httpd的常用配置
(1)安装httpd:
[root@localhost named]# yum install -y httpd
(2)配置文件:
主配置文件:/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
### Section 1: Global Environment全局配置
### Section 2: 'Main' server configuration主服务配置
### Section 3: Virtual Hosts虚拟主机配置
辅助配置文件:/etc/httpd/conf.d/*.conf,注意是以.conf结尾的文件
(3)配置格式:
指令 值
指令是不区分字符大小写的
但是值为路径时,是否区分大小写,取决于文件系统
(4)常用的配置
A:修改监听的ip与端口
Listern [IP]:port
省略ip表示ip为0.0.0.0;
Listern指令可重复出现多次
修改端口后,只有重启服务才能生效
B:持久连接:
Connection:tcp连续建立后,每个资源获取完成后不全断开连接,而是继续等待其它资源请求的进行;
如何断开连接?
可以通过数量的限制以及时间的限制断开,但是这样存在一定的副作用,对并发访问量较大的服务器,长连接机制会使得后续某些请求无法得到正常的响应;比较折衷的办法就是使用较短的持久连接时长,以及较少的请求数量;
KeepAlive On|Off KeepAliveTimeout 15 MaxKeepAliveRequests 100
3、MPM
httpd-2.2不支持同时编译多个MPM模块,所以只能编译选定要使用的那个;CentOS 6的rpm包为此专门提供了三个应用程序文件,httpd(prefork), httpd.worker, httpd.event,分别用于实现对不同的MPM机制的支持;确认现在使用的是哪下程序文件的方法:
[root@server modules]# ps aux | grep httpd root 2627 0.0 0.1 103160 832 pts/1 S+ 16:00 0:00 grep httpd
默认使用的为/usr/sbin/httpd,其为prefork的MPM模块 ;
查看httpd程序的模块列表:
查看静态编译的模块:
[root@server modules]# httpd -l Compiled in modules: core.c prefork.c http_core.c mod_so.c
查看静态编译及动态编译的模块:
[root@server modules]# httpd -M httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using ::1 for ServerName Loaded Modules: core_module (static) mpm_prefork_module (static) http_module (static) so_module (static) auth_basic_module (shared) auth_digest_module (shared) authn_file_module (shared) authn_alias_module (shared) authn_anon_module (shared) authn_dbm_module (shared) authn_default_module (shared) authz_host_module (shared) authz_user_module (shared) authz_owner_module (shared) authz_groupfile_module (shared) authz_dbm_module (shared) ......
更换使用httpd程序,以支持其它MPM机制;
/etc/sysconfig/httpd
HTTPD=/usr/sbin/httpd.{worker,event}
[root@server httpd]# vim /etc/sysconfig/httpd # Configuration file for the httpd service. # # The default processing model (MPM) is the process-based # 'prefork' model. A thread-based model, 'worker', is also # available, but does not work with some modules (such as PHP). # The service must be stopped before changing this variable. # #HTTPD=/usr/sbin/httpd.worker # # To pass additional options (for instance, -D definitions) to the # httpd binary at startup, set OPTIONS here. # #OPTIONS= # # By default, the httpd process is started in the C locale; to # change the locale in which the server runs, the HTTPD_LANG # variable can be set. # #HTTPD_LANG=C # # By default, the httpd process will create the file # /var/run/httpd/httpd.pid in which it records its process # identification number when it starts. If an alternate location is # specified in httpd.conf (via the PidFile directive), the new # location needs to be reported in the PIDFILE. # #PIDFILE=/var/run/httpd/httpd.pid
注意:重启服务进程方可生效
MPM配置:/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
prefork的配置
<IfModule prefork.c> StartServers 8 #开始启动的服务器进程的初始数量 MinSpareServers 5 #至少保持备用的服务器进程数 MaxSpareServers 20 #其中保存备用服务器的最大进程数 ServerLimit 256 #限制服务器生命周期连接客户端的最大数 MaxClients 256 #允许连接的最大服务进程数 MaxRequestsPerChild 4000 #服务器进程请求的最大数目 </IfModule>
worker的配置:
<IfModule worker.c> StartServers 4 MaxClients 300 MinSpareThreads 25 MaxSpareThreads 75 ThreadsPerChild 25 MaxRequestsPerChild 0 </IfModule>
PV,UV
PV:Page View
UV: User View
4、DSO(动态共享对象)
配置指定实现模块加载
LoadModule <mod_name> <mod_path>
