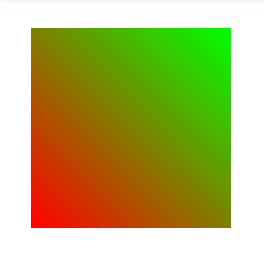Shape Drawable的学习
使用XML方式定义的基本形状的drawable,包括矩形、椭圆形、直线和圆环。
完整的shape定义语法有:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape=["rectangle" | "oval" | "line" | "ring"]
android:innerRadius="integer"
android:innerRadiusRatio="integer"
android:thickness="integer"
android:thicknessRatio="integer"
android:useLevel="boolean"
>
<corners
android:radius="integer"
android:topLeftRadius="integer"
android:topRightRadius="integer"
android:bottomLeftRadius="integer"
android:bottomRightRadius="integer" />
<gradient
android:angle="integer"
android:centerX="float"
android:centerY="float"
android:centerColor="integer"
android:endColor="color"
android:gradientRadius="integer"
android:startColor="color"
android:type=["linear" | "radial" | "sweep"]
android:useLevel=["true" | "false"] />
<padding
android:left="integer"
android:top="integer"
android:right="integer"
android:bottom="integer" />
<size
android:width="integer"
android:height="integer" />
<solid
android:color="color" />
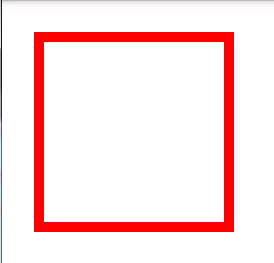
<stroke
android:width="integer"
android:color="color"
android:dashWidth="integer"
android:dashGap="integer" />
</shape>
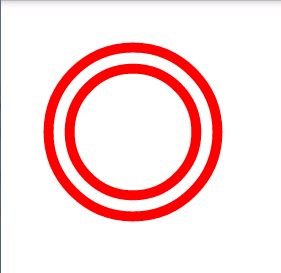
节点一:<shape>
该节点有7个属性,其中后5个是当android:shape="ring"时才有效的。
android:shape指定当前定义的是哪一种形状,可取的值有rectangle(矩形)、oval(椭圆)、line(直线)、ring(圆环)
当android:shape="ring"时,<shape>节点的后5个属性才有效果
android:innerRadius——指定圆环内圆的半径,比如50dp、100dp之类的。
android:innerRadiusRatio——该值是以比例的形式来指定内圆半径。内圆半径等于该shape的宽除以该值。或者说该值的倒数代表了内圆半径占整个shape宽的比例。默认值是9。当该值等于2的时候,内圆就将占满整个shape,从而我们将看不到圆环。
android:thickness——指定圆环的宽窄,也就是内圆与外圆的距离。
android:thicknessRatio——以比例的形式来指定圆环的宽窄。其算法与innerRadiusRatio相同。
android:useLevel——值为true意味着这是一个levelListDrawable(关于levelListDrawable又是另一个话题了)。当我们要画一个圆环是,应当而且必须将该值设为false,否则会看不到画面。
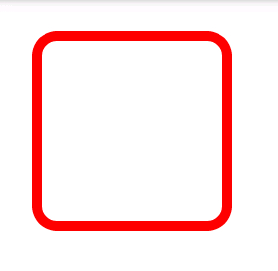
节点二:<corners>
只用于矩形(android:shape="rectangle"),用于设置矩形的4个角的圆角半径,生成圆角矩形。
android:radius——同时设置矩形4个角的圆角半径,如上图就是值为10dp的效果。
android:topLeftRadius——左上角圆角半径
android:topRightRadius——右上角圆角半径
android:bottomLeftRadius——左下角圆角半径
