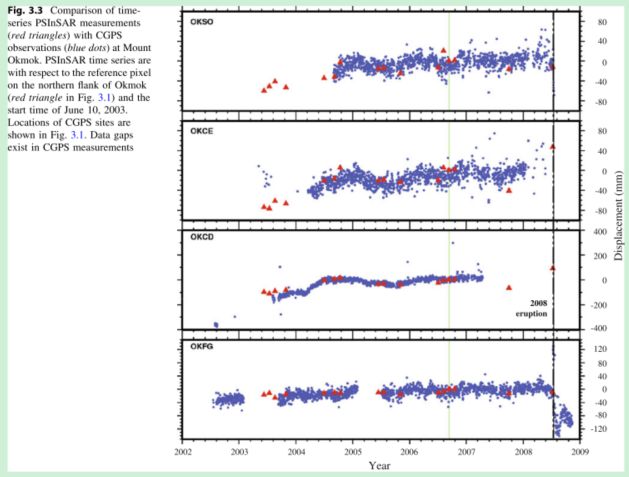
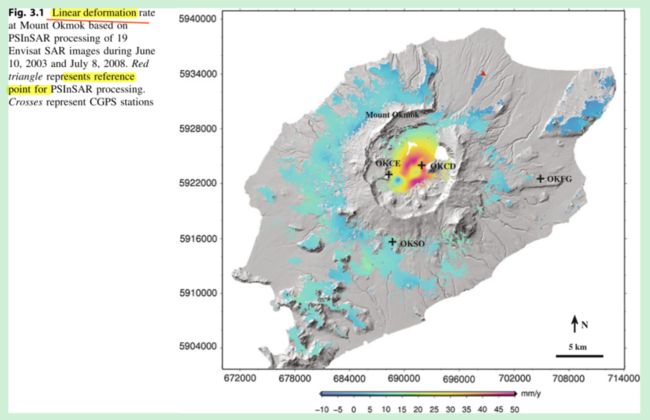
- 流量压测,CDN跑量
JAVA拾贝
ddos压测攻击网络攻击模型
这里写自定义目录标题背景灵机一动平台部署总结背景自己经营了个网站,有一点收益,经常被竞争对手DDOS,客户流失,无奈只能上防御平台,气不过也找人去DDOS对方(不建议,费钱且违法),对方也上了高防CDN,于是一直陷入伤敌一千自损八百的循环~灵机一动常规的CDN套餐除了时间还有请求数和流量的限制,那如果可以一直刷对方流量岂不是,可以间接掏空对方钱包了?如是赶紧找了下有没有类似的平台~平台官网:Img
- FTTR(Fiber to the Room)一主一从
FTTR(FibertotheRoom)一主一从是家庭或企业光纤组网中的一种设备配置方式,具体含义如下:1.基本概念FTTR:指光纤直接延伸到每个房间(替代传统网线),实现全屋千兆/万兆覆盖。一主一从:由一台主光猫(主网关)和一台从光猫(从网关)组成的网络架构,通过光纤连接,形成主从协作的网络系统。2.主设备和从设备的作用主光猫(主网关)直接连接运营商的光纤入户线路,负责拨号、路由、Wi-Fi覆盖
- Charles中文版抓包工具:如何加速API调试与网络优化
2501_91592143
httpudphttpswebsocket网络安全网络协议tcp/ip
在软件开发的过程中,网络请求和API接口的调试与优化是最常见的挑战之一。无论是Web开发、移动应用调试,还是后端API性能优化,开发者都需要一个高效的工具来帮助诊断和解决网络流量中的潜在问题。Charles抓包工具作为一款行业领先的网络调试软件,凭借其强大的功能和简便的操作,帮助开发者提升开发效率、优化网络请求。本文将探讨如何通过Charles中文版抓包工具加速API调试与网络优化,确保开发过程中
- iOS 抓包实战:时间戳偏差导致的数据同步异常排查记录
00后程序员张
httpudphttpswebsocket网络安全网络协议tcp/ip
“这条数据不是我填的”“我的更新被覆盖了”“两个设备显示不一致”——这些是产品上线后最令人头疼的反馈。最近我们在一次用户同步问题排查中,发现表面是“数据丢失”问题,实则是多端数据提交时间戳处理不一致,导致后台认为老数据为新,覆盖了正确内容。这类问题通常日志无法直接反映,需要从网络请求行为层级来全面还原。本文是一次跨平台同步数据错乱排查的抓包实录,目标是展示如何用多工具组合方式,精确还原并定位导致数
- iOS 应用安全加固指南:通过 IPA 混淆与防破解技术实现全面防护
00后程序员张
httpudphttpswebsocket网络安全网络协议tcp/ip
在现代移动应用开发中,安全性已不再是一个可以忽视的领域。随着黑客技术的日益成熟以及用户对隐私保护的重视,开发者必须将安全性嵌入到应用的每一个开发环节中,而不仅仅是在开发的后期进行加固。尤其是对于那些涉及用户数据、支付信息等敏感内容的应用,确保应用的安全性是至关重要的。本文将介绍iOS应用开发中的安全实践,并结合具体的安全加固技术,如使用IpaGuard、Obfuscator-LLVM,从应用的设计
- 网安知识“大乱炖“
Lovely_18
网安知识积累
网安知识"大乱炖"Windows安全事件日志常用EventID:EventID含义说明4624登录成功表示用户成功登录系统4625登录失败✅表示登录尝试失败,是暴力破解最关键的日志标志4672特权登录表示具有管理员权限的账户登录(用于检测高权限账户活动)4648显式凭证登录用户在使用runas或远程方式提供用户名/密码登录暴力破解相关日志特征:连续触发大量4625登录失败来自同一个IP或多个IP的
- 多个 Job 并发运行时共享配置文件导致上下文污染,固化 Jenkins Job 上下文
要站在顶端
Jenkinsjenkinsservlet运维
基于context.py固化JenkinsJob上下文的完整方案,适用于你当前的工作流(Python+JenkinsPipeline),解决:多个Job并发运行时共享配置文件导致上下文污染;读取环境变量或JSON文件时被其他Job修改的问题;后续阶段(如发送通知)读取错误上下文的问题;✅目标在每个JenkinsJob开始时,将关键变量一次性固化到内存中,并在整个Job生命周期内始终使用这些值。整体
- DOP数据开放平台(真实线上项目)