# Configuration and logfile names: If the filenames you specify for many # of the server's control files begin with "/" (or "drive:/" for Win32), the # server will use that explicit path. If the filenames do *not* begin # with "/", the value of ServerRoot is prepended -- so "logs/foo.log" # with ServerRoot set to "/etc/httpd" will be interpreted by the # server as "/etc/httpd/logs/foo.log". #上面表明相对路径在/etc/httpd # Example: # LoadModule foo_module modules/mod_foo.so #模块的路径是相对路径,完整的应该是/etc/httpd/moudules/*.so LoadModule auth_basic_module modules/mod_auth_basic.so LoadModule auth_digest_module modules/mod_auth_digest.so LoadModule authn_file_module modules/mod_authn_file.so
[root@server modules]# pwd /etc/httpd/modules [root@server modules]# ls mod_actions.so mod_authz_user.so mod_filter.so mod_proxy_scgi.so mod_alias.so mod_autoindex.so mod_headers.so mod_proxy.so mod_asis.so mod_cache.so mod_ident.so mod_reqtimeout.so
5、定义'Main' server的文档页面路径
DocumentRoot ""
文档路径映射:
DoucmentRoot指向的路径为URL路径的起始位置
其相当于站点URL的根路径;
(FileSystem) /web/host1/index.html --> (URL) /index.html
# DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your # documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but # symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations. #DocumentRoot标明了文件的其实位置,当然也可以使用符号链接或者别名指向其他的位置 DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"
6、站点访问控制常见机制
可基于两种机制指明对哪些资源进行何种访问控制
文件系统路径:
<Directory "">
...
</Directory>
<File "">
...
</File>
<FileMatch "PATTERN">
...
</FileMatch>
URL路径:
<Location "">
...
</Location>
<LocationMatch "">
...
</LocationMatch>
<Directory>中“基于源地址”实现访问控制:
(1) Options
后跟1个或多个以空白字符分隔的“选项”列表;
Indexes:指明的URL路径下不存在与定义的主页面资源相符的资源文件时,返回索引列表给用户;
FollowSymLinks:允许跟踪符号链接文件所指向的源文件;
None:
All:
(2) AllowOverride
与访问控制相关的哪些指令可以放在.htaccess文件(每个目录下都可以有一个)中;
All:
None:
(3) order和allow、deny
order:定义生效次序;写在后面的表示默认法则;
Allow from, Deny from
来源地址:
IP
NetAdd
172.16
172.16.0.0
172.16.0.0/16
172.16.0.0/255.255.0.0
7、定义站点主页面:
DirectoryIndex index.html index.html.var
8、定义路径别名
格式:
Alias /URL/ "/PATH/TO/SOMEDIR/"
DocumentRoot "/www/htdocs"
http://www.magedu.com/download/bash-4.4.2-3.el6.x86_64.rpm
/www/htdocs/download/bash-4.4.2-3.el6.x86_64.rpm
Alias /download/ "/rpms/pub/"
http://www.magedu.com/download/bash-4.4.2-3.el6.x86_64.rpm
/rpms/pub/bash-4.4.2-3.el6.x86_64.rpm
http://www.magedu.com/images/logo.png
/www/htdocs/images/logo.png
9、设定默认字符集
AddDefaultCharset UTF-8
中文字符集:GBK, GB2312, GB18030
10、日志设定
日志类型:访问日志 和 错误日志
错误日志:
ErrorLog logs/error_log #错误日志存放的位置 LogLevel warn #日志的级别 Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit, alert, emerg. #可能存在"调式,信息,通知,警告,错误..."
访问日志:
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
CustomLog logs/access_log combined
LogFormat format strings:
http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/mod_log_config.html#formats
%h:客户端IP地址;
%l:Remote User, 通常为一个减号(“-”);
%u:Remote user (from auth; may be bogus if return status (%s) is 401);非为登录访问时,其为一个减号;
%t:服务器收到请求时的时间;
%r:First line of request,即表示请求报文的首行;记录了此次请求的“方法”,“URL”以及协议版本;
%>s:响应状态码;
%b:响应报文的大小,单位是字节;不包括响应报文的http首部;
%{Referer}i:请求报文中首部“referer”的值;即从哪个页面中的超链接跳转至当前页面的;
%{User-Agent}i:请求报文中首部“User-Agent”的值;即发出请求的应用程序;
11、基于用户的访问控制
认证质询:
WWW-Authenticate:响应码为401,拒绝客户端请求,并说明要求客户端提供账号和密码;
认证:
Authorization:客户端用户填入账号和密码后再次发送请求报文;认证通过时,则服务器发送响应的资源;
认证方式有两种:
basic:明文
digest:消息摘要认证
安全域:需要用户认证后方能访问的路径;应该通过名称对其进行标识,以便于告知用户认证的原因;
用户的账号和密码存放于何处?
