Netfilter的原理和实现浅析
关于Netfilter入门级概括性使用信息记录 转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/zhangskd/article/details/22678659
A. 概念描述
Netfilter为多种网络协议(IPv4、IPv6、ARP等)各提供了一套钩子函数。
在IPv4中定义了5个钩子函数,这些钩子函数在数据包流经协议栈的5个关键点被调用。
这就像有5个钓鱼台,在每个钓鱼台放了一个鱼钩(钩子函数),把经过的数据包钓上来,然后根据自定义的规则,来决定数据包的命运:
可以原封不动的放回IPv4协议,继续向上层递交;可以进行修改,再放回IPv4协议;也可以直接丢弃。
Netfilter主要采用连接跟踪(Connection Tracking)、包过滤(Packet Filtering)、地址转换(NAT)、包处理(Packet Mangling)四种技术。
(1) IP层的5个钓鱼台
enum nf_inet_hooks {
NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING,
NF_INET_LOCAL_IN,
NF_INET_FORWARD,
NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT,
NF_INET_POST_ROUTING,
NF_INET_NUMHOOKS
}; 支持的协议类型:
enum {
NFPROTO_UNSPEC = 0,
NFPROTO_IPV4 = 2,
NFPROTO_ARP = 3,
NFPROTO_BRIDGE = 7,
NFPROTO_IPV6 = 10,
NFPROTO_DECNET = 12,
NFPROTO_NUMPROTO,
};
(2) 钩子函数
typedef unsigned int nf_hookfn(unsigned int hooknum,
struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct net_device *in,
const struct net_device *out,
int (*okfn) (struct sk_buff *));
/* 处理函数返回值 */
#define NF_DROP 0 /* drop the packet, don't continue traversal */
#define NF_ACCEPT 1 /* continue traversal as normal */
#define NF_STOLEN 2 /* I've taken over the packet, don't continue traversal */
#define NF_QUEUE 3 /* queue the packet (usually for userspace handling) */
#define NF_REPEAT 4 /* call this hook again */
#define NF_STOP 5
#define NF_MAX_VERDICT NF_STOP
(3) Netfilter实体
在使用Netfilter时,需要定义一个nf_hook_ops实例。struct nf_hook_ops {
struct list_head list; /*链表成员
nf_hookfn *hook; /*要注册的钩子函数*/
struct module *owner;
u_int8_t pf; /*协议类型*/
unsigned int hooknum; /*哪个钓鱼台*/
int priority; /*数值越小,优先级越高*/
};
typedef __u8 u_int8_t;
(4) 注册与注销
/* Functions to register/unregister hook points. */
int nf_register_hook(struct nf_hook_ops *reg);
void nf_unregister_hook(struct nf_hook_ops *reg);
B. 具体实现细节
Netfilter定义了一个全局链表:
struct list_head nf_hooks[NFPROTO_NUMPROTO][NF_MAX_HOOKS]; EXPORT_SYMBOL(nf_hooks); static DEFINE_MUTEX(nf_hook_mutex);
(1) 注册函数
注册函数会把nf_hook_ops放入nf_hooks相应的位置中。
int nf_register_hook(struct nf_hook_ops *reg)
{
struct nf_hook_ops *elem;
int err;
err = mutex_lock_interruptible(&nf_hook_mutex);
if (err < 0)
return err;
list_for_each_entry(elem, &nf_hooks[reg->pf][reg->hooknum], list) {
if (reg->priority < elem->priority)
break;
}
list_add_rcu(®->list, elem->list.prev); /* 把netfilter实例添加到队列中 */
mutex_unlock(&nf_hook_mutex);
return 0;
}
(2) 注销函数
void nf_unregister_hook(struct nf_hook_ops *reg)
{
mutex_lock(&nf_hook_mutex);
list_del_rcu(®->list); /* 把netfilter实例从队列中删除 */
mutex_unlock(&nf_hook_mutex);
synchronize_net();
}
(3) 内核接口
内核的Netfilter钩子函数调用:
NF_HOOK
|--> NF_HOOK_THRESH
|--> nf_hook_thresh
|--> nf_hook_slow
|--> nf_iterate
static inline int NF_HOOK(uint8_t pf, unsigned int hook, struct sk_buff *skb,
struct net_device *in, struct net_device *out, int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *))
{
/* INT_MIN表示要调用钓鱼台的所有钩子函数 */
return NF_HOOK_THRESH(pf, hook, skb, in, out, okfn, INT_MIN);
}
static inline int NF_HOOK_THRESH(uint8_t pf, unsigned int hook, struct sk_buff *skb,
struct net_device *in, struct net_device *out, int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *), int thresh)
{
int ret = nf_hook_thresh(pf, hook, skb, in, out, okfn, thresh);
if (ret == 1)
ret = okfn(skb); /* 如果skb没被处理掉,调用此函数 */
return ret;
}
/**
* nf_hook_thresh - call a netfilter hook
* Returns 1 if the hook has allowed the packet to pass.