JAVA拾贝
java数据开放平台接口开放平台监控限流接口过滤自动文档
什么是数据开放平台?数据开放平台是一种通过公开应用程序编程接口(API)或结构化数据,允许第三方开发者或机构访问、使用和共享数据的平台,旨在促进数据流通、打破信息孤岛并激发创新应用。DOP数据开放平台简单演示DOP数据开放平台(JAVA语言)DOP数据开放平台优势网址:DOP数据开放平台商户可自行注册,管理员开放权限访问接口向下兼容,方便版本迭代响应报文过滤,数据更安全支持监控限流,服务更稳定自
- Docker 入门教程(七):容器数据卷
千233
Docker(for科研er)dockerjavaeureka
文章目录Docker入门教程(七):容器数据卷一、为什么需要数据卷?二、三种挂载方式示例:MySQL数据持久化三、数据卷容器模式(旧式技术)Docker入门教程(七):容器数据卷一、为什么需要数据卷?容器默认的写层具有两个关键缺点:不持久:容器一旦被删除,数据也随之丢失不可共享:每个容器的数据互相隔离为了解决这个问题,Docker提供了数据卷(Volume)机制,将数据从容器中解耦出来,形成独立、
- CentOS DHCP服务器部署指南
title:DHCP服务器部署以及配置search:2024-03-21tags:“#DHCP服务器部署以及配置”CentOSDHCP服务器部署指南背景:因上了Linux的实验课程,在课程中,老师要求我们自己搭建DHCP服务器构建局域网,在构建的时候问题百出,不过也极其有意思一、补充网络基本概念(了解的可以直接跳过)IP地址:通俗来讲,我认为IP就是相当于在互联网的身份证,是用来标识自己在互联网上
- 数据标注工具详解
Sally璐璐
ai大数据
数据标注工具是构建高质量AI训练数据集的核心基础设施,其功能覆盖图像、文本、视频、音频、3D点云等多模态数据的标注与管理。以下从工具类型、核心功能、行业应用及技术趋势等方面进行系统介绍:一、主流数据标注工具分类与特性1.通用型标注平台LabelStudio由Heartex开发的开源工具,支持文本、图像、视频、音频及时间序列数据标注,可通过YAML自定义标注界面19。其内置质量控制机制(如标注审核、
- Joda-Time 日期时间库介绍
hweiyu00
技术栈杂谈开发语言java
一、Joda-Time是什么?Joda-Time是由StephenColebourne开发的开源日期时间库,用于替代Java标准库中的java.util.Date和java.util.Calendar。它因设计更合理、使用更便捷,曾是Java开发中处理日期时间的主流选择,尤其在Java8推出新的日期时间API(java.time包)之前被广泛使用。二、Joda-Time解决了Java标准库的哪些问
- MyBatis 简介
hweiyu00
技术栈杂谈mybatis
MyBatis简介MyBatis是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射,能够帮助开发者将Java对象与数据库表进行灵活映射,简化数据持久化操作。以下从多个维度详细介绍MyBatis:一、核心定位与优势轻量级框架:相比Hibernate等全自动ORM框架,MyBatis更“轻”,开发者需手动编写SQL语句,灵活性更高,便于优化性能。ORM映射功能:通过XML或注解方式,将J
- Go 语言高效连接 SQL Server(MSSQL)数据库实战指南
程序员爱钓鱼
数据库golangsqlserver
在Go语言的开发过程中,与MicrosoftSQLServer(MSSQL)数据库的交互是常见需求之一。本文将详细介绍如何使用Go语言高效、安全地连接SQLServer,并进行基本的CRUD(增删改查)操作。1.安装MSSQL驱动Go语言使用github.com/denisenkom/go-mssqldb作为SQLServer驱动,首先需要安装它:goget-ugithub.com/denisen
- Spring AI 结合 MCP MySQL 实现对话式数据库查询
没刮胡子
软件开发技术实战专栏人工智能AISpring数据库spring人工智能spring-aimcp-servermysql
