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//注册中断信号SIGINT
signal(SIGINT, handler);
signal(SIGQUIT, handler);
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid < 0){
cout << "fork error..." << endl;
exit(-1);
}
if(pid == 0){
signal(SIGALRM, child_handler);
signal(SIGQUIT, child_handler);
alarm(2);
cout << "this is child process..." << endl;
while(1){
pause();
}
exit(0);
}
cout << "main process is waiting for the signal of SIGINT and SIGQUIT..." << endl;
while(1){
pause();
}
cout << "main process exit.." << endl;
exit(0);
}
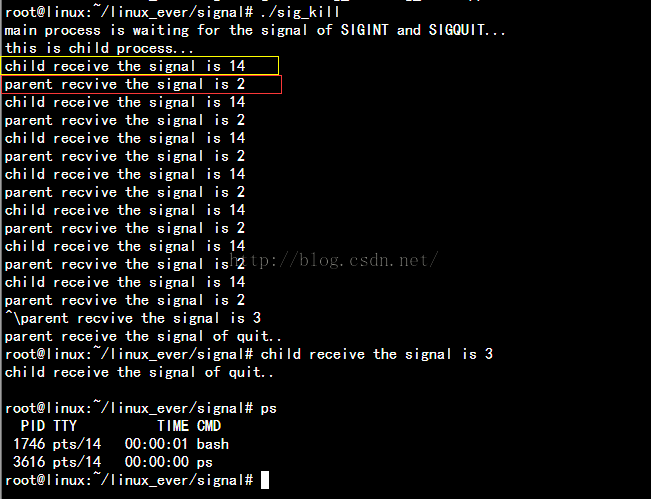
值得注意的是,最后从键盘发送了一个SIGQUIT信号,但是两个进程(父子进程)都收到了该信号;如果没有在子进程中安装该信号,那么父进程会连续收到两个SIGQUIT信号;