android:bottomRightRadius——右下角圆角半径
这四个单独的设置的值会覆盖android:radius设置的值。
节点三:<padding>
此内边距设置显示于该shape之上的内容与该shape的边界的距离。比如如果将该shape设为一个TextView的背景,那么这里的内边距就会影响TextView上文字的位置。
节点四:<size>
用于矩形时,设置矩形的宽高;
用于椭圆时,设置椭圆外切矩形的宽高,当宽与高相等时,为正圆,否则为椭圆;
用于直线时,宽代表了直线的长度,高没有效果
用于圆环时,宽会影响内圆半径和圆环的宽窄,高没有效果。
当我们将一个shape drawable作为一个View组件的背景或是内容时,通常这个drawable都会被缩放。所以实际显示的时候可能与这里的size设置不相符。
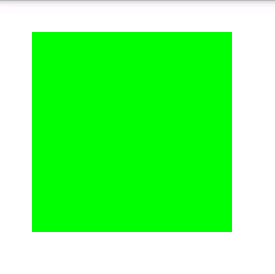
节点五:<solid>
solid有“实心的,纯质的”的意思,比如solid gold意为“纯金”,solid color意味“纯色”。
这里这个节点只有一个属性——android:color,用这种颜色来填充该shape内部,如果不设置该shape的边框,就能得到一张纯色的drawable。
用于直线时无效。
节点六:<stroke>
stroke有“用笔画出来的轨迹,笔画”的意思,这里指shape的边框。
用于矩形和椭圆时,设置其外边界
用于直线时,呃,直线就是用这个节点来设置的。
用于圆环时,会同时影响内圆和外圆。
android:width——边框线条的宽度,特别地,用于直线时设置直线的粗细。
android:color——设置线条的颜色
android:dashWidth——设置虚线效果里实点的长度
android:dashGap——设置虚线效果里空白点的长度
上图是dashWidth="10dp" dashGap="5dp"时的效果
节点七:<gradient>
把这个节点放在最后说,因为这个节点最复杂。
该节点总共有9个属性,用来设置图形里的颜色渐变效果,与<solid>都是填充的一种,如:
其中必须的是startColor或endColor,指定渐变的起始颜色和结束颜色。注意我用的“或”而不是“和”。这二者如果都没有,则看不到渐变效果;如果只有其一,那么默认另一个就是白色。
如果同时有<solid>节点填充,则写在后面的会覆盖写在前面的,让写在前面的设置无效。这与<corners>节点里先写android:radius后写android:topRightRadius还是先写android:topRightRadius后写android:radius不同。android:topRightRadius的优先级总是比android:radius高。
android:type——设置渐变的类型。有三种类型的渐变:
linear(线性渐变):
这也是默认值。
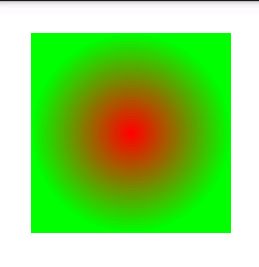
radial(径向渐变):
需要注意的是使用radial渐变时还必须设置android:gradientRadius属性,即设置渐变区域(一个圆)的半径。
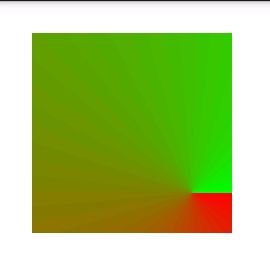
sweep(扫描渐变):
就像雷达扫描一样。方向是顺时针方向渐变。
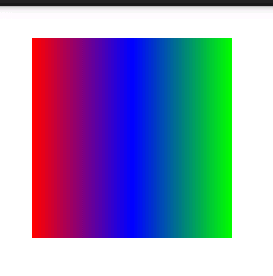
android:angle——当android:type的值为linear时有效,即只用于线性渐变。指定线性渐变的角度,其实就是指定线性渐变的方向。默认值是0,从左向右渐变。该属性的值必须是45的倍数,否则运行时error。这也意味着其实线性渐变只有8个方向:从左向右、左下到右上、从下向上、右下到左上、从右向左、右上到左下、从上向下、左上到右下。
值为0时:
值为45时:
android:centerX、android:centerY——用于径向渐变和扫描渐变,使用相对比例坐标设置渐变的中心点位置。取值范围为0到1。
比如两个均取值为0.8时的扫描渐变效果:
android:centerColor——设置渐变的中间颜色,即先由startColor渐变到centerColor,再由centerColor渐变到endColor。比如:
android:useLevel——值为true时代表这是一个levelListDrawable。
与<shape>节点里当android:shape="ring"时必须设置android:useLevel="false"不同,这里可以不设置(默认就是false)。
在程序当中,使用该shape drawable时,最终将编译成一个GradientDrawable对像。