在现代应用开发中,将人工智能与数据库查询结合可以创造更自然、更智能的用户交互方式。下面我将详细介绍如何使用SpringAI框架结合MCP(可能指MySQL连接池或相关组件)实现对话中的数据库查询功能。什么是SpringAI和MCPMySQLSpringAI框架概述SpringAI是基于Spring生态的人工智能集成框架,它提供了:与大型语言模型(LLM)的集成能力对话管理和自然语言处理功能业务逻辑
- AingDesk开源免费的本地 AI 模型管理工具(搭建和调用MCP)
没刮胡子
Linux服务器技术软件开发技术实战专栏人工智能AI开源人工智能AI助手mcpsse知识库智能体
说明AingDesk是一款开源免费的本地AI模型管理工具,旨在简化AI模型部署流程并提升用户体验。AingDesk支持本地AI模型及API+知识库搭建。支持知识库、模型API、分享、联网搜索、智能体。✨产品亮点跨平台支持客户端支持Windows、macOS,服务端可通过Docker部署高效下载与网络优化自动选择最优下载线路,支持断点续传,提升大模型部署速度兼容OpenAIAPI格式,方便第三方模型
- 【Docker基础】Docker容器管理:docker stats及其参数详解
IT成长日记
容器技术深度解析与实践docker容器运维dockerstats
目录1Docker监控概述2dockerstats基本用法2.1基本命令格式2.2常用操作示例3dockerstats参数详解3.1常用参数说明3.2输出字段解析3.3格式化输出示例4dockerstats工作原理4.1监控数据采集流程4.2数据源解析5常见问题解答5.1为什么CPU使用率会超过100%?5.2内存统计中的cache/buffer包含在哪里?5.3如何监控已停止的容器?6总结1Do
- sqlserver 中的go的作用
NaiQai
SqlServer
如果只是执行一条语句,有没有go都一样,如果多条语句之间用go分隔开就不一样了,每个被go分隔的语句都是一个单独的事务,一个语句执行失败不会影响其他语句执行。例如:首先同时执行下边的语句select*fromsysobjectswhereid=aselectgetdate()你会发现会报错,并且不会显示任何结果集而你再执行select*fromsysobjectswhereid=agoselect
- MiniMax - M1:开源大模型的革命性突破
开源大模型MiniMax-M1研究报告一、引言在人工智能技术飞速发展的当下,大模型领域的竞争愈发激烈。开源大模型以其开放性、可定制性和社区协作的优势,逐渐成为推动人工智能技术进步的重要力量。MiniMax-M1作为全球首个开源大规模混合架构的推理模型,一经发布便引起了广泛关注。它在长上下文处理、推理效率和成本控制等方面展现出了卓越的性能,为人工智能的发展带来了新的思路和方向。本文将对MiniMax
- Ubuntu基础(上传文件和部署Python)
aaiier
ubuntulinux运维
首先打开
[email protected]然后写yes,在输入密码然后就是输入ls/查看根目录ls/结果是ubuntu@x0-x-xx-xx:~$ls/binbootdevhomelib.usr-is-mergedlost+foundmntprocrunsbin.usr-is-mergedsrvtmpvarbin.usr-is-mergeddataetclibli
- Flutter基础(UI监听)
aaiier
flutter前端
文本按钮(TextButton)文本按钮是没有边框的按钮,当点击时会有涟漪效果。TextButton(onPressed:(){//点击按钮后要执行的代码print('文本按钮被点击了');},child:Text('点击我'),)手势检测器(GestureDetector)GestureDetector能够检测多种手势,不只是点击,还包括滑动、长按等。GestureDetector(onTap:
- Flutter基础(项目创建)
aaiier
flutter
一、使用命令行创建项目1.确认Flutter环境正常要保证FlutterSDK已经正确安装,并且环境变量配置无误。可以通过执行以下命令来验证:flutterdoctor要保证所有检查项都显示绿色对勾,要是有问题,可按照提示进行修复。2.创建新项目打开终端,执行下面的命令来创建一个新的Flutter应用:fluttercreatemy_flutter_appcdmy_flutter_app这里的my
- print(str(3+5))的结果是什么?为什么?
Lauren_Lu
python
