Spark读写和Lost Excutor错误的分析和解决过程
Spark读写和Lost Excutor错误的分析和解决过程
http://www.aboutyun.com/thread-15842-1-1.html
http://www.aboutyun.com/thread-15842-1-1.html
问题导读
1.大规模数据往HDFS中写时候,报了HDFS读写超时,本文是如何分析的?
2.大规模数据往HDFS中写时候,报了超时如何解决?
3.总结你遇到问题,是如何解决的?
![]()
一、概述
上篇blog记录了些在用spark-sql时遇到的一些问题,今天继续记录用Spark提供的RDD转化方法开发公司第一期标签分析系统(一部分scala作业逻辑代码后面blog再给大家分享)遇到的一些SPARK作业错误信息。其中有些问题可能一些数据量或者shuffle量比较小的作业时不会遇到的,我们整套标签系统的初级输入数据大概是8T左右,这里也是个参考。(下面的Spark部署模式为spark on yarn)
二、问题
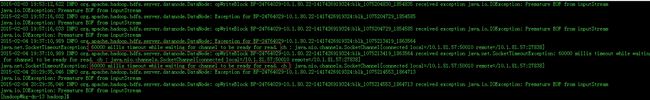
1、大规模数据往HDFS中写时候,报了HDFS读写超时,具体日志看下面。
(1)具体到某个Excutor的错误日志:
(2)具体到各个数据节点DataNode的日志:
分析:
从这两个错误信息首先可以将错误定位到整个HDFS的读写过程中,其中对于读写超时可以定位到2个参数:dfs.client.socket-timeout(默认60s)、dfs.datanode.socket.write.timeout(默认80s)。在spark的程序中按照自己的实际情况设置这两个值,问题可以解决。给个例子:
[Bash shell]
纯文本查看
复制代码
01 |
val dwd_new_pc_list_patch = "/user/hive/warehouse/pc.db/dwd_new_pc_list/2015-01-*/action=play" |
02 |
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("TagSystem_compositeTag") |
03 |
.set("spark.kryoserializer.buffer.max.mb", "128").set("spark.rdd.compress","true") |
04 |
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf) |
05 |
//hdfs客户端的读写超时时间 |
06 |
//默认60000 |
07 |
sc.hadoopConfiguration.set("dfs.client.socket-timeout", "180000") |
08 |
//默认80000 |
09 |
sc.hadoopConfiguration.set("dfs.datanode.socket.write.timeout", "180000") |
10 |
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc) |
11 |
val hiveSqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.hive.HiveContext(sc) |
12 |
|
13 |
//(user_id,fo,fo_2,sty,fs) |
14 |
val source = sc.textFile(dwd_new_pc_list_patch).filter(p => (p.trim != "" && p.split("\\|").length >= 105)).mapPartitions({ it => |
15 |
for { |
16 |
line <- it |
17 |
} yield (line.split("\\|")(21), line.split("\\|")(9), line.split("\\|")(104), line.split("\\|")(40), line.split("\\|")(7)) |
18 |
}).persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER) |
19 |
. |
20 |
. |
21 |
. |
另外相似问题: https://jira.spring.io/si/jira.i ... P-404/SHDP-404.html
2、由spark.reducer.maxMbInFlight引起的Lost Excutor问题。
这个错误主要是发生在shuffle中的fetch阶段,由于Excutor 已经lost掉了,由于容错机制另外重新启动一个Excutor,但是在之前lost掉的Excutor中保存的blockManager已经完全丢失,所以之前的stage需要重新计算。具体在dirver或者CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend的日志主要提示超时和读写文件失败,截了下超时的错误提示:
解决方法:
处理Lost Excutor问题还是花了比较长的时间,调整了很多参数都不行。最后将spark.reducer.maxMbInFlight调小或者将spark.shuffle.copier.threads调小问题解决。在家里还是详细的研究了下spark.reducer.maxMbInFlight这个参数的具体机制含义。spark.reducer.maxMbInFlight官方的配置文档的说明有些笼统:大概的意思是同事从reduce task中取出的ShuffleTask输出最大值(默认48MB)。这个从字面上理解还是不怎么容易的,从源码上search这个参数,定位到org.apache.spark.storage.BlockFetcherIterator.BasicBlockFetcherIterator#splitLocalRemoteBlocks
[Bash shell]
纯文本查看
复制代码
01 |
protected def splitLocalRemoteBlocks(): ArrayBuffer[FetchRequest] = { |
02 |
// Make remote requests at most maxBytesInFlight / 5 in length; the reason to keep them |
