线程的创建,等待与终止
一.线程的创建
基础知识
线程,有时被称为轻量级进程(Lightweight Process,LWP),是程序执行流的最小单元。一个标准的线程由线程ID,当前指令指针(PC),寄存器集合和堆栈组成。
线程是进程中的一个实体,是被系统独立调度和分派的基本单位,线程自己不拥有系统资源,只拥有一点儿在运行中必不可少的资源,但它可与同属一个进程的其它线程共享进程所拥有的全部资源。
一个线程可以创建和撤消另一个线程,同一进程中的多个线程之间可以并发执行。由于线程之间的相互制约,致使线程在运行中呈现出间断性。
线程也有就绪、阻塞和运行三种基本状态。就绪状态是指线程具备运行的所有条件,逻辑上可以运行,在等待处理机;运行状态是指线程占有处理机正在运行;阻塞状态是指线程在等待一个事件(如某个信号量),逻辑上不可执行。每一个程序都至少有一个线程,若程序只有一个线程,那就是程序本身。
在单个程序中同时运行多个线程完成不同的工作,称为多线程。
2. 相关函数
3. 代码实现
//create.c
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<pthread.h>
4
5 pthread_t tid;
6 void* thread_run(void* val)
7 {
8 printf("%s:pid is :%d,tid is:%u\n", (char*)val,(int)getpid(),(unsigned long long)pthread_self());
9 }
10 int main()
11 {
12 int err=pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_run,"other thread run");
13 if(err!=0)
14 {
15 printf("create thread error! info is:%s\n",strerror(err));
16 exit(err);
17 }
18 printf("main thread run:pid is:%d,tid is:%u\n",(int)getpid(),(unsigned long long)pthread_self());
19 sleep(5);
20 return 0;
21 }
//makefile
1 create:create.c
2 gcc -o $@ $^ -lpthread
3 .PHONY:clean
4 clean:
5 rm -f create
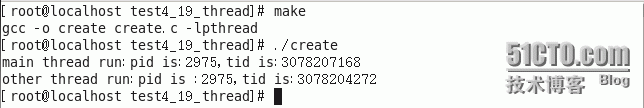
输出结果:
结果分析:
1.属于同一进程的不同线程可通过getpid()和pthread_self()得到相同的pid与不同的tid。
2.pthread_create()的错误码没有保存在error中,所以不能通过perror()得到,可通strerror()把错误码转换成错误信息再打印。
3.任意一个线程调用了exit()或_exit(),该进程所有线程将结束。从main()函数中return相当于调用了exit。
4.为了防止新创建的线程还没有执行就终止,在main函数return前sleep了1秒,但不是很好的办法,因为1秒内,不一定会调用新线程。下面在终止线程上进行优化。
二.线程的终止
基础知识
只终止某个线程而不终止整个进程,可以有三种方法:
1. 从线程函数return。这种方法对主线程不适用,从main函数return相当于调用exit。
2. 一个线程可以调用pthread_cancel终止同一进程中的另一个线程。
3. 线程可以调用pthread_exit终止自己。
注意:pthread_exit或者return返回的指针所指向的内存单元必须是全局的或者是用malloc分配的,不能在线程函数的栈上分配,因为当其它线程得到这个返回指针时线程函数已经退出了。
2.函数
pthread_cancel
三.线程等待
函数
调用该函数的线程将挂起等待,直到id为thread的线程终止。
基础知识:
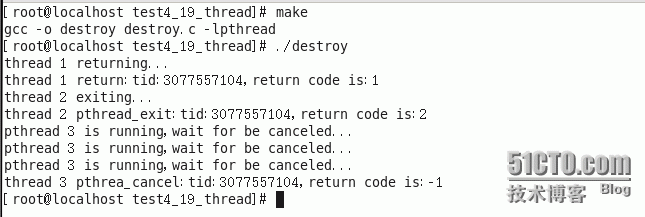
thread线程以不同的方法终止,通过pthread_join得到的终止状态是不同的,总结如下:
1. 如果thread线程通过return返回,value_ptr所指向的单元存放的是thread线程函数的返回值。
2. 如果thread线程被别的线程调用pthread_cancel异常终掉,value_ptr所指向的单元里存放的是常数PTHREAD_CANCELED。
3. 如果thread线程是自己调用pthread_exit终止的,value_ptr所指向的单元存放的是传给pthread_exit的参数。 如果对thread线程的终止状态不感兴趣,可以传NULL给value_ptr
2.代码实现:
//destory.c
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<pthread.h>
4
5 void* thread1(void* val)
6 {
7 printf("thread 1 returning...\n");
8 return (void*)1;
9 }
10 void* thread2(void* val)
11 {
12 printf("thread 2 exiting...\n");
13 pthread_exit((void*)2);
14 }
15 void* thread3(void* val)
16 {
17 while(1)
18 {
19 printf("pthread 3 is running,wait for be canceled...\n");
20 sleep(1);
21 }
22 return NULL;
23 }
24 int main()
25 {
26 pthread_t tid;
27 void* tret;
28
29 //thread 1
30 pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread1,NULL);
31 pthread_join(tid,&tret);
32 printf("thread 1 return:tid:%u,return code is:%d\n",(unsigned long)tid,tret);
33
34 //thread 2
35 pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread2,NULL);
36 pthread_join(tid,&tret);
37 printf("thread 2 pthread_exit:tid:%u,return code is:%d\n",(unsigned long)tid,tret);
38
39 //thread 3
40 pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread3,NULL);
41 sleep(3);
42 pthread_cancel(tid);
43 pthread_join(tid,&tret);
44 printf("thread 3 pthrea_cancel:tid:%u,return code is:%d\n",(unsigned long)tid,tret);
45
46 return 0;
47 }
//makefile
1 destroy:destroy.c
2 gcc -o $@ $^ -lpthread
3 .PHONY:clean
4 clean:
5 rm -f destroy
输出结果: