ImageLoader介绍
本文出自xiaanming的博客(http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming/article/details/26810303)
ImageLoader(一)基本介绍及使用
大家好!差不多两个来月没有写文章了,前段时间也是在忙换工作的事,准备笔试面试什么的事情,现在新工作找好了,新工作自己也比较满意,唯一遗憾的就是自己要去一个新的城市,新的环境新的开始,希望自己能尽快的适应新环境,现在在准备交接的事情,自己也有一些时间了,所以就继续给大家分享Android方面的东西。
相信大家平时做Android应用的时候,多少会接触到异步加载图片,或者加载大量图片的问题,而加载图片我们常常会遇到许多的问题,比如说图片的错乱,OOM等问题,对于新手来说,这些问题解决起来会比较吃力,所以就有很多的开源图片加载框架应运而生,比较著名的就是Universal-Image-Loader,相信很多朋友都听过或者使用过这个强大的图片加载框架,今天这篇文章就是对这个框架的基本介绍以及使用,主要是帮助那些没有使用过这个框架的朋友们。该项目存在于Github上面https://github.com/nostra13/Android-Universal-Image-Loader,我们可以先看看这个开源库存在哪些特征
- 多线程下载图片,图片可以来源于网络,文件系统,项目文件夹assets中以及drawable中等
- 支持随意的配置ImageLoader,例如线程池,图片下载器,内存缓存策略,硬盘缓存策略,图片显示选项以及其他的一些配置
- 支持图片的内存缓存,文件系统缓存或者SD卡缓存
- 支持图片下载过程的监听
- 根据控件(ImageView)的大小对Bitmap进行裁剪,减少Bitmap占用过多的内存
- 较好的控制图片的加载过程,例如暂停图片加载,重新开始加载图片,一般使用在ListView,GridView中,滑动过程中暂停加载图片,停止滑动的时候去加载图片
- 提供在较慢的网络下对图片进行加载
当然上面列举的特性可能不全,要想了解一些其他的特性只能通过我们的使用慢慢去发现了,接下来我们就看看这个开源库的简单使用吧
新建一个Android项目,下载JAR包添加到工程libs目录下
新建一个MyApplication继承Application,并在onCreate()中创建ImageLoader的配置参数,并初始化到ImageLoader中代码如下
- package com.example.uil;
- import com.nostra13.universalimageloader.core.ImageLoader;
- import com.nostra13.universalimageloader.core.ImageLoaderConfiguration;
- import android.app.Application;
- public class MyApplication extends Application {
- @Override
- public void onCreate() {
- super.onCreate();
- //创建默认的ImageLoader配置参数
- ImageLoaderConfiguration configuration = ImageLoaderConfiguration
- .createDefault(this);
- //Initialize ImageLoader with configuration.
- ImageLoader.getInstance().init(configuration);
- }
- }
- File cacheDir = StorageUtils.getCacheDirectory(context);
- ImageLoaderConfiguration config = new ImageLoaderConfiguration.Builder(context)
- .memoryCacheExtraOptions(480, 800) // default = device screen dimensions
- .diskCacheExtraOptions(480, 800, CompressFormat.JPEG, 75, null)
- .taskExecutor(...)
- .taskExecutorForCachedImages(...)
- .threadPoolSize(3) // default
- .threadPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY - 1) // default
- .tasksProcessingOrder(QueueProcessingType.FIFO) // default
- .denyCacheImageMultipleSizesInMemory()
- .memoryCache(new LruMemoryCache(2 * 1024 * 1024))
- .memoryCacheSize(2 * 1024 * 1024)
- .memoryCacheSizePercentage(13) // default
- .diskCache(new UnlimitedDiscCache(cacheDir)) // default
- .diskCacheSize(50 * 1024 * 1024)
- .diskCacheFileCount(100)
- .diskCacheFileNameGenerator(new HashCodeFileNameGenerator()) // default
- .imageDownloader(new BaseImageDownloader(context)) // default
- .imageDecoder(new BaseImageDecoder()) // default
- .defaultDisplayImageOptions(DisplayImageOptions.createSimple()) // default
- .writeDebugLogs()
- .build();
上面的这些就是所有的选项配置,我们在项目中不需要每一个都自己设置,一般使用createDefault()创建的ImageLoaderConfiguration就能使用,然后调用ImageLoader的init()方法将ImageLoaderConfiguration参数传递进去,ImageLoader使用单例模式。
配置Android Manifest文件
- <manifest>
- <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
- <!-- Include next permission if you want to allow UIL to cache images on SD card -->
- <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
- ...
- <application android:name="MyApplication">
- ...
- </application>
- </manifest>
接下来我们就可以来加载图片了,首先我们定义好Activity的布局文件
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent">
- <ImageView
- android:layout_gravity="center"
- android:id="@+id/image"
- android:src="@drawable/ic_empty"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
- </FrameLayout>
里面只有一个ImageView,很简单,接下来我们就去加载图片,我们会发现ImageLader提供了几个图片加载的方法,主要是这几个displayImage(), loadImage(),loadImageSync(),loadImageSync()方法是同步的,android4.0有个特性,网络操作不能在主线程,所以loadImageSync()方法我们就不去使用
.