✅语句:print(str(3+5))✅执行顺序与含义:括号优先:先计算3+5+是加法运算符3+5是一个表达式,结果为整数8使用str()函数将结果转换为字符串str(8)返回字符串'8'使用print()打印这个字符串print('8')的输出就是:8✅为什么要运算?因为:Python遇到表达式3+5时,必须先计算出结果;str()需要一个值作为参数,而不是一个没计算的表达式;这是Python表
- CentOS 入门必备基础知识与操作指南
码上有潜
linuxcentoslinux运维
标题:CentOS入门必备基础知识与操作指南简介CentOS是基于RedHatEnterpriseLinux(RHEL)的社区版本,适合企业级服务器的稳定性和安全性要求。本文将带领你了解CentOS的基础知识、安装过程、常用命令以及一些常见的运维操作。1.什么是CentOS?定义:CentOS是一个开放源代码的企业级操作系统,免费提供,但与RHEL完全兼容。优势:稳定、安全、适合长时间运行的服务器
- CentOS网络配置与管理完全指南
Sally璐璐
运维运维centos
1.网络状态查看与诊断1.1ifconfig命令(传统方式)#安装net-tools(CentOS7/8默认可能未安装)sudoyuminstallnet-tools-y#基础查看命令ifconfig#显示所有接口的IP、MAC、收发包统计等完整信息ifconfigeth0#查看eth0网卡的详细状态,包括:#-RX/TXpackets:收发包数量#-errors/dropped:错误和丢包统计#
- SQL Server 中 GO 的作用
Lauren_Lu
golang数据库oracle
CREATEDATABASEMyDatabase;USEMyDatabase;GO--定义局部变量DECLARE@s_novarchar(8),@s_avgradenumeric(4,1);--对局部变量赋值SETs_no='20170208';SET@s_avgrade=95.0;--使用局部变量UPDATEstudentSETs_avgrade=@s_avgradeWHEREs_no=@s_n
- Flutter基础(对接 API)
aaiier
flutter
1.添加依赖首先在pubspec.yaml中添加http包:dependencies:flutter:sdk:flutterhttp:^1.1.0#网络请求库然后运行flutterpubget来获取依赖包。2.创建API服务类创建一个专门的类来处理所有API请求,方便统一管理。import'dart:convert';//用于JSON编解码import'package:http/http.dart
- RNN循环神经网络原理解读
zhishidi
ai笔记rnn人工智能深度学习
我们把循环神经网络想象成一个有记忆的助手,特别擅长处理按顺序出现的信息,比如句子、语音、股票价格、音乐旋律等。核心思想:记住过去的信息,帮助理解现在。普通神经网络的局限(没有记忆)想象一个普通的神经网络(比如用于识别图片的):输入:你给它一张图片。处理:它分析这张图片的像素。输出:告诉你图片里是“猫”还是“狗”。问题:它每次只看一个独立的输入(一张图片),输入之间没有联系。给它看一个视频(连续很多
- 信息抽取领域关键Benchmark方法:分类体系
信息抽取领域关键Benchmark方法:分类体系摘要信息抽取(InformationExtraction,IE)作为自然语言处理的核心任务之一,旨在从非结构化文本中识别并结构化关键信息(如实体、关系、事件等),广泛应用于知识图谱构建、智能问答和数据分析等领域。近年来,随着深度学习技术的快速发展,信息抽取方法在性能和应用范围上取得了显著进步,但同时也面临着任务多样性、跨领域泛化性以及低资源场景下的适
- ss928v100模型的导出、量化和转换
yunken28
python开发语言
1、yolov8导出为onnxfromultralyticsimportYOLOmodel=YOLO("./best.pt")model.export(format="onnx",imgsz=640,dynamic=False,simplify=True,opset=11,batch=1,half=False)以下是model.export()方法各参数的详细解释:format="onnx"指
- Java开发中,spring mvc 的线程怎么调用?
小麦麦子
springmvc
今天逛知乎,看到最近很多人都在问spring mvc 的线程http://www.maiziedu.com/course/java/ 的启动问题,觉得挺有意思的,那哥们儿问的也听仔细,下面的回答也很详尽,分享出来,希望遇对遇到类似问题的Java开发程序猿有所帮助。
问题:
在用spring mvc架构的网站上,设一线程在虚拟机启动时运行,线程里有一全局
- maven依赖范围
bitcarter
maven
1.test 测试的时候才会依赖,编译和打包不依赖,如junit不被打包
2.compile 只有编译和打包时才会依赖
3.provided 编译和测试的时候依赖,打包不依赖,如:tomcat的一些公用jar包
4.runtime 运行时依赖,编译不依赖
5.默认compile
依赖范围compile是支持传递的,test不支持传递
1.传递的意思是项目A,引用
- Jaxb org.xml.sax.saxparseexception : premature end of file
darrenzhu
xmlprematureJAXB
如果在使用JAXB把xml文件unmarshal成vo(XSD自动生成的vo)时碰到如下错误:
org.xml.sax.saxparseexception : premature end of file
很有可能时你直接读取文件为inputstream,然后将inputstream作为构建unmarshal需要的source参数。InputSource inputSource = new In
- CSS Specificity
周凡杨
html权重Specificitycss
有时候对于页面元素设置了样式,可为什么页面的显示没有匹配上呢? because specificity
CSS 的选择符是有权重的,当不同的选择符的样式设置有冲突时,浏览器会采用权重高的选择符设置的样式。
规则:
HTML标签的权重是1
Class 的权重是10
Id 的权重是100
- java与servlet
g21121
servlet
servlet 搞java web开发的人一定不会陌生,而且大家还会时常用到它。
下面是java官方网站上对servlet的介绍: java官网对于servlet的解释 写道
Java Servlet Technology Overview Servlets are the Java platform technology of choice for extending and enha
- eclipse中安装maven插件
510888780
eclipsemaven
1.首先去官网下载 Maven:
http://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.cgi/maven/binaries/apache-maven-3.2.3-bin.tar.gz
下载完成之后将其解压,
我将解压后的文件夹:apache-maven-3.2.3,
并将它放在 D:\tools目录下,
即 maven 最终的路径是:D:\tools\apache-mave
- jpa@OneToOne关联关系
布衣凌宇
jpa
Nruser里的pruserid关联到Pruser的主键id,实现对一个表的增删改,另一个表的数据随之增删改。
Nruser实体类
//*****************************************************************
@Entity
@Table(name="nruser")
@DynamicInsert @Dynam
- 我的spring学习笔记11-Spring中关于声明式事务的配置
aijuans
spring事务配置
这两天学到事务管理这一块,结合到之前的terasoluna框架,觉得书本上讲的还是简单阿。我就把我从书本上学到的再结合实际的项目以及网上看到的一些内容,对声明式事务管理做个整理吧。我看得Spring in Action第二版中只提到了用TransactionProxyFactoryBean和<tx:advice/>,定义注释驱动这三种,我承认后两种的内容很好,很强大。但是实际的项目当中
- java 动态代理简单实现
antlove
javahandlerproxydynamicservice
dynamicproxy.service.HelloService
package dynamicproxy.service;
