字符串插入块链实现——数据结构上机实验
1、相关类型说明
#define chunksize 8
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "string.h"
typedef struct chunk
{ char ch[chunksize];
structchunk *next;
}chunk;//块链结点类型
typedef struct
{ chunk *head,*tail; //块链指向头尾结点的指针
int curlen;//块链中串的长度
}lstring; //块链类型
2、需要实现的算法。
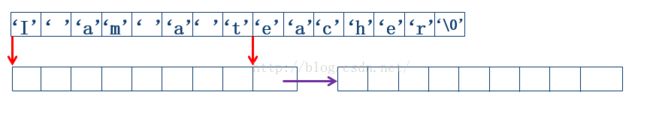
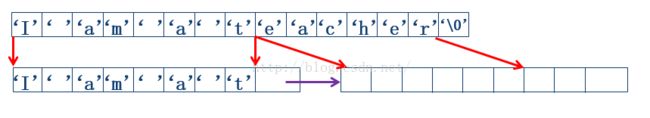
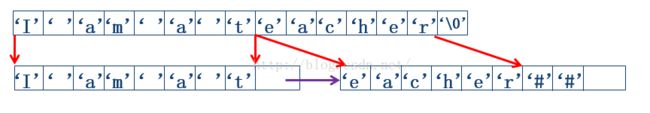
void strassign(lstring&T,char *str)
将一个不包含’#’字符串str赋值到块链类型变量T中
链表生成
void clrstring(lstring &T)
将一个块链T中的所有结点释放,最终使得T.head=T.tail=null T.curlen=0
void strprint(lstring T)
打印一个存放在块链T中的字符串
2、需要实现的算法及功能动画演示。
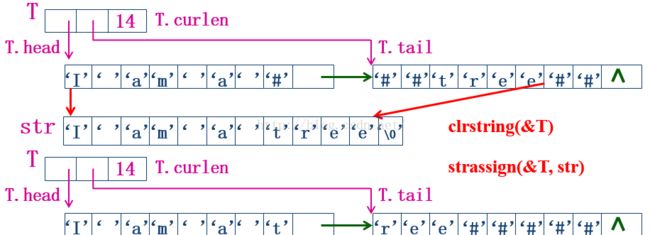
void strinsert(lstring&T,int pos,lstring S)
将块链S插入到块链T中第pos个字符之前
如下例所示 strinsert(&T, 7 , S)
3、需要实现的算法。
void zip(lstring&T)
实验代码
#define chunksize 8
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "string.h"
typedef struct chunk
{ char ch[chunksize];
struct chunk *next;
}chunk;//块链节点类型
typedef struct
{
chunk *head,*tail;//块链指向头尾指针
int curlen; //块链中串的长度
}lstring; //块链的类型
void strassign(lstring &T,char *str)
{
chunk *aa;
int n1,n2;
int len;
aa=new chunk;
T.head=T.tail=aa;
T.head->next=T.tail->next=NULL;
len=strlen(str);
T.curlen=len;
n1=len/8;
int o;
o=n1;
n2=len%8;
int cnm=0;
int y;
y=0;
int ff;
if(o!=0)
{
while(n1--)
{
if(cnm==0)
{
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
{
T.tail->ch[i]=str[y];
y++;
}
cnm=1;
}
else
{
aa=new chunk;
T.tail->next=aa;
T.tail=aa;
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
{
T.tail->ch[i]=str[y];
y++;
}
}
}
if(n2!=0)
{
aa=new chunk;
T.tail->next=aa;
T.tail=aa;
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
{
if(i<n2)
{
T.tail->ch[i]=str[y];
y++;
}
else
{
T.tail->ch[i]='#';
}
}
}
T.tail->next=NULL;
}
else
{
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
{
if(i<n2)
{
T.tail->ch[i]=str[y];
y++;
}
else
{
T.tail->ch[i]='#';
}
}
T.tail->next=NULL;
}
}
void clrstring(lstring &T)
{
chunk *aa;
while(T.head!=0)
{
aa=T.head;
free(T.head);
T.head=aa;
}
T.tail=T.head=NULL;
T.curlen=0;
}
void strprint(lstring T)//shuchu
{
chunk *bb;
int yy=0;
bb=T.head;
while(bb!=NULL)
{
if(yy==0)
{
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
printf("%c",bb->ch[i]);
yy=1;
}
else
{
printf("->");
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
{
printf("%c",bb->ch[i]);
}
}
bb=bb->next;
}
}
void strinsert(lstring &T,int pos,lstring S)
{
chunk *pp;
pp=T.head;
int qyx=0;
while(pp!=NULL)
{
pp=pp->next;
qyx++;
}
if(pos==1)//通过
{
S.tail->next=T.head;
T.head=S.head;
return;
}
else if(pos==qyx*8+1)//通过
{
T.tail->next=S.head;
T.tail=S.tail;
return;
}
else
{
int z=0;
chunk *aa;
aa=T.head;
while(aa!=NULL)
{
aa=aa->next;
z++;
}
if(pos<=8)//通过
{
chunk *wc1,*wc2;
wc1=new chunk;
wc2=new chunk;