虚拟账号:仅用于访问某服务时用到的认证标识
存储:
文本文件;
SQL数据库;
ldap目录存储;
basic认证配置示例:
基于用户的普通认证:
(1) 定义安全域
<Directory ""> Options None AllowOverride None AuthType Basic AuthName "String“ AuthUserFile "/PATH/TO/HTTPD_USER_PASSWD_FILE" Require user username1 username2 ... </Directory>
允许账号文件中的所有用户登录访问:
Require valid-user
(2) 提供账号和密码存储(文本文件)
使用专用命令完成此类文件的创建及用户管理
htpasswd [options] /PATH/TO/HTTPD_PASSWD_FILE username
-c:自动创建此处指定的文件,因此,仅应该在此文件不存在时使用;
-m:md5格式加密
-s: sha格式加密
-D:删除指定用户
[root@server htpasswd]# htpasswd -c -m ./userpasswd yi New password: Re-type new password: Adding password for user yi [root@server htpasswd]# clear [root@server htpasswd]# htpasswd -m ./userpasswd er #注意已经存在的密码文件不需要-c New password: Re-type new password: Updating password for user er [root@server htpasswd]# cat userpasswd yi:$apr1$lB/ZcOqc$6Ax4ktgU7u9YF4kmT4sWv/ er:$apr1$EpvoKEs3$.k//SodNKtfwSPBJgjvKy0
完成基于用户的认证:
(1)在/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf文件中注释
#DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"
(2)在/www/html文件中创建一个index.html网页
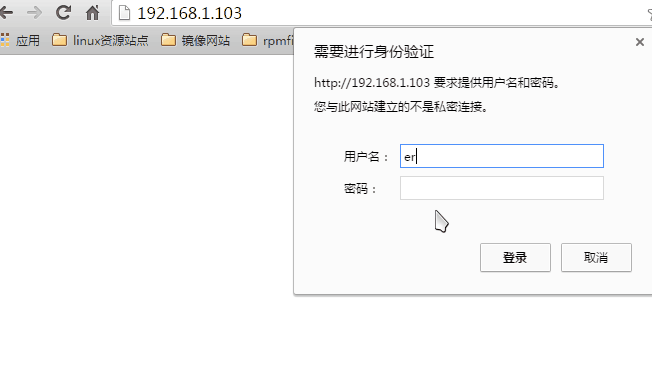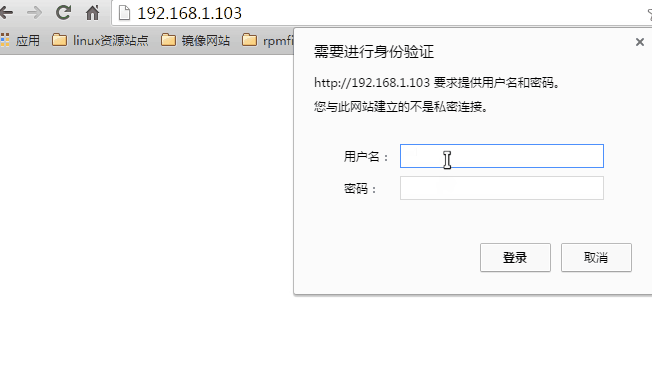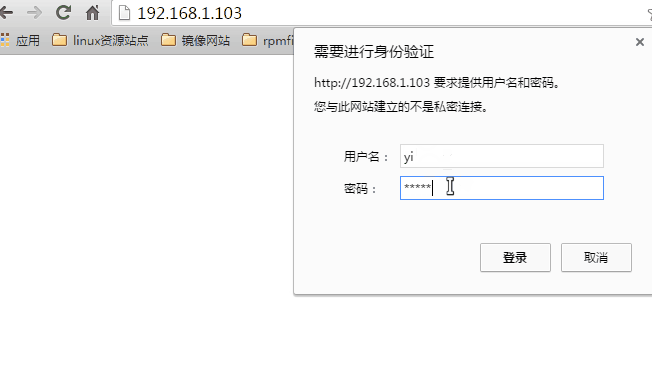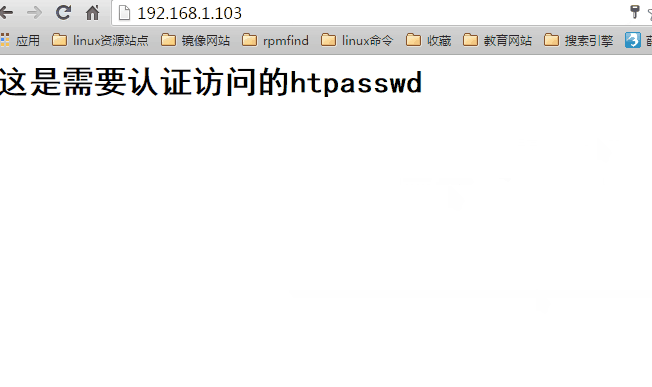
[root@server conf.d]# cat /www/html/index.html <h1>这是需要认证访问的htpasswd<h1>
(3)在httpd辅助配置目录/etc/httpd/conf.d/中新建一个配置文件vhost.conf
[root@server conf.d]# ls mod_dnssd.conf README vhost.conf welcome.conf [root@server conf.d]# cat vhost.conf DocumentRoot "/www/html" <Directory "/www/html"> Options None AllowOverride None AuthType Basic #明文认证 AuthName "String“ #认证时显示的字符串 AuthUserFile "/htpasswd/userpasswd" #认证文件的路径 Require user yi er #注意这两个用户是上面我们完成的 </Directory>
(3)访问
另外:基于组账号进行认证;
(1) 定义安全域
<Directory ""> Options None AllowOverride None AuthType Basic AuthName "String“ AuthUserFile "/PATH/TO/HTTPD_USER_PASSWD_FILE" AuthGroupFile "/PATH/TO/HTTPD_GROUP_FILE" Require group grpname1 grpname2 ... </Directory>
(2) 创建用户账号和组账号文件;
组文件:每一行定义一个组
GRP_NAME: username1 username2 ...