public interface HelloService {
public void sayHello();
}
dynamicproxy.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl
package dynamicp
- JDBC连接数据库
百合不是茶
JDBC编程JAVA操作oracle数据库
如果我们要想连接oracle公司的数据库,就要首先下载oralce公司的驱动程序,将这个驱动程序的jar包导入到我们工程中;
JDBC链接数据库的代码和固定写法;
1,加载oracle数据库的驱动;
&nb
- 单例模式中的多线程分析
bijian1013
javathread多线程java多线程
谈到单例模式,我们立马会想到饿汉式和懒汉式加载,所谓饿汉式就是在创建类时就创建好了实例,懒汉式在获取实例时才去创建实例,即延迟加载。
饿汉式:
package com.bijian.study;
public class Singleton {
private Singleton() {
}
// 注意这是private 只供内部调用
private static
- javascript读取和修改原型特别需要注意原型的读写不具有对等性
bijian1013
JavaScriptprototype
对于从原型对象继承而来的成员,其读和写具有内在的不对等性。比如有一个对象A,假设它的原型对象是B,B的原型对象是null。如果我们需要读取A对象的name属性值,那么JS会优先在A中查找,如果找到了name属性那么就返回;如果A中没有name属性,那么就到原型B中查找name,如果找到了就返回;如果原型B中也没有
- 【持久化框架MyBatis3六】MyBatis3集成第三方DataSource
bit1129
dataSource
MyBatis内置了数据源的支持,如:
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<data
- 我程序中用到的urldecode和base64decode,MD5
bitcarter
cMD5base64decodeurldecode
这里是base64decode和urldecode,Md5在附件中。因为我是在后台所以需要解码:
string Base64Decode(const char* Data,int DataByte,int& OutByte)
{
//解码表
const char DecodeTable[] =
{
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
- 腾讯资深运维专家周小军:QQ与微信架构的惊天秘密
ronin47
社交领域一直是互联网创业的大热门,从PC到移动端,从OICQ、MSN到QQ。到了移动互联网时代,社交领域应用开始彻底爆发,直奔黄金期。腾讯在过去几年里,社交平台更是火到爆,QQ和微信坐拥几亿的粉丝,QQ空间和朋友圈各种刷屏,写心得,晒照片,秀视频,那么谁来为企鹅保驾护航呢?支撑QQ和微信海量数据背后的架构又有哪些惊天内幕呢?本期大讲堂的内容来自今年2月份ChinaUnix对腾讯社交网络运营服务中心
- java-69-旋转数组的最小元素。把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个排好序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素
bylijinnan
java
public class MinOfShiftedArray {
/**
* Q69 旋转数组的最小元素
* 把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个排好序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。
* 例如数组{3, 4, 5, 1, 2}为{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。
*/
publ
- 看博客,应该是有方向的
Cb123456
反省看博客
看博客,应该是有方向的:
我现在就复习以前的,在补补以前不会的,现在还不会的,同时完善完善项目,也看看别人的博客.
我刚突然想到的:
1.应该看计算机组成原理,数据结构,一些算法,还有关于android,java的。
2.对于我,也快大四了,看一些职业规划的,以及一些学习的经验,看看别人的工作总结的.
