tableView继续优化。
提高表视图的性能
UITableView作为应用中最常用的视图,它的性能优化问题几乎是经常提及。下面对在非网络访问情况下的表视图性能优化进行了主要的几点说明:
1.自定义类或XIB文件时
在系统提供的样式不能满足我们的时候,我们经常会创建自定义类或者XIB文件来自定义单元格样式。
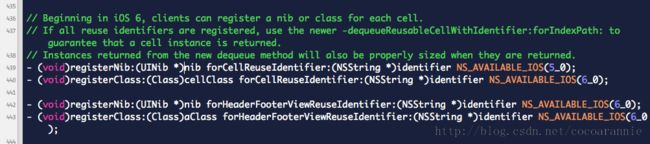
在之前,我们通常通过loadNib的方式或者在代理方法中继续使用老的方法来设置重用,管理缓存池。在IOS6以后,我们可以通过注册的方式在注册单元格甚至表头视图,让系统来更高效的进行管理。
2.InterfaceBuilder
据说有很多偏执的工程狮们坚持手打代码来完成工程,讨厌拖拖拽拽。不过随着IB的不断强大,已经有越来越多的人喜欢上了使用IB来建立和管理界面。在新的Xcode5中,IB又进步了不少。回到正题,尽管如此,在使用高性能的Cell时,还是推荐使用代码来创建单元格类。当UITableViewCell拥有多个子视图时,IOS的渲染机制会拖慢速度。重写drawRect直接绘制内容的方式可以提高性能,而不是在类初始化的时候初始化一些label或者imageview等。
3.图层颜色问题
透明图层对渲染性能会有一定的影响,系统必须将透明图层与下面的视图混合起来计算颜色,并绘制出来。减少透明图层并使用不透明的图层来替代它们,可以极大地提高渲染速度。
4.渲染中注意的问题
绘制时要尽可能的避免分配资源,比如UIFont,NSDateFormatter或者任何在绘制时需要的对象,推荐使用类层级的初始化方法中执行分配,并将其存储为静态变量。
5.为代理方法瘦身
我们经常能看到在项目中,
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
这个方法中的代码多的吓人,我们可以讲一些数据绑定到cell中,或者在有多个tableview的时候,将其绑定到其他的tableviewcontroller中去。这样可以方便维护和管理,其实也对程序运行性能有很大的帮助。
手工绘制单元格
下面就绘制一个表视图单元格,并在表视图中显示。
初始化数据
- (void)loadAnimals
{
_animalList = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:rAnimalCount];
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < rAnimalCount; i++)
{
Animal *animal = [[Animal alloc] init];
NSString *name = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Animal-%03d", i+1];
NSString *detail = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"dog or cat?"];
NSInteger seed = arc4random()%8 + 1;
NSString *imageName = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"head%02d", seed+1];
animal.name = name;
animal.detail = detail;
animal.imageName = imageName;
[_animalList addObject:animal];
}
}
重点在于绘制,我首先创建了一个继承自UITableViewCell的父类一会让我们的单元格继承它,父类中有一个UIView类型的contentView成员,所有的绘制将在这个成员上进行。
@interface HRCellView : UIView
@end
@implementation HRCellView
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect
{
[(HRCell *)[self superview] drawContentView:rect];
}
@end
@implementation HRCell
- (id)initWithStyle:(UITableViewCellStyle)style reuseIdentifier:(NSString *)reuseIdentifier
{
self = [super initWithStyle:style reuseIdentifier:reuseIdentifier];
if (self) {
contentView = [[HRCellView alloc] init];
contentView.opaque = YES; //不透明,提升渲染性能
[self addSubview:contentView];
}
return self;
}
- (void)setFrame:(CGRect)frame
{
[super setFrame:frame];
CGRect b = [self bounds];
b.size.height -= 1; // 给分割线留出位置
contentView.frame = b;
}