* The function okfn must be invoked by the caller in this case.
* Any other return value indicates the packet has been consumed by the hook.
*/
static inline int nf_hook_thresh(u_int8_t pf, unsigned int hook, struct sk_buff *skb,
struct net_device *indev, struct net_device *outdev, int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *), int thresh)
{
#ifndef CONFIG_NETFILTER_DEBUG
/* 如果协议pf的hook点上没有已注册的nf_hook_ops实例,直接返回1 */
if (list_empty(&nf_hooks[pf][hook]))
return 1;
#endif
return nf_hook_slow(pf, hook, skb, indev, outdev, okfn, thresh);
}
/* Returns 1 if okfn() needs to be executed by the caller, -EPERM for NF_DROP, 0 otherwise. */
int nf_hook_slow(u_int8_t pf, unsigned int hook, struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *indev,
struct net_device *outdev, int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *), int hook_thresh)
{
struct list_head *elem;
unsigned int verdict;
int ret = 0;
/* We may already have this, but read-locks nest anyway */
rcu_read_lock();
elem = &nf_hooks[pf][hook];
next_hook:
verdict = nf_iterate(&nf_hooks[pf][hook], skb, hook, indev, outdev, &elem, okfn, hook_thresh);
if (verdict == NF_ACCEPT || verdict == NF_STOP) {
ret = 1;
} else if (verdict == NF_DROP) {
kfree_skb(skb);
ret = -EPERM;
} else if ((verdict & NF_VERDICT_MASK) == NF_QUEUE) {
if (! nf_queue(skb, elem, ph, hook, indev, outdev, okfn, verdict >> NF_VERDICT_BITS))
goto next_hook;
}
rcu_read_unlock();
return ret;
}
unsigned int nf_iterate(struct list_head *head, struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int hook,
const struct net_device *indev, const struct net_device *outdev, struct list_head **i,
int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *), int hook_thresh)
{
unsigned int verdict;
/*
* The caller must not block between calls to this function because of risk of
* continuing from deleted element.
*/
list_for_each_continue_rcu(*i, head) {
struct nf_hook_ops *elem = (struct nf_hook_ops *) *i;
/* 优先级>=hook_thresh的都会被执行 */
if (hook_thresh > elem_priority)
continue;
verdict = elem->hook(hook, skb, indev, outdev, okfn); /* 已注册的执行函数 */
if (verdict != NF_ACCEPT) {
#ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER_DEBUG
if (unlikely((verdict & NF_VERDICT_MASK) > NF_MAX_VERDICT)) {
NFDEBUG("Evil return from %p(%u).\n", elem->hook, hook);
continue;
}
#endif
if (verdict != NF_REPEAT)
return verdict;
*i = (*i)->prev;
}
}
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
C. 使用举例
以下是一个简单的模块,加载到一个HTTP服务器上。
通过在PRE_ROUTING处注册my_hookfn,改变接收数据包的源IP为8.8.8.8(Google DNS server)。
当客户端向服务器发送一个请求时,肯定收不到服务器的响应:)
#include <linux/netfilter.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/netfilter_ipv4.h>
#include <linux/ip.h>
#include <linux/inet.h>
/**
* Hook function to be called.
* We modify the packet's src IP.