03 |
// smaller than maxBytesInFlight is to allow multiple, parallel fetches from up to 5 |
04 |
// nodes, rather than blocking on reading output from one node. |
05 |
//每个fetch线程获取的数据量大小(默认5个fetch线程) |
06 |
val targetRequestSize = math.max(maxBytesInFlight / 5, 1L) |
07 |
logInfo("maxBytesInFlight: " + maxBytesInFlight + ", targetRequestSize: " + targetRequestSize) |
08 |
09 |
// Split local and remote blocks. Remote blocks are further split into FetchRequests of size |
10 |
// at most maxBytesInFlight in order to limit the amount of data in flight. |
11 |
val remoteRequests = new ArrayBuffer[FetchRequest] |
12 |
var totalBlocks = 0 |
13 |
for ((address, blockInfos) <- blocksByAddress) { // address实际上是executor_id |
14 |
totalBlocks += blockInfos.size |
15 |
if (address == blockManagerId) { |
16 |
// Filter out zero-sized blocks |
17 |
localBlocksToFetch ++= blockInfos.filter(_._2 != 0).map(_._1) |
18 |
_numBlocksToFetch += localBlocksToFetch.size |
19 |
} else { |
20 |
val iterator = blockInfos.iterator |
21 |
var curRequestSize = 0L |
22 |
var curBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, Long)] |
23 |
while (iterator.hasNext) { |
24 |
// blockId 是org.apache.spark.storage.ShuffleBlockId, |
25 |
// 格式:"shuffle_" + shuffleId + "_" + mapId + "_" + reduceId |
26 |
val (blockId, size) = iterator.next() |
27 |
// Skip empty blocks |
28 |
if (size > 0) { |
29 |
curBlocks += ((blockId, size)) |
30 |
remoteBlocksToFetch += blockId |
31 |
_numBlocksToFetch += 1 |
32 |
curRequestSize += size |
33 |
} else if (size < 0) { |
34 |
throw new BlockException(blockId, "Negative block size " + size) |
35 |
} |
36 |
// 避免一次请求的数据量过大 |
37 |
if (curRequestSize >= targetRequestSize) { |
38 |
// Add this FetchRequest |
39 |
remoteRequests += new FetchRequest(address, curBlocks) |
40 |
curBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, Long)] |
41 |
logDebug(s"Creating fetch request of $curRequestSize at $address") |
42 |
curRequestSize = 0 |
43 |
} |
44 |
} |
45 |
// Add in the final request |
46 |
// 将剩余的请求放到最后一个request中。 |
47 |
if (!curBlocks.isEmpty) { |
48 |
remoteRequests += new FetchRequest(address, curBlocks) |
49 |
} |
50 |
} |
51 |
} |
52 |
logInfo("Getting " + _numBlocksToFetch + " non-empty blocks out of " + |
53 |
totalBlocks + " blocks") |
54 |
remoteRequests |
55 |
} |
从代码上看我的个人理解是在shuffle节点每个reduce task会启动5个fetch线程(可以由spark.shuffle.copier.threads配置)去最多spark.reducer.maxMbInFlight个(默认5)其他Excuctor中获取文件位置,然后去fetch它们,并且每次fetch的抓取量不会超过spark.reducer.maxMbInFlight(默认值为48MB)/5。这种机制我个人理解,第一:可以减少单个fetch连接的网络IO、第二:这种将fetch数据并行执行有助于抓取速度提高,减少请求数据的抓取时间总和。
回来结合我现在的问题分析,我将spark.reducer.maxMbInFlight调小,从而减少了每个reduce task中的每个fetch线程的抓取数据量,进而减少了每个fetch连接的持续连接时间,降低了由于reduce task过多导致每个Excutor中存在的fetch线程太多而导致的fetch超时,另外降低内存的占用。
上述分析为个人理解,如有更深入的想法欢迎交流。
出处 http://zengzhaozheng.blog.51cto.com/8219051/1615792