- (void)setNeedsDisplay
{
[super setNeedsDisplay];
[contentView setNeedsDisplay];
}
- (void)drawContentView:(CGRect)rect
{
//子类实现
}
@end
下面是绘制单元格
在初始化类方法中初始化字体资源
static UIFont *NameFont;
static UIFont *DetailFont;
@implementation HRCustomCell
+ (void)initialize
{
NameFont = [UIFont fontWithName:@"American Typewriter" size:rNameFontSize];
DetailFont = [UIFont fontWithName:@"American Typewriter" size:rDetailFontSize];
}
将数据绑定到这个单元格中
- (void)bindAnimal:(Animal *)animal
{
if (_nameText != animal.name)
{
_nameText = animal.name;
}
if (_detailText != animal.detail)
{
_detailText = animal.detail;
}
if (_imageName != animal.imageName)
{
_imageName = animal.imageName;
}
[self setNeedsDisplay];
}
实现父类的drawContentView方法,实现绘制
- (void)drawContentView:(CGRect)rect
{
static UIColor *nameColor;
nameColor = [UIColor blackColor];
static UIColor *detailColor;
detailColor = [UIColor darkGrayColor];
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGRect cellRect = self.frame;
if (self.highlighted || self.selected) //选择或高亮时对应的颜色
{
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(context, [UIColor lightGrayColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillRect(context, CGRectMake(0, 0, cellRect.size.width, cellRect.size.height));
}
else
{
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(context, [UIColor whiteColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillRect(context, CGRectMake(0, 0, cellRect.size.width, cellRect.size.height));
}
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:_imageName];
[image drawInRect:CGRectMake(5, 5, 50, 50)];
[nameColor set];
[_nameText drawAtPoint:CGPointMake(65, 10)
forWidth:200
withFont:NameFont
fontSize:rNameFontSize
lineBreakMode:NSLineBreakByWordWrapping
baselineAdjustment:UIBaselineAdjustmentAlignBaselines];
[detailColor set];
[_detailText drawAtPoint:CGPointMake(180, 40)
forWidth:120
withFont:DetailFont
fontSize:rDetailFontSize
lineBreakMode:NSLineBreakByWordWrapping
baselineAdjustment:UIBaselineAdjustmentAlignBaselines];
}
虽然方法很长,但是只要会简单的quartz绘图这些都是最基础的方法。
完成后我们讲这个类注册到tableview中
[self.tableView registerClass:[HRCustomCell class] forCellReuseIdentifier:CellIdentifier];
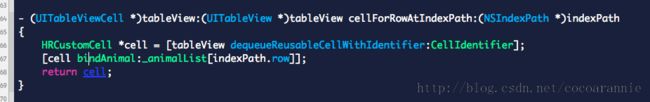
再来看我们的代理方法
就只有3行,比把数据都从这里赋值的方法要简洁许多。
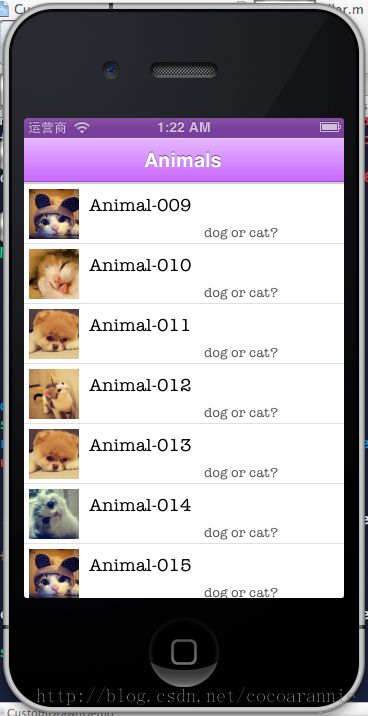
完成的效果图
如果用真机调试,性能也要比使用非手工绘制的性能要好很多。
demo示例 点击打开链接