loadimage()加载图片
我们先使用ImageLoader的loadImage()方法来加载网络图片
- final ImageView mImageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
- String imageUrl = "https://lh6.googleusercontent.com/-55osAWw3x0Q/URquUtcFr5I/AAAAAAAAAbs/rWlj1RUKrYI/s1024/A%252520Photographer.jpg";
- ImageLoader.getInstance().loadImage(imageUrl, new ImageLoadingListener() {
- @Override
- public void onLoadingStarted(String imageUri, View view) {
- }
- @Override
- public void onLoadingFailed(String imageUri, View view,
- FailReason failReason) {
- }
- @Override
- public void onLoadingComplete(String imageUri, View view, Bitmap loadedImage) {
- mImageView.setImageBitmap(loadedImage);
- }
- @Override
- public void onLoadingCancelled(String imageUri, View view) {
- }
- });
- final ImageView mImageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
- String imageUrl = "https://lh6.googleusercontent.com/-55osAWw3x0Q/URquUtcFr5I/AAAAAAAAAbs/rWlj1RUKrYI/s1024/A%252520Photographer.jpg";
- ImageLoader.getInstance().loadImage(imageUrl, new SimpleImageLoadingListener(){
- @Override
- public void onLoadingComplete(String imageUri, View view,
- Bitmap loadedImage) {
- super.onLoadingComplete(imageUri, view, loadedImage);
- mImageView.setImageBitmap(loadedImage);
- }
- });
- final ImageView mImageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
- String imageUrl = "https://lh6.googleusercontent.com/-55osAWw3x0Q/URquUtcFr5I/AAAAAAAAAbs/rWlj1RUKrYI/s1024/A%252520Photographer.jpg";
- ImageSize mImageSize = new ImageSize(100, 100);
- ImageLoader.getInstance().loadImage(imageUrl, mImageSize, new SimpleImageLoadingListener(){
- @Override
- public void onLoadingComplete(String imageUri, View view,
- Bitmap loadedImage) {
- super.onLoadingComplete(imageUri, view, loadedImage);
- mImageView.setImageBitmap(loadedImage);
- }
- });
上面只是很简单的使用ImageLoader来加载网络图片,在实际的开发中,我们并不会这么使用,那我们平常会怎么使用呢?我们会用到DisplayImageOptions,他可以配置一些图片显示的选项,比如图片在加载中ImageView显示的图片,是否需要使用内存缓存,是否需要使用文件缓存等等,可供我们选择的配置如下
- DisplayImageOptions options = new DisplayImageOptions.Builder()
- .showImageOnLoading(R.drawable.ic_stub) // resource or drawable
- .showImageForEmptyUri(R.drawable.ic_empty) // resource or drawable
- .showImageOnFail(R.drawable.ic_error) // resource or drawable
- .resetViewBeforeLoading(false) // default
- .delayBeforeLoading(1000)
- .cacheInMemory(false) // default
- .cacheOnDisk(false) // default
- .preProcessor(...)
- .postProcessor(...)
- .extraForDownloader(...)
- .considerExifParams(false) // default
- .imageScaleType(ImageScaleType.IN_SAMPLE_POWER_OF_2) // default
- .bitmapConfig(Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888) // default
- .decodingOptions(...)
- .displayer(new SimpleBitmapDisplayer()) // default
- .handler(new Handler()) // default
- .build();
我们将上面的代码稍微修改下
- final ImageView mImageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
- String imageUrl = "https://lh6.googleusercontent.com/-55osAWw3x0Q/URquUtcFr5I/AAAAAAAAAbs/rWlj1RUKrYI/s1024/A%252520Photographer.jpg";
- ImageSize mImageSize = new ImageSize(100, 100);
- //显示图片的配置
- DisplayImageOptions options = new DisplayImageOptions.Builder()
- .cacheInMemory(true)
- .cacheOnDisk(true)
- .bitmapConfig(Bitmap.Config.RGB_565)
- .build();
- ImageLoader.getInstance().loadImage(imageUrl, mImageSize, options, new SimpleImageLoadingListener(){
- @Override
- public void onLoadingComplete(String imageUri, View view,
- Bitmap loadedImage) {
- super.onLoadingComplete(imageUri, view, loadedImage);
- mImageView.setImageBitmap(loadedImage);
- }
- });
我们使用了DisplayImageOptions来配置显示图片的一些选项,这里我添加了将图片缓存到内存中已经缓存图片到文件系统中,这样我们就不用担心每次都从网络中去加载图片了,是不是很方便呢,但是DisplayImageOptions选项中有些选项对于loadImage()方法是无效的,比如showImageOnLoading, showImageForEmptyUri等,
displayImage()加载图片
接下来我们就来看看网络图片加载的另一个方法displayImage(),代码如下
- final ImageView mImageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
- String imageUrl = "https://lh6.googleusercontent.com/-55osAWw3x0Q/URquUtcFr5I/AAAAAAAAAbs/rWlj1RUKrYI/s1024/A%252520Photographer.jpg";
- //显示图片的配置
- DisplayImageOptions options = new DisplayImageOptions.Builder()
- .showImageOnLoading(R.drawable.ic_stub)
- .showImageOnFail(R.drawable.ic_error)
- .cacheInMemory(true)
- .cacheOnDisk(true)
- .bitmapConfig(Bitmap.Config.RGB_565)
- .build();
- ImageLoader.getInstance().displayImage(imageUrl, mImageView, options);
从上面的代码中,我们可以看出,使用displayImage()比使用loadImage()方便很多,也不需要添加ImageLoadingListener接口,我们也不需要手动设置ImageView显示Bitmap对象,直接将ImageView作为参数传递到displayImage()中就行了,图片显示的配置选项中,我们添加了一个图片加载中ImageVIew上面显示的图片,以及图片加载出现错误显示的图片,效果如下,刚开始显示ic_stub图片,如果图片加载成功显示图片,加载产生错误显示ic_error
- public class MyApplication extends Application {
- @Override
- public void onCreate() {
- super.onCreate();
- //创建默认的ImageLoader配置参数
- ImageLoaderConfiguration configuration = new ImageLoaderConfiguration.Builder(this)
- .writeDebugLogs() //打印log信息
- .build();
- //Initialize ImageLoader with configuration.
- ImageLoader.getInstance().init(configuration);
- }
- }
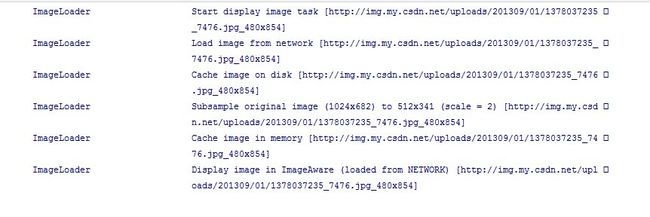
我们来看下图片加载的Log信息
第一条信息中,告诉我们开始加载图片,打印出图片的url以及图片的最大宽度和高度,图片的宽高默认是设备的宽高,当然如果我们很清楚图片的大小,我们也可以去设置这个大小,在ImageLoaderConfiguration的选项中memoryCacheExtraOptions(int maxImageWidthForMemoryCache, int maxImageHeightForMemoryCache)
第二条信息显示我们加载的图片来源于网络
第三条信息显示图片的原始大小为1024 x 682 经过裁剪变成了512 x 341
第四条显示图片加入到了内存缓存中,我这里没有加入到sd卡中,所以没有加入文件缓存的Log
我们在加载网络图片的时候,经常有需要显示图片下载进度的需求,Universal-Image-Loader当然也提供这样的功能,只需要在displayImage()方法中传入ImageLoadingProgressListener接口就行了,代码如下
- imageLoader.displayImage(imageUrl, mImageView, options, new SimpleImageLoadingListener(), new ImageLoadingProgressListener() {
- @Override
- public void onProgressUpdate(String imageUri, View view, int current,
- int total) {
- }
- });
加载其他来源的图片
使用Universal-Image-Loader框架不仅可以加载网络图片,还可以加载sd卡中的图片,Content provider等,使用也很简单,只是将图片的url稍加的改变下就行了,下面是加载文件系统的图片
- //显示图片的配置
- DisplayImageOptions options = new DisplayImageOptions.Builder()
- .showImageOnLoading(R.drawable.ic_stub)
- .showImageOnFail(R.drawable.ic_error)
- .cacheInMemory(true)
- .cacheOnDisk(true)
- .bitmapConfig(Bitmap.Config.RGB_565)
- .build();
- final ImageView mImageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
- String imagePath = "/mnt/sdcard/image.png";
- String imageUrl = Scheme.FILE.wrap(imagePath);
- // String imageUrl = "http://img.my.csdn.net/uploads/201309/01/1378037235_7476.jpg";
- imageLoader.displayImage(imageUrl, mImageView, options);
- //图片来源于Content provider
- String contentprividerUrl = "content://media/external/audio/albumart/13";
- //图片来源于assets
- String assetsUrl = Scheme.ASSETS.wrap("image.png");
- //图片来源于
- String drawableUrl = Scheme.DRAWABLE.wrap("R.drawable.image");
GirdView,ListView加载图片
相信大部分人都是使用GridView,ListView来显示大量的图片,而当我们快速滑动GridView,ListView,我们希望能停止图片的加载,而在GridView,ListView停止滑动的时候加载当前界面的图片,这个框架当然也提供这个功能,使用起来也很简单,它提供了PauseOnScrollListener这个类来控制ListView,GridView滑动过程中停止去加载图片,该类使用的是代理模式
- listView.setOnScrollListener(new PauseOnScrollListener(imageLoader, pauseOnScroll, pauseOnFling));
- gridView.setOnScrollListener(new PauseOnScrollListener(imageLoader, pauseOnScroll, pauseOnFling));
OutOfMemoryError
虽然这个框架有很好的缓存机制,有效的避免了OOM的产生,一般的情况下产生OOM的概率比较小,但是并不能保证OutOfMemoryError永远不发生,这个框架对于OutOfMemoryError做了简单的catch,保证我们的程序遇到OOM而不被crash掉,但是如果我们使用该框架经常发生OOM,我们应该怎么去改善呢?
- 减少线程池中线程的个数,在ImageLoaderConfiguration中的(.threadPoolSize)中配置,推荐配置1-5
- 在DisplayImageOptions选项中配置bitmapConfig为Bitmap.Config.RGB_565,因为默认是ARGB_8888, 使用RGB_565会比使用ARGB_8888少消耗2倍的内存
- 在ImageLoaderConfiguration中配置图片的内存缓存为memoryCache(new WeakMemoryCache()) 或者不使用内存缓存
- 在DisplayImageOptions选项中设置.imageScaleType(ImageScaleType.IN_SAMPLE_INT)或者imageScaleType(ImageScaleType.EXACTLY)
通过上面这些,相信大家对Universal-Image-Loader框架的使用已经非常的了解了,我们在使用该框架的时候尽量的使用displayImage()方法去加载图片,loadImage()是将图片对象回调到ImageLoadingListener接口的onLoadingComplete()方法中,需要我们手动去设置到ImageView上面,displayImage()方法中,对ImageView对象使用的是Weak references,方便垃圾回收器回收ImageView对象,如果我们要加载固定大小的图片的时候,使用loadImage()方法需要传递一个ImageSize对象,而displayImage()方法会根据ImageView对象的测量值,或者android:layout_width and android:layout_height设定的值,或者android:maxWidth and/or android:maxHeight设定的值来裁剪图片。
续为大家介绍Universal-Image-Loader这个开源的图片加载框架,介绍的是图片缓存策略方面的,如果大家对这个开源框架的使用还不了解,大家可以看看我之前写的一篇文章Android 开源框架Universal-Image-Loader完全解析(一)--- 基本介绍及使用,我们一般去加载大量的图片的时候,都会做缓存策略,缓存又分为内存缓存和硬盘缓存,我之前也写了几篇异步加载大量图片的文章,使用的内存缓存是LruCache这个类,LRU是Least Recently Used 近期最少使用算法,我们可以给LruCache设定一个缓存图片的最大值,它会自动帮我们管理好缓存的图片总大小是否超过我们设定的值, 超过就删除近期最少使用的图片,而作为一个强大的图片加载框架,Universal-Image-Loader自然也提供了多种图片的缓存策略,下面就来详细的介绍下
ImageLoader(二)——图片缓存策略详解
内存缓存
首先我们来了解下什么是强引用和什么是弱引用?
强引用是指创建一个对象并把这个对象赋给一个引用变量, 强引用有引用变量指向时永远不会被垃圾回收。即使内存不足的时候宁愿报OOM也不被垃圾回收器回收,我们new的对象都是强引用
弱引用通过weakReference类来实现,它具有很强的不确定性,如果垃圾回收器扫描到有着WeakReference的对象,就会将其回收释放内存
现在我们来看Universal-Image-Loader有哪些内存缓存策略
1. 只使用的是强引用缓存
- LruMemoryCache(这个类就是这个开源框架默认的内存缓存类,缓存的是bitmap的强引用,下面我会从源码上面分析这个类)
2.使用强引用和弱引用相结合的缓存有
- UsingFreqLimitedMemoryCache(如果缓存的图片总量超过限定值,先删除使用频率最小的bitmap)
- LRULimitedMemoryCache(这个也是使用的lru算法,和LruMemoryCache不同的是,他缓存的是bitmap的弱引用)
- FIFOLimitedMemoryCache(先进先出的缓存策略,当超过设定值,先删除最先加入缓存的bitmap)
- LargestLimitedMemoryCache(当超过缓存限定值,先删除最大的bitmap对象)
- LimitedAgeMemoryCache(当 bitmap加入缓存中的时间超过我们设定的值,将其删除)
3.只使用弱引用缓存
- WeakMemoryCache(这个类缓存bitmap的总大小没有限制,唯一不足的地方就是不稳定,缓存的图片容易被回收掉)
上面介绍了Universal-Image-Loader所提供的所有的内存缓存的类,当然我们也可以使用我们自己写的内存缓存类,我们还要看看要怎么将这些内存缓存加入到我们的项目中,我们只需要配置ImageLoaderConfiguration.memoryCache(...),如下
- ImageLoaderConfiguration configuration = new ImageLoaderConfiguration.Builder(this)
- .memoryCache(new WeakMemoryCache())
- .build();
下面我们来分析LruMemoryCache这个类的源代码
- package com.nostra13.universalimageloader.cache.memory.impl;
- import android.graphics.Bitmap;
- import com.nostra13.universalimageloader.cache.memory.MemoryCacheAware;
- import java.util.Collection;
- import java.util.HashSet;
- import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
- import java.util.Map;
- /**
- * A cache that holds strong references to a limited number of Bitmaps. Each time a Bitmap is accessed, it is moved to
- * the head of a queue. When a Bitmap is added to a full cache, the Bitmap at the end of that queue is evicted and may
- * become eligible for garbage collection.<br />
- * <br />
- * <b>NOTE:</b> This cache uses only strong references for stored Bitmaps.
