使用MinGW编译boost
一、Boost
Boost库是一个可移植、提供源代码的C++库,作为标准库的后备,是C++标准化进程的发动机之一。其官方网站为http://www.boost.org/,目前最新版本为1.46.0,以下以此版本为准。
Boost库大部分的子库都是C++模版提供,大部分情况下直接包含头文件就可以了。其中部分子库需要编译,如下图所示:
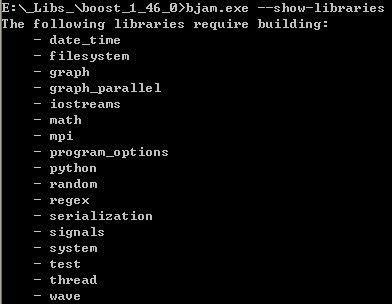
上图中bjam.exe是boost提供的编译工具,下面会介绍如何获得。
二、Mingw: Minimalist GNU for Windows
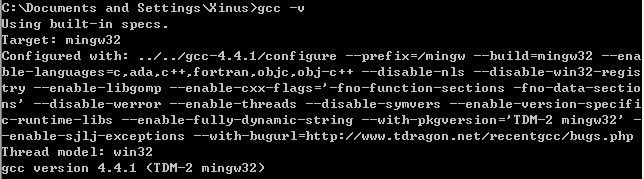
官方网站: http://www.mingw.org/ 部分同学可能和我一样,使用自带Mingw环境的IDE,比如Code::Blocks,其官方网站: http://www.codeblocks.org/。请确保Mingw工具链目录添加到系统的环境变量PATH中,比如我路径为:"D:\Program Files\CodeBlocks\MinGW\bin",并将这个目录下的mingw32-make.exe复制并重命名为make.exe。然后验证gcc等能否正常使用:开始->运行->输入"cmd"回车->命令窗口输出"gcc -v"查看gcc版本信息,如果看到如下类似输出,那么就可以继续正是编译Boost了。
三、bjam.exe
bjam是boost自带的工具,用来方便地编译boost,当然也可以用来编译你自己的工程。bjam在boost源码中一起提供,需要编译才能使用,下载boost的时候会提示下载一个编译好的bjam,我不是很推荐,因为我用下载来的bjam编译boost的时候,出现一些错误,而用自己编译的bjam却顺利完成。
在"E:\_Libs_\boost_1_46_0\tools\build\v2\engine\src"下,使用命令"build mingw",会在此目录下生成文件bin.ntx86\bjam.exe,将bjam.exe拷贝到boost源文件的根目录下,如"E:\_Libs_\boost_1_46_0\"。在这个目录下的"./Jamroot"文件,详细描述了bjam的用法,建议用文本打开这个文件并阅读前面部分的注释,摘抄如下:
# Usage:
#
# bjam [options] [properties] [install|stage]
#
# Builds and installs Boost.
#
# Targets and Related Options:
#
# install Install headers and compiled library files to the
# ======= configured locations (below).
#
# --prefix=<PREFIX> Install architecture independent files here.
# Default; C:\Boost on Win32
# Default; /usr/local on Unix. Linux, etc.
#
# --exec-prefix=<EPREFIX> Install architecture dependent files here.
# Default; <PREFIX>
#
# --libdir=<DIR> Install library files here.
# Default; <EPREFIX>/lib
#
# --includedir=<HDRDIR> Install header files here.
# Default; <PREFIX>/include
#
# stage Build and install only compiled library files
# ===== to the stage directory.
#
# --stagedir=<STAGEDIR> Install library files here
# Default; ./stage
#
# Other Options:
#
# --build-type=<type> Build the specified pre-defined set of variations
# of the libraries. Note, that which variants get
# built depends on what each library supports.
#
# minimal (default) - Builds a minimal set of
# variants. On Windows, these are static
# multithreaded libraries in debug and release
# modes, using shared runtime. On Linux, these
# are static and shared multithreaded libraries
# in release mode.
#
# complete - Build all possible variations.
#
# --build-dir=DIR Build in this location instead of building
# within the distribution tree. Recommended!
#
# --show-libraries Displays the list of Boost libraries that require
# build and installation steps, then exit.
#
# --layout=<layout> Determines whether to choose library names
# and header locations such that multiple
# versions of Boost or multiple compilers can
# be used on the same system.
#
# versioned - Names of boost binaries
# include the Boost version number, name and
# version of the compiler and encoded build
# properties. Boost headers are installed in a
# subdirectory of <HDRDIR> whose name contains
# the Boost version number.
#
# tagged -- Names of boost binaries include the
# encoded build properties such as variant and
# threading, but do not including compiler name
# and version, or Boost version. This option is
# useful if you build several variants of Boost,
# using the same compiler.
#
# system - Binaries names do not include the
# Boost version number or the name and version
# number of the compiler. Boost headers are
# installed directly into <HDRDIR>. This option
# is intended for system integrators who are
# building distribution packages.
#
# The default value is 'versioned' on Windows, and
# 'system' on Unix.
#
# --buildid=ID Adds the specified ID to the name of built
# libraries. The default is to not add anything.
#
# --python-buildid=ID Adds the specified ID to the name of built
# libraries that depend on Python. The default
# is to not add anything. This ID is added in
# addition t --buildid.
#
#
# --help This message.
#
# --with-<library> Build and install the specified <library>
# If this option is used, only libraries
# specified using this option will be built.
#
# --without-<library> Do not build, stage, or install the specified
# <library>. By default, all libraries are built.
#
# Properties:
#
# toolset=toolset Indicates the toolset to build with.
#
# variant=debug|release Select the build variant
#
# link=static|shared Whether to build static or shared libraries
#
# threading=single|multi Whether to build single or multithreaded binaries
#
# runtime-link=static|shared
# Whether to link to static or shared C and C++ runtime.
#
四、分享
bjam --build-type=complete toolset=gcc stage
上面的命令将编译所有需要编译的子库(除python)的各种版本,编译时间稍长,约40分钟~1小时。生成的文件在./stage/lib目录下。 不同版本可以通过名称来区别,例如date_time库一共生成有16个相关文件:
libboost_date_time-mgw44-1_46.a
libboost_date_time-mgw44-1_46.dll
libboost_date_time-mgw44-1_46.dll.a
libboost_date_time-mgw44-d-1_46.a
libboost_date_time-mgw44-d-1_46.dll
libboost_date_time-mgw44-d-1_46.dll.a
libboost_date_time-mgw44-mt-1_46.a
libboost_date_time-mgw44-mt-1_46.dll
libboost_date_time-mgw44-mt-1_46.dll.a
libboost_date_time-mgw44-mt-d-1_46.a
libboost_date_time-mgw44-mt-d-1_46.dll
libboost_date_time-mgw44-mt-d-1_46.dll.a
libboost_date_time-mgw44-mt-s-1_46.a
libboost_date_time-mgw44-mt-sd-1_46.a
libboost_date_time-mgw44-s-1_46.a
libboost_date_time-mgw44-sd-1_46.a
如上,mgw44代表编译器Mingw4.4版本:
mt: threading=multi
s: runtime-link=static
d: variant=debug
.dll: link=shared
.dll.a: 对应DLL的导入库文件