为什么要写
- [开源与商业]做开源项目的人生活上一定要朴素,尽量减少对官方和商业体系的依赖
comsci
开源项目
为什么这样说呢? 因为科学和技术的发展有时候需要一个平缓和长期的积累过程,但是行政和商业体系本身充满各种不稳定性和不确定性,如果你希望长期从事某个科研项目,但是却又必须依赖于某种行政和商业体系,那其中的过程必定充满各种风险。。。
所以,为避免这种不确定性风险,我
- 一个 sql优化 ([精华] 一个查询优化的分析调整全过程!很值得一看 )
cwqcwqmax9
sql
见 http://www.itpub.net/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=239011
Web翻页优化实例
提交时间: 2004-6-18 15:37:49 回复 发消息
环境:
Linux ve
- Hibernat and Ibatis
dashuaifu
Hibernateibatis
Hibernate VS iBATIS 简介 Hibernate 是当前最流行的O/R mapping框架,当前版本是3.05。它出身于sf.net,现在已经成为Jboss的一部分了 iBATIS 是另外一种优秀的O/R mapping框架,当前版本是2.0。目前属于apache的一个子项目了。 相对Hibernate“O/R”而言,iBATIS 是一种“Sql Mappi
- 备份MYSQL脚本
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
#!/bin/sh
# this shell to backup mysql
#
[email protected] (QQ:1413161683 DuChengJiu)
_dbDir=/var/lib/mysql/
_today=`date +%w`
_bakDir=/usr/backup/$_today
[ ! -d $_bakDir ] && mkdir -p
- iOS第三方开源库的吐槽和备忘
dcj3sjt126com
ios
转自
ibireme的博客 做iOS开发总会接触到一些第三方库,这里整理一下,做一些吐槽。 目前比较活跃的社区仍旧是Github,除此以外也有一些不错的库散落在Google Code、SourceForge等地方。由于Github社区太过主流,这里主要介绍一下Github里面流行的iOS库。 首先整理了一份
Github上排名靠
- html wlwmanifest.xml
eoems
htmlxml
所谓优化wp_head()就是把从wp_head中移除不需要元素,同时也可以加快速度。
步骤:
加入到function.php
remove_action('wp_head', 'wp_generator');
//wp-generator移除wordpress的版本号,本身blog的版本号没什么意义,但是如果让恶意玩家看到,可能会用官网公布的漏洞攻击blog
remov
- 浅谈Java定时器发展
hacksin
java并发timer定时器
java在jdk1.3中推出了定时器类Timer,而后在jdk1.5后由Dou Lea从新开发出了支持多线程的ScheduleThreadPoolExecutor,从后者的表现来看,可以考虑完全替代Timer了。
Timer与ScheduleThreadPoolExecutor对比:
1.
Timer始于jdk1.3,其原理是利用一个TimerTask数组当作队列
- 移动端页面侧边导航滑入效果
ini
jqueryWebhtml5cssjavascirpt
效果体验:http://hovertree.com/texiao/mobile/2.htm可以使用移动设备浏览器查看效果。效果使用到jquery-2.1.4.min.js,该版本的jQuery库是用于支持HTML5的浏览器上,不再兼容IE8以前的浏览器,现在移动端浏览器一般都支持HTML5,所以使用该jQuery没问题。HTML文件代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<h
- AspectJ+Javasist记录日志
kane_xie
aspectjjavasist
在项目中碰到这样一个需求,对一个服务类的每一个方法,在方法开始和结束的时候分别记录一条日志,内容包括方法名,参数名+参数值以及方法执行的时间。
@Override
public String get(String key) {
// long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// System.out.println("Be
- redis学习笔记
MJC410621
redisNoSQL
1)nosql数据库主要由以下特点:非关系型的、分布式的、开源的、水平可扩展的。
1,处理超大量的数据
2,运行在便宜的PC服务器集群上,
3,击碎了性能瓶颈。
1)对数据高并发读写。
2)对海量数据的高效率存储和访问。
3)对数据的高扩展性和高可用性。
redis支持的类型:
Sring 类型
set name lijie
get name lijie
set na
- 使用redis实现分布式锁
qifeifei
在多节点的系统中,如何实现分布式锁机制,其中用redis来实现是很好的方法之一,我们先来看一下jedis包中,有个类名BinaryJedis,它有个方法如下:
public Long setnx(final byte[] key, final byte[] value) {
checkIsInMulti();
client.setnx(key, value);
ret
- BI并非万能,中层业务管理报表要另辟蹊径
张老师的菜
大数据BI商业智能信息化
BI是商业智能的缩写,是可以帮助企业做出明智的业务经营决策的工具,其数据来源于各个业务系统,如ERP、CRM、SCM、进销存、HER、OA等。
BI系统不同于传统的管理信息系统,他号称是一个整体应用的解决方案,是融入管理思想的强大系统:有着系统整体的设计思想,支持对所有
- 安装rvm后出现rvm not a function 或者ruby -v后提示没安装ruby的问题
wudixiaotie
function
1.在~/.bashrc最后加入
[[ -s "$HOME/.rvm/scripts/rvm" ]] && source "$HOME/.rvm/scripts/rvm"
2.重新启动terminal输入:
rvm use ruby-2.2.1 --default
把当前安装的ruby版本设为默