【Android学习笔记】XmlResourceParser解析xml文件
最近学习Android时,需要用到解析XML文件里的数据,可以用XmlResourceParser来解析xml文件,正好将此记录下来。
XmlResourceParser里常用的字段和方法
首先先给出源码里面一些比较基础的,常用的方法和字段。
常用的字段
int START_DOCUMENT = 0;
int END_DOCUMENT = 1;
int START_TAG = 2;
int END_TAG = 3;
int TEXT = 4; getEventType()
/**
* Returns the type of the current event (START_TAG, END_TAG, TEXT, etc.)
* 大意就是返回当前的事件类型(返回的字段都是xml文件中某些特定位置,比如标签开始标志,标签结束标志,文档结束标志等)
*
*/
int getEventType();getName()
/**
* For START_TAG or END_TAG events, the (local) name of the current
* element is returned when namespaces are enabled. When namespace
* processing is disabled, the raw name is returned.
* 大意就是对于 START_TAG,END_TAG,这两种事件,有无使用命名空间情况下返回的标签名。至于命名空间的详情,可以去参考xml的具体介绍(囧:我也不懂)
*
*/
String getName();
getText()
/**
* Returns the text content of the current event as String.
* 返回text内容
*
*/
String getText();
getAttributeName(int index)
/**
* Returns the local name of the specified attribute
* if namespaces are enabled or just attribute name if namespaces are disabled.
* 大意就是返回指定位置的属性名,位置从0开始
*
* @param index zero-based index of attribute
* @return attribute name (null is never returned)
*/
String getAttributeName(int index);getAttributeValue(int index)
/**
* Returns the given attributes value.
* 大意就是返回指定位置的属性值,位置从0开始
*
* @param index zero-based index of attribute
* @return value of attribute (null is never returned)
*/
String getAttributeValue(int index);getAttributeValue(String namespace,String name)
/**
* Returns the attributes value identified by namespace URI and namespace localName.
* If namespaces are disabled namespace must be null.
* 大意就是返回指定的属性名对应的属性值,如果没有使用命名空间,则第一个参数传入null
*
* @param namespace Namespace of the attribute if namespaces are enabled otherwise must be null
* @param name If namespaces enabled local name of attribute otherwise just attribute name
* @return value of attribute or null if attribute with given name does not exist
*/
String getAttributeValue(String namespace,String name);next()
/**
* Get next parsing event - element content will be coalesced and only one
* TEXT event must be returned for whole element content
* 大意就是获取下一个要解析的事件,通俗点说就是类似于将光标往下移
*/
int next() 对于一些基础的操作,上述提供的信息就够用了。至于每个字段,方法都是干嘛用的,其实也就是字面上的意思。下面先上一张图:
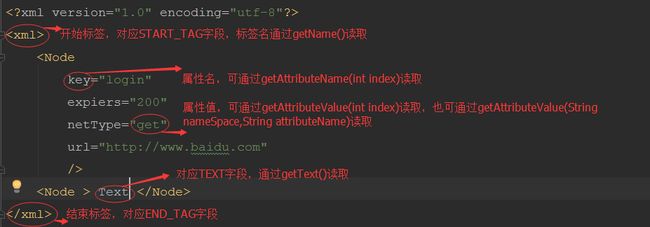
XmlResourceParser具体如何解析xml不清楚,但解析过程有点类似于sqlite cursor遍历。首先都是初始定位在文档开始处,通过调用 next() 来将光标往下移,通过 getEventType() 来获取当前光标停留在哪里,然后再通过对应的 get××××() 方法来获取我们想要的数据。
实例
首先在res/目录下建一个xml文件夹,然后新建一个xml文件命名为xml.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<xml>
<Node att1="hello" att2="world"/>
HelloWorld!
</xml> 然后是java代码,布局文件就一个按钮控件:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
private Button btn1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btn1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn1);
btn1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
logXmlData();
}
});
}
public void logXmlData() {
XmlResourceParser xmlParser = getResources().getXml(R.xml.xml);
try {
int event = xmlParser.getEventType(); //先获取当前解析器光标在哪
while (event != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT){ //如果还没到文档的结束标志,那么就继续往下处理
switch (event){
case XmlPullParser.START_DOCUMENT:
Log.i(TAG,"xml解析开始");
break;
case XmlPullParser.START_TAG:
//一般都是获取标签的属性值,所以在这里数据你需要的数据
Log.d(TAG,"当前标签是:"+xmlParser.getName());
if (xmlParser.getName().equals("Node")){
//两种方法获取属性值
Log.d(TAG,"第一个属性:" + xmlParser.getAttributeName(0)
+ ": " + xmlParser.getAttributeValue(0));
Log.d(TAG,"第二个属性:" + xmlParser.getAttributeName(1)+": "
+ xmlParser.getAttributeValue(null,"att2"));
}
break;
case XmlPullParser.TEXT:
Log.d(TAG,"Text:" + xmlParser.getText());
break;
case XmlPullParser.END_TAG:
break;
default:
break;
}
event = xmlParser.next(); //将当前解析器光标往下一步移
}
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} 