- *
- * @author Sergey Tarasevich (nostra13[at]gmail[dot]com)
- * @since 1.8.1
- */
- public class LruMemoryCache implements MemoryCacheAware<String, Bitmap> {
- private final LinkedHashMap<String, Bitmap> map;
- private final int maxSize;
- /** Size of this cache in bytes */
- private int size;
- /** @param maxSize Maximum sum of the sizes of the Bitmaps in this cache */
- public LruMemoryCache(int maxSize) {
- if (maxSize <= 0) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
- }
- this.maxSize = maxSize;
- this.map = new LinkedHashMap<String, Bitmap>(0, 0.75f, true);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the Bitmap for {@code key} if it exists in the cache. If a Bitmap was returned, it is moved to the head
- * of the queue. This returns null if a Bitmap is not cached.
- */
- @Override
- public final Bitmap get(String key) {
- if (key == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
- }
- synchronized (this) {
- return map.get(key);
- }
- }
- /** Caches {@code Bitmap} for {@code key}. The Bitmap is moved to the head of the queue. */
- @Override
- public final boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
- if (key == null || value == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
- }
- synchronized (this) {
- size += sizeOf(key, value);
- Bitmap previous = map.put(key, value);
- if (previous != null) {
- size -= sizeOf(key, previous);
- }
- }
- trimToSize(maxSize);
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * Remove the eldest entries until the total of remaining entries is at or below the requested size.
- *
- * @param maxSize the maximum size of the cache before returning. May be -1 to evict even 0-sized elements.
- */
- private void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
- while (true) {
- String key;
- Bitmap value;
- synchronized (this) {
- if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
- throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName() + ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
- }
- if (size <= maxSize || map.isEmpty()) {
- break;
- }
- Map.Entry<String, Bitmap> toEvict = map.entrySet().iterator().next();
- if (toEvict == null) {
- break;
- }
- key = toEvict.getKey();
- value = toEvict.getValue();
- map.remove(key);
- size -= sizeOf(key, value);
- }
- }
- }
- /** Removes the entry for {@code key} if it exists. */
- @Override
- public final void remove(String key) {
- if (key == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
- }
- synchronized (this) {
- Bitmap previous = map.remove(key);
- if (previous != null) {
- size -= sizeOf(key, previous);
- }
- }
- }
- @Override
- public Collection<String> keys() {
- synchronized (this) {
- return new HashSet<String>(map.keySet());
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void clear() {
- trimToSize(-1); // -1 will evict 0-sized elements
- }
- /**
- * Returns the size {@code Bitmap} in bytes.
- * <p/>
- * An entry's size must not change while it is in the cache.
- */
- private int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap value) {
- return value.getRowBytes() * value.getHeight();
- }
- @Override
- public synchronized final String toString() {
- return String.format("LruCache[maxSize=%d]", maxSize);
- }
- }
我们来看将bitmap加入到LruMemoryCache的方法put(String key, Bitmap value), 第61行,sizeOf()是计算每张图片所占的byte数,size是记录当前缓存bitmap的总大小,如果该key之前就缓存了bitmap,我们需要将之前的bitmap减掉去,接下来看trimToSize()方法,我们直接看86行,如果当前缓存的bitmap总数小于设定值maxSize,不做任何处理,如果当前缓存的bitmap总数大于maxSize,删除LinkedHashMap中的第一个元素,size中减去该bitmap对应的byte数
我们可以看到该缓存类比较简单,逻辑也比较清晰,如果大家想知道其他内存缓存的逻辑,可以去分析分析其源码,在这里我简单说下FIFOLimitedMemoryCache的实现逻辑,该类使用的HashMap来缓存bitmap的弱引用,然后使用LinkedList来保存成功加入到FIFOLimitedMemoryCache的bitmap的强引用,如果加入的FIFOLimitedMemoryCache的bitmap总数超过限定值,直接删除LinkedList的第一个元素,所以就实现了先进先出的缓存策略,其他的缓存都类似,有兴趣的可以去看看。
硬盘缓存
接下来就给大家分析分析硬盘缓存的策略,这个框架也提供了几种常见的缓存策略,当然如果你觉得都不符合你的要求,你也可以自己去扩展
- FileCountLimitedDiscCache(可以设定缓存图片的个数,当超过设定值,删除掉最先加入到硬盘的文件)
- LimitedAgeDiscCache(设定文件存活的最长时间,当超过这个值,就删除该文件)
- TotalSizeLimitedDiscCache(设定缓存bitmap的最大值,当超过这个值,删除最先加入到硬盘的文件)
- UnlimitedDiscCache(这个缓存类没有任何的限制)
下面我们就来分析分析TotalSizeLimitedDiscCache的源码实现
- /*******************************************************************************
- * Copyright 2011-2013 Sergey Tarasevich
- *
- * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
- * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
- * You may obtain a copy of the License at
- *
- * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
- *
- * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
- * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
- * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
- * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
- * limitations under the License.
- *******************************************************************************/
- package com.nostra13.universalimageloader.cache.disc.impl;
- import com.nostra13.universalimageloader.cache.disc.LimitedDiscCache;
- import com.nostra13.universalimageloader.cache.disc.naming.FileNameGenerator;
- import com.nostra13.universalimageloader.core.DefaultConfigurationFactory;
- import com.nostra13.universalimageloader.utils.L;
- import java.io.File;
- /**
- * Disc cache limited by total cache size. If cache size exceeds specified limit then file with the most oldest last
- * usage date will be deleted.
- *
- * @author Sergey Tarasevich (nostra13[at]gmail[dot]com)
- * @see LimitedDiscCache
- * @since 1.0.0
- */
- public class TotalSizeLimitedDiscCache extends LimitedDiscCache {
- private static final int MIN_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE_IN_MB = 2;
- private static final int MIN_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE = MIN_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE_IN_MB * 1024 * 1024;
- /**
- * @param cacheDir Directory for file caching. <b>Important:</b> Specify separate folder for cached files. It's
- * needed for right cache limit work.
- * @param maxCacheSize Maximum cache directory size (in bytes). If cache size exceeds this limit then file with the
- * most oldest last usage date will be deleted.
- */
- public TotalSizeLimitedDiscCache(File cacheDir, int maxCacheSize) {
- this(cacheDir, DefaultConfigurationFactory.createFileNameGenerator(), maxCacheSize);
- }
- /**
- * @param cacheDir Directory for file caching. <b>Important:</b> Specify separate folder for cached files. It's
- * needed for right cache limit work.
- * @param fileNameGenerator Name generator for cached files
- * @param maxCacheSize Maximum cache directory size (in bytes). If cache size exceeds this limit then file with the
- * most oldest last usage date will be deleted.
- */
- public TotalSizeLimitedDiscCache(File cacheDir, FileNameGenerator fileNameGenerator, int maxCacheSize) {
- super(cacheDir, fileNameGenerator, maxCacheSize);
- if (maxCacheSize < MIN_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE) {
- L.w("You set too small disc cache size (less than %1$d Mb)", MIN_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE_IN_MB);
- }
- }
- @Override
- protected int getSize(File file) {
- return (int) file.length();
- }
- }
- /*******************************************************************************
- * Copyright 2011-2013 Sergey Tarasevich
- *
- * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
- * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
- * You may obtain a copy of the License at
- *
- * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
- *
- * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
- * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
- * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
- * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
- * limitations under the License.
- *******************************************************************************/
- package com.nostra13.universalimageloader.cache.disc;
- import com.nostra13.universalimageloader.cache.disc.naming.FileNameGenerator;
- import com.nostra13.universalimageloader.core.DefaultConfigurationFactory;
- import java.io.File;
- import java.util.Collections;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.Map;
- import java.util.Map.Entry;
- import java.util.Set;
- import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
- /**
- * Abstract disc cache limited by some parameter. If cache exceeds specified limit then file with the most oldest last
- * usage date will be deleted.
- *
- * @author Sergey Tarasevich (nostra13[at]gmail[dot]com)
- * @see BaseDiscCache
- * @see FileNameGenerator
- * @since 1.0.0
- */
- public abstract class LimitedDiscCache extends BaseDiscCache {
- private static final int INVALID_SIZE = -1;
- //记录缓存文件的大小
- private final AtomicInteger cacheSize;
- //缓存文件的最大值
- private final int sizeLimit;
- private final Map<File, Long> lastUsageDates = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<File, Long>());
- /**
- * @param cacheDir Directory for file caching. <b>Important:</b> Specify separate folder for cached files. It's
- * needed for right cache limit work.
- * @param sizeLimit Cache limit value. If cache exceeds this limit then file with the most oldest last usage date
- * will be deleted.
- */
- public LimitedDiscCache(File cacheDir, int sizeLimit) {
- this(cacheDir, DefaultConfigurationFactory.createFileNameGenerator(), sizeLimit);
- }
- /**
- * @param cacheDir Directory for file caching. <b>Important:</b> Specify separate folder for cached files. It's
- * needed for right cache limit work.
- * @param fileNameGenerator Name generator for cached files
- * @param sizeLimit Cache limit value. If cache exceeds this limit then file with the most oldest last usage date
- * will be deleted.
- */
- public LimitedDiscCache(File cacheDir, FileNameGenerator fileNameGenerator, int sizeLimit) {
- super(cacheDir, fileNameGenerator);