[root@server htpasswd]# vim group [root@server htpasswd]# pwd /htpasswd [root@server htpasswd]# cat group group1:yi group2:er #常见用户组 DocumentRoot "/www/html" <Directory "/www/html"> Options None AllowOverride None AuthType Basic AuthName "String“ AuthUserFile "/htpasswd/userpasswd" AuthGroupFile "/htpasswd/group" #指定组文件 Require group group1 #允许group1有权限 </Directory> [root@server htpasswd]# httpd -t #测试配置语句的语法是否有问题 httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using ::1 for ServerName Syntax OK [root@server htpasswd]# !ser #重新加载配置文件 service httpd reload 重新载入 httpd: [root@server htpasswd]#
结果:
12、虚拟主机
站点标识: socket
IP相同,但端口不同;
IP不同,但端口均为默认端口;
FQDN不同;
请求报文中首部
Host: www.linuxedu.com
有三种实现方案:
基于ip:
为每个虚拟主机准备至少一个ip地址;
基于port:
为每个虚拟主机使用至少一个独立的port;
基于FQDN:
为每个虚拟主机使用至少一个FQDN;
注意:一般虚拟机不要与中心主机混用;因此,要使用虚拟主机,得先禁用'main'主机;
禁用方法:注释中心主机的DocumentRoot指令即可;
虚拟主机的配置方法:
<VirtualHost IP:PORT> ServerName FQDN DocumentRoot "" </VirtualHost>
其它可用指令:
ServerAlias:虚拟主机的别名;可多次使用; ErrorLog: CustomLog: <Directory ""> ... </Directory> Alias ...
基于IP的虚拟主机示例:(新建几个虚拟网卡)
<VirtualHost 172.16.100.6:80> ServerName www.a.com DocumentRoot "/www/a.com/htdocs" </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost 172.16.100.7:80> ServerName www.b.net DocumentRoot "/www/b.net/htdocs" </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost 172.16.100.8:80> ServerName www.c.org DocumentRoot "/www/c.org/htdocs" </VirtualHost>
基于端口的虚拟主机:
<VirtualHost 172.16.100.6:80> ServerName www.a.com DocumentRoot "/www/a.com/htdocs" </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost 172.16.100.6:808> ServerName www.b.net DocumentRoot "/www/b.net/htdocs" </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost 172.16.100.6:8080> ServerName www.c.org DocumentRoot "/www/c.org/htdocs" </VirtualHost>
基于FQDN的虚拟主机:
NameVirtualHost 172.16.100.6:80 <VirtualHost 172.16.100.6:80> ServerName www.a.com DocumentRoot "/www/a.com/htdocs" </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost 172.16.100.6:80> ServerName www.b.net DocumentRoot "/www/b.net/htdocs" </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost 172.16.100.6:80> ServerName www.c.org DocumentRoot "/www/c.org/htdocs" </VirtualHost>
13、status页面
LoadModule status_module modules/mod_status.so <Location /server-status> SetHandler server-status Order allow,deny Allow from 172.16 </Location>