chunk *wc11,*wc22;
wc11=wc1;
wc22=wc2;
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
wc1->ch[i]='#';
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
wc2->ch[i]='#';
int wyx=0;
int i;
for(i=0;i<pos-1;i++)
{
wc11->ch[i]=T.head->ch[i];
}
for(;i<=7;i++)
{
wc22->ch[wyx]=T.head->ch[i];
wyx++;
}
chunk *rnm;
rnm=T.head->next;
T.head=wc11;
wc11->next=S.head;
S.tail->next=wc22;
wc22->next=rnm;
}
else if(pos>=(z-1)*8+1&&pos<=z*8)//通过
{
int rr;
rr=pos%8;
if(rr==0)
{
rr=8;
}
if(pos==(z-1)*8+1)
{
chunk *op;
op=T.head;
while(op->next!=T.tail)
{
op=op->next;
}
op->next=S.head;
S.tail->next=T.tail;
return;
}
else
{
chunk *op;
op=T.head;
while(op->next!=T.tail)
{
op=op->next;
}
chunk *wc1,*wc2;
wc1=new chunk;
wc2=new chunk;
chunk *wc11,*wc22;
wc11=wc1;
wc22=wc2;
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
wc1->ch[i]='#';
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
wc2->ch[i]='#';
int wyx=0;
int i;
for(i=0;i<rr-1;i++)
{
wc11->ch[i]=T.tail->ch[i];
}
for(;i<=7;i++)
{
wc22->ch[wyx]=T.tail->ch[i];
wyx++;
}
op->next=wc11;
wc11->next=S.head;
S.tail->next=wc22;
T.tail=wc22;
T.tail->next=NULL;
return;
}
}
else
{
int rr;
rr=pos%8;
if(rr==0)
{
rr=8;
}
int ee=0;
chunk *w1,*w2;
w2=w1=T.head;
while(pos-8>ee)
{
ee+=8;
w2=w1;
w1=w1->next;
}
if(rr==1)//通过
{
w2->next=S.head;
S.tail->next=w1;
}
else
{
chunk *wc1,*wc2;
wc1=new chunk;
wc2=new chunk;
chunk *wc11,*wc22;
wc11=wc1;
wc22=wc2;
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
wc1->ch[i]='#';
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
wc2->ch[i]='#';
int wyx=0;
int i;
for(i=0;i<rr-1;i++)
{
wc11->ch[i]=w1->ch[i];
}
for(;i<=7;i++)
{
wc22->ch[wyx]=w1->ch[i];
wyx++;
}
chunk *opop;
opop=w1->next;
w2->next=wc11;
wc11->next=S.head;
S.tail->next=wc22;
wc22->next=opop;
return;
}
}
}
}
void zip(lstring T,char *map)
{
memset(map,'\0',sizeof(map));
chunk *oo;
oo=T.head;
int you=0;
while(oo!=NULL)
{
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
{
if(oo->ch[i]>='a'&&oo->ch[i]<='z')
{
map[you++]=oo->ch[i];
printf("%c",oo->ch[i]);
}
}
oo=oo->next;
}
}
int main()
{
char s[100]; lstring T1,T2,T3;
int len;
printf("\n请输入第一个长度不超过100个字符的字符串(不包含字符'#'):\n");
gets(s);
len=strlen(s);
if(len%8!=0)
{
len=(len/8+1)*8;
}
strassign(T1,s);
printf("\n第一次输入时形成的链表,表示如下:\n");
strprint(T1);
printf("\n请输入第二个长度不超过100个字符的字符串(不包含字符'#'):\n");
gets(s);
strassign(T2,s);
printf("\n第二次输入时形成的链表,表示如下:\n");
strprint(T2);
int k;
printf("\n请输入您需要插入的位置(在第几位之前插入取值范围在1~%d):",len+1);
scanf("%d",&k);
while(1)
{
if(k<1||k>len+1)
{
printf("插入错误,请重新输入插入位置\n");
scanf("%d",&k);
}
else
{
break;
}
}
strinsert(T1,k,T2);
strprint(T1);
getchar();
printf("\n输出压缩后的字符串:\n");
char map[200];
zip(T1,map);
strassign(T3,map);
printf("\n压缩形成的链表,表示如下:\n");
strprint(T3);
}