- this.sizeLimit = sizeLimit;
- cacheSize = new AtomicInteger();
- calculateCacheSizeAndFillUsageMap();
- }
- /**
- * 另开线程计算cacheDir里面文件的大小,并将文件和最后修改的毫秒数加入到Map中
- */
- private void calculateCacheSizeAndFillUsageMap() {
- new Thread(new Runnable() {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- int size = 0;
- File[] cachedFiles = cacheDir.listFiles();
- if (cachedFiles != null) { // rarely but it can happen, don't know why
- for (File cachedFile : cachedFiles) {
- //getSize()是一个抽象方法,子类自行实现getSize()的逻辑
- size += getSize(cachedFile);
- //将文件的最后修改时间加入到map中
- lastUsageDates.put(cachedFile, cachedFile.lastModified());
- }
- cacheSize.set(size);
- }
- }
- }).start();
- }
- /**
- * 将文件添加到Map中,并计算缓存文件的大小是否超过了我们设置的最大缓存数
- * 超过了就删除最先加入的那个文件
- */
- @Override
- public void put(String key, File file) {
- //要加入文件的大小
- int valueSize = getSize(file);
- //获取当前缓存文件大小总数
- int curCacheSize = cacheSize.get();
- //判断是否超过设定的最大缓存值
- while (curCacheSize + valueSize > sizeLimit) {
- int freedSize = removeNext();
- if (freedSize == INVALID_SIZE) break; // cache is empty (have nothing to delete)
- curCacheSize = cacheSize.addAndGet(-freedSize);
- }
- cacheSize.addAndGet(valueSize);
- Long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- file.setLastModified(currentTime);
- lastUsageDates.put(file, currentTime);
- }
- /**
- * 根据key生成文件
- */
- @Override
- public File get(String key) {
- File file = super.get(key);
- Long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- file.setLastModified(currentTime);
- lastUsageDates.put(file, currentTime);
- return file;
- }
- /**
- * 硬盘缓存的清理
- */
- @Override
- public void clear() {
- lastUsageDates.clear();
- cacheSize.set(0);
- super.clear();
- }
- /**
- * 获取最早加入的缓存文件,并将其删除
- */
- private int removeNext() {
- if (lastUsageDates.isEmpty()) {
- return INVALID_SIZE;
- }
- Long oldestUsage = null;
- File mostLongUsedFile = null;
- Set<Entry<File, Long>> entries = lastUsageDates.entrySet();
- synchronized (lastUsageDates) {
- for (Entry<File, Long> entry : entries) {
- if (mostLongUsedFile == null) {
- mostLongUsedFile = entry.getKey();
- oldestUsage = entry.getValue();
- } else {
- Long lastValueUsage = entry.getValue();
- if (lastValueUsage < oldestUsage) {
- oldestUsage = lastValueUsage;
- mostLongUsedFile = entry.getKey();
- }
- }
- }
- }
- int fileSize = 0;
- if (mostLongUsedFile != null) {
- if (mostLongUsedFile.exists()) {
- fileSize = getSize(mostLongUsedFile);
- if (mostLongUsedFile.delete()) {
- lastUsageDates.remove(mostLongUsedFile);
- }
- } else {
- lastUsageDates.remove(mostLongUsedFile);
- }
- }
- return fileSize;
- }
- /**
- * 抽象方法,获取文件大小
- * @param file
- * @return
- */
- protected abstract int getSize(File file);
- }
然后是将文件加入硬盘缓存的方法put(),在106行判断当前文件的缓存总数加上即将要加入缓存的文件大小是否超过缓存设定值,如果超过了执行removeNext()方法,接下来就来看看这个方法的具体实现,150-167中找出最先加入硬盘的文件,169-180中将其从文件硬盘中删除,并返回该文件的大小,删除成功之后成员变量cacheSize需要减掉改文件大小。
FileCountLimitedDiscCache这个类实现逻辑跟TotalSizeLimitedDiscCache是一样的,区别在于getSize()方法,前者返回1,表示为文件数是1,后者返回文件的大小。
等我写完了这篇文章,我才发现FileCountLimitedDiscCache和TotalSizeLimitedDiscCache在最新的源码中已经删除了,加入了LruDiscCache,由于我的是之前的源码,所以我也不改了,大家如果想要了解LruDiscCache可以去看最新的源码,我这里就不介绍了,还好内存缓存的没变化,下面分析的是最新的源码中的部分,我们在使用中可以不自行配置硬盘缓存策略,直接用DefaultConfigurationFactory中的就行了
我们看DefaultConfigurationFactory这个类的createDiskCache()方法
- /**
- * Creates default implementation of {@link DiskCache} depends on incoming parameters
- */
- public static DiskCache createDiskCache(Context context, FileNameGenerator diskCacheFileNameGenerator,
- long diskCacheSize, int diskCacheFileCount) {
- File reserveCacheDir = createReserveDiskCacheDir(context);
- if (diskCacheSize > 0 || diskCacheFileCount > 0) {
- File individualCacheDir = StorageUtils.getIndividualCacheDirectory(context);
- LruDiscCache diskCache = new LruDiscCache(individualCacheDir, diskCacheFileNameGenerator, diskCacheSize,
- diskCacheFileCount);
- diskCache.setReserveCacheDir(reserveCacheDir);
- return diskCache;
- } else {
- File cacheDir = StorageUtils.getCacheDirectory(context);
- return new UnlimitedDiscCache(cacheDir, reserveCacheDir, diskCacheFileNameGenerator);
- }
- }
ImageLoader完全解析(三)---源代码解读
本篇文章主要是带大家从源码的角度上面去解读这个强大的图片加载框架,自己很久没有写文章了,感觉生疏了许多,距离上一篇文章三个月多了,确实是自己平常忙,换了工作很多东西都要去看去理解,然后加上自己也懒了,没有以前那么有激情了,我感觉这节奏不对,我要继续保持以前的激情,正所谓好记性不如烂笔头,有时候自己也会去翻看下之前写的东西,我觉得知识写下来比在脑海中留存的更久,今天就给大家来读一读这个框架的源码,我感觉这个图片加载框架确实写的很不错,读完代码自己也学到了很多。我希望大家可以先去看下Android 开源框架Universal-Image-Loader完全解析(一)--- 基本介绍及使用, Android 开源框架Universal-Image-Loader完全解析(二)--- 图片缓存策略详解 ,我希望大家可以坚持看完,看完了对你绝对是有收获的。
- ImageView mImageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
- String imageUrl = "https://lh6.googleusercontent.com/-55osAWw3x0Q/URquUtcFr5I/AAAAAAAAAbs/rWlj1RUKrYI/s1024/A%252520Photographer.jpg";
- //显示图片的配置
- DisplayImageOptions options = new DisplayImageOptions.Builder()
- .showImageOnLoading(R.drawable.ic_stub)
- .showImageOnFail(R.drawable.ic_error)
- .cacheInMemory(true)
- .cacheOnDisk(true)
- .bitmapConfig(Bitmap.Config.RGB_565)
- .build();
- ImageLoader.getInstance().displayImage(imageUrl, mImageView, options);
- public void displayImage(String uri, ImageView imageView, DisplayImageOptions options) {