*/
unsigned int my_hookfn(unsigned int hooknum,
struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct net_device *in,
const struct net_device *out,
int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *))
{
struct iphdr *iph;
iph = ip_hdr(skb);
/* log the original src IP */
printk(KERN_INFO"src IP %pI4\n", &iph->saddr);
/* modify the packet's src IP */
iph->saddr = in_aton("8.8.8.8");
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
/* A netfilter instance to use */
static struct nf_hook_ops nfho = {
.hook = my_hookfn,
.pf = PF_INET,
.hooknum = NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING,
.priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
};
static int __init sknf_init(void)
{
if (nf_register_hook(&nfho)) {
printk(KERN_ERR"nf_register_hook() failed\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
static void __exit sknf_exit(void)
{
nf_unregister_hook(&nfho);
}
module_init(sknf_init);
module_exit(sknf_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("zhangsk");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
附录:
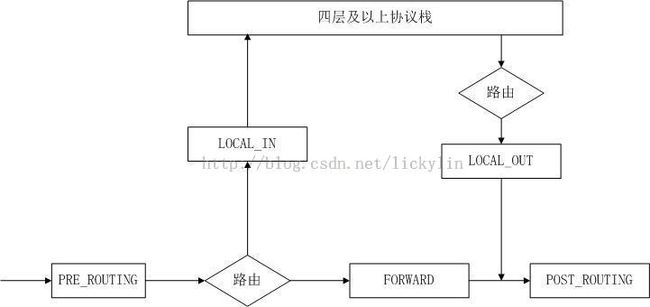
三层netfilter hook点的调用
三层netfilter的hook回调函数是在哪些函数里调用的。下面我们主要分析ip协议在五个hook点的调用
上图便是五个hook点调用的地方,对应于代码,我们来分析一下。
1.1 PRE_ROUTING
看这个名字,我们知道在这里执行hook回调函数时,数据包还没有经过路由,对于ip报文来说,在ip_rcv函数里,只是对数据包进行了合理性检查,还没有对数据包进行查找路由操作,所以PRE_ROUTINGhook点的回调函数的调用,即是在该函数的末尾通过调用函数NF_HOOK实现
return NF_HOOK(PF_INET, NF_IP_PRE_ROUTING, skb, dev, NULL,
ip_rcv_finish);
1.2 LOCAL_IN
当进入该hook点之前,数据包已经进行了路由操作,通过对协议栈的流程分析我们知道,在 ip_rcv_finish进行了路由选择后,对于属于本地接收的报文会调用函数ip_local_deliver,那很显然,LOCAL_IN HOOK点的回调函数的调用执行,肯定是在这个函数的末尾执行的了。函数片断如下:
return NF_HOOK(PF_INET, NF_IP_LOCAL_IN, skb, skb->dev, NULL,
ip_local_deliver_finish);
1.3 FORWARD
在进行了路由后,对于需要转发的数据,通过调用函数dst_input(skb),间接调用函数 ip_forward进行数据转发操作(关于为何会调用到ip_forward及ip_local_deliver,这是通过建立路由缓存时填充dst_entry指针实现的)。所以该HOOK点的hook回调函数的执行也是在该函数的末尾通过调用NF_HOOK实现的。
return NF_HOOK(PF_INET, NF_IP_FORWARD, skb, skb->dev, rt->u.dst.dev,
ip_forward_finish);
1.4 LOCAL_OUT
对于该hook点,是本地发送数据的hook调用,由于本地发送的数据既可以是UDP数据也可以是TCP数据,亦可以是组播数据。所以OUThook点的调用函数不止一处。其代码书写如下:
return NF_HOOK(PF_INET, NF_IP_LOCAL_OUT, skb, NULL, rt->u.dst.dev,
dst_output);
一般是本地数据找到路由之后,且没有调用skb->dst.out准备将数据包发送出去之前调用NF_HOOK
1.5 POST_ROUTING
在函数经过了FORWARD或者OUT节点后,就会通过skb->dst.out,执行到函数ip_output,所以函数
return NF_HOOK_COND(PF_INET, NF_IP_POST_ROUTING, skb, NULL, dev,
ip_finish_output,
!(IPCB(skb)->flags & IPSKB_REROUTED));