- displayImage(uri, new ImageViewAware(imageView), options, null, null);
- }
接下来看具体的displayImage方法啦,由于这个方法代码量蛮多的,所以这里我分开来读
- checkConfiguration();
- if (imageAware == null) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException(ERROR_WRONG_ARGUMENTS);
- }
- if (listener == null) {
- listener = emptyListener;
- }
- if (options == null) {
- options = configuration.defaultDisplayImageOptions;
- }
- if (TextUtils.isEmpty(uri)) {
- engine.cancelDisplayTaskFor(imageAware);
- listener.onLoadingStarted(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView());
- if (options.shouldShowImageForEmptyUri()) {
- imageAware.setImageDrawable(options.getImageForEmptyUri(configuration.resources));
- } else {
- imageAware.setImageDrawable(null);
- }
- listener.onLoadingComplete(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView(), null);
- return;
- }
12-21行主要是针对url为空的时候做的处理,第13行代码中,ImageLoaderEngine中存在一个HashMap,用来记录正在加载的任务,加载图片的时候会将ImageView的id和图片的url加上尺寸加入到HashMap中,加载完成之后会将其移除,然后将DisplayImageOptions的imageResForEmptyUri的图片设置给ImageView,最后回调给ImageLoadingListener接口告诉它这次任务完成了。
- ImageSize targetSize = ImageSizeUtils.defineTargetSizeForView(imageAware, configuration.getMaxImageSize());
- String memoryCacheKey = MemoryCacheUtils.generateKey(uri, targetSize);
- engine.prepareDisplayTaskFor(imageAware, memoryCacheKey);
- listener.onLoadingStarted(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView());
- Bitmap bmp = configuration.memoryCache.get(memoryCacheKey);
- if (bmp != null && !bmp.isRecycled()) {
- L.d(LOG_LOAD_IMAGE_FROM_MEMORY_CACHE, memoryCacheKey);
- if (options.shouldPostProcess()) {
- ImageLoadingInfo imageLoadingInfo = new ImageLoadingInfo(uri, imageAware, targetSize, memoryCacheKey,
- options, listener, progressListener, engine.getLockForUri(uri));
- ProcessAndDisplayImageTask displayTask = new ProcessAndDisplayImageTask(engine, bmp, imageLoadingInfo,
- defineHandler(options));
- if (options.isSyncLoading()) {
- displayTask.run();
- } else {
- engine.submit(displayTask);
- }
- } else {
- options.getDisplayer().display(bmp, imageAware, LoadedFrom.MEMORY_CACHE);
- listener.onLoadingComplete(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView(), bmp);
- }
- }
第7行从内存缓存中获取Bitmap对象,我们可以再ImageLoaderConfiguration中配置内存缓存逻辑,默认使用的是LruMemoryCache,这个类我在前面的文章中讲过
第11行中有一个判断,我们如果在DisplayImageOptions中设置了postProcessor就进入true逻辑,不过默认postProcessor是为null的,BitmapProcessor接口主要是对Bitmap进行处理,这个框架并没有给出相对应的实现,如果我们有自己的需求的时候可以自己实现BitmapProcessor接口(比如将图片设置成圆形的)
第22 -23行是将Bitmap设置到ImageView上面,这里我们可以在DisplayImageOptions中配置显示需求displayer,默认使用的是SimpleBitmapDisplayer,直接将Bitmap设置到ImageView上面,我们可以配置其他的显示逻辑, 他这里提供了FadeInBitmapDisplayer(透明度从0-1)RoundedBitmapDisplayer(4个角是圆弧)等, 然后回调到ImageLoadingListener接口
- if (options.shouldShowImageOnLoading()) {
- imageAware.setImageDrawable(options.getImageOnLoading(configuration.resources));
- } else if (options.isResetViewBeforeLoading()) {
- imageAware.setImageDrawable(null);
- }
- ImageLoadingInfo imageLoadingInfo = new ImageLoadingInfo(uri, imageAware, targetSize, memoryCacheKey,
- options, listener, progressListener, engine.getLockForUri(uri));
- LoadAndDisplayImageTask displayTask = new LoadAndDisplayImageTask(engine, imageLoadingInfo,
- defineHandler(options));
- if (options.isSyncLoading()) {
- displayTask.run();
- } else {
- engine.submit(displayTask);
- }
接下来我们就看LoadAndDisplayImageTask的run(), 这个类还是蛮复杂的,我们还是一段一段的分析
- if (waitIfPaused()) return;
- if (delayIfNeed()) return;
如果waitIfPaused(), delayIfNeed()返回true的话,直接从run()方法中返回了,不执行下面的逻辑, 接下来我们先看看waitIfPaused()
- private boolean waitIfPaused() {
- AtomicBoolean pause = engine.getPause();
- if (pause.get()) {
- synchronized (engine.getPauseLock()) {
- if (pause.get()) {
- L.d(LOG_WAITING_FOR_RESUME, memoryCacheKey);
- try {
- engine.getPauseLock().wait();
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- L.e(LOG_TASK_INTERRUPTED, memoryCacheKey);
- return true;
- }
- L.d(LOG_RESUME_AFTER_PAUSE, memoryCacheKey);
- }
- }
- }
- return isTaskNotActual();
- }
这个方法是干嘛用呢,主要是我们在使用ListView,GridView去加载图片的时候,有时候为了滑动更加的流畅,我们会选择手指在滑动或者猛地一滑动的时候不去加载图片,所以才提出了这么一个方法,那么要怎么用呢? 这里用到了PauseOnScrollListener这个类,使用很简单ListView.setOnScrollListener(new PauseOnScrollListener(pauseOnScroll, pauseOnFling )), pauseOnScroll控制我们缓慢滑动ListView,GridView是否停止加载图片,pauseOnFling 控制猛的滑动ListView,GridView是否停止加载图片
除此之外,这个方法的返回值由isTaskNotActual()决定,我们接着看看isTaskNotActual()的源码
- private boolean isTaskNotActual() {
- return isViewCollected() || isViewReused();
- }
- ReentrantLock loadFromUriLock = imageLoadingInfo.loadFromUriLock;
- L.d(LOG_START_DISPLAY_IMAGE_TASK, memoryCacheKey);
- if (loadFromUriLock.isLocked()) {
- L.d(LOG_WAITING_FOR_IMAGE_LOADED, memoryCacheKey);
- }
- loadFromUriLock.lock();
- Bitmap bmp;
- try {
- checkTaskNotActual();
- bmp = configuration.memoryCache.get(memoryCacheKey);
- if (bmp == null || bmp.isRecycled()) {
- bmp = tryLoadBitmap();
- if (bmp == null) return; // listener callback already was fired
- checkTaskNotActual();
- checkTaskInterrupted();
- if (options.shouldPreProcess()) {
- L.d(LOG_PREPROCESS_IMAGE, memoryCacheKey);
- bmp = options.getPreProcessor().process(bmp);
- if (bmp == null) {
- L.e(ERROR_PRE_PROCESSOR_NULL, memoryCacheKey);
- }
- }
- if (bmp != null && options.isCacheInMemory()) {
- L.d(LOG_CACHE_IMAGE_IN_MEMORY, memoryCacheKey);
- configuration.memoryCache.put(memoryCacheKey, bmp);
- }
- } else {
- loadedFrom = LoadedFrom.MEMORY_CACHE;
- L.d(LOG_GET_IMAGE_FROM_MEMORY_CACHE_AFTER_WAITING, memoryCacheKey);
- }
- if (bmp != null && options.shouldPostProcess()) {
- L.d(LOG_POSTPROCESS_IMAGE, memoryCacheKey);
- bmp = options.getPostProcessor().process(bmp);
- if (bmp == null) {
- L.e(ERROR_POST_PROCESSOR_NULL, memoryCacheKey);
- }
- }
- checkTaskNotActual();
- checkTaskInterrupted();
- } catch (TaskCancelledException e) {
- fireCancelEvent();
- return;
- } finally {
- loadFromUriLock.unlock();
- }
- ReentrantLock getLockForUri(String uri) {
- ReentrantLock lock = uriLocks.get(uri);
- if (lock == null) {
- lock = new ReentrantLock();
- uriLocks.put(uri, lock);
- }
- return lock;
- }
来到第12行,它们会先从内存缓存中获取一遍,如果内存缓存中没有在去执行下面的逻辑,所以ReentrantLock的作用就是避免这种情况下重复的去从网络上面请求图片。
第14行的方法tryLoadBitmap(),这个方法确实也有点长,我先告诉大家,这里面的逻辑是先从文件缓存中获取有没有Bitmap对象,如果没有在去从网络中获取,然后将bitmap保存在文件系统中,我们还是具体分析下
- File imageFile = configuration.diskCache.get(uri);
- if (imageFile != null && imageFile.exists()) {
- L.d(LOG_LOAD_IMAGE_FROM_DISK_CACHE, memoryCacheKey);
- loadedFrom = LoadedFrom.DISC_CACHE;
- checkTaskNotActual();
- bitmap = decodeImage(Scheme.FILE.wrap(imageFile.getAbsolutePath()));
- }
- if (bitmap == null || bitmap.getWidth() <= 0 || bitmap.getHeight() <= 0) {
- L.d(LOG_LOAD_IMAGE_FROM_NETWORK, memoryCacheKey);
- loadedFrom = LoadedFrom.NETWORK;
- String imageUriForDecoding = uri;
- if (options.isCacheOnDisk() && tryCacheImageOnDisk()) {
- imageFile = configuration.diskCache.get(uri);
- if (imageFile != null) {
- imageUriForDecoding = Scheme.FILE.wrap(imageFile.getAbsolutePath());
- }
- }
- checkTaskNotActual();
- bitmap = decodeImage(imageUriForDecoding);
- if (bitmap == null || bitmap.getWidth() <= 0 || bitmap.getHeight() <= 0) {
- fireFailEvent(FailType.DECODING_ERROR, null);
- }
- }
- private Bitmap decodeImage(String imageUri) throws IOException {
- ViewScaleType viewScaleType = imageAware.getScaleType();
- ImageDecodingInfo decodingInfo = new ImageDecodingInfo(memoryCacheKey, imageUri, uri, targetSize, viewScaleType,
- getDownloader(), options);
- return decoder.decode(decodingInfo);
- }
- /** @return <b>true</b> - if image was downloaded successfully; <b>false</b> - otherwise */
- private boolean tryCacheImageOnDisk() throws TaskCancelledException {
- L.d(LOG_CACHE_IMAGE_ON_DISK, memoryCacheKey);
- boolean loaded;
- try {
- loaded = downloadImage();
- if (loaded) {
- int width = configuration.maxImageWidthForDiskCache;
- int height = configuration.maxImageHeightForDiskCache;
- if (width > 0 || height > 0) {
- L.d(LOG_RESIZE_CACHED_IMAGE_FILE, memoryCacheKey);
- resizeAndSaveImage(width, height); // TODO : process boolean result
- }
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- L.e(e);
- loaded = false;
- }
- return loaded;
- }
- private boolean downloadImage() throws IOException {
- InputStream is = getDownloader().getStream(uri, options.getExtraForDownloader());
- return configuration.diskCache.save(uri, is, this);
- }
第16-17行,获取ImageLoaderConfiguration是否设置保存在文件系统中的图片大小,如果设置了maxImageWidthForDiskCache和maxImageHeightForDiskCache,会调用resizeAndSaveImage()方法对图片进行裁剪然后在替换之前的原图,保存裁剪后的图片到文件系统的,之前有同学问过我说这个框架保存在文件系统的图片都是原图,怎么才能保存缩略图,只要在Application中实例化ImageLoaderConfiguration的时候设置maxImageWidthForDiskCache和maxImageHeightForDiskCache就行了
- if (bmp == null) return; // listener callback already was fired
- checkTaskNotActual();
- checkTaskInterrupted();
- if (options.shouldPreProcess()) {
- L.d(LOG_PREPROCESS_IMAGE, memoryCacheKey);
- bmp = options.getPreProcessor().process(bmp);
- if (bmp == null) {
- L.e(ERROR_PRE_PROCESSOR_NULL, memoryCacheKey);
- }
- }
- if (bmp != null && options.isCacheInMemory()) {
- L.d(LOG_CACHE_IMAGE_IN_MEMORY, memoryCacheKey);
- configuration.memoryCache.put(memoryCacheKey, bmp);
- }
- DisplayBitmapTask displayBitmapTask = new DisplayBitmapTask(bmp, imageLoadingInfo, engine, loadedFrom);
- runTask(displayBitmapTask, syncLoading, handler, engine);
- @Override
- public void run() {
- if (imageAware.isCollected()) {
- L.d(LOG_TASK_CANCELLED_IMAGEAWARE_COLLECTED, memoryCacheKey);
- listener.onLoadingCancelled(imageUri, imageAware.getWrappedView());
- } else if (isViewWasReused()) {
- L.d(LOG_TASK_CANCELLED_IMAGEAWARE_REUSED, memoryCacheKey);
- listener.onLoadingCancelled(imageUri, imageAware.getWrappedView());
- } else {
- L.d(LOG_DISPLAY_IMAGE_IN_IMAGEAWARE, loadedFrom, memoryCacheKey);
- displayer.display(bitmap, imageAware, loadedFrom);
- engine.cancelDisplayTaskFor(imageAware);
- listener.onLoadingComplete(imageUri, imageAware.getWrappedView(), bitmap);
- }
- }
假如ImageView被回收了或者被重用了,回调给ImageLoadingListener接口,否则就调用BitmapDisplayer去显示Bitmap
文章写到这里就已经写完了,不知道大家对这个开源框架有没有进一步的理解,这个开源框架设计也很灵活,用了很多的设计模式,比如建造者模式,装饰模式,代理模式,策略模式等等,这样方便我们去扩展,实现我们想要的功能,今天的讲解就到这了,有对这个框架不明白的地方可以在下面留言,我会尽量为大家解答的。