干货三:CountDownTimer倒计时工具类
概述
毫无疑问,我们先来看下官方文档中给的介绍
CountDownTimer
官方定义如下:
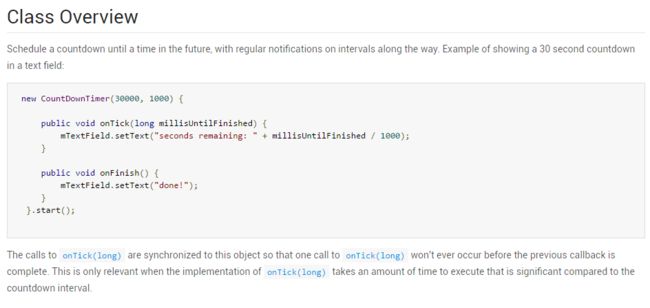
Schedule a countdown until a time in the future, with regular
notifications on intervals along the way.
同时官方也给出了使用的demo:
构造函数 方法 以及参数含义请参考官方文档,已经很明确的说明了,这里就不重复了~
Code
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.CountDownTimer;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import com.turing.base.R;
/** * 倒计时演示 * <p/> * Android中有个countDownTimer类, * 从名字上就可以看出来,它的功能是记录下载时间, * 将后台线程的创建和Handler队列封装成为了一个方便的调用. * <p/> * CountDownTimer由系统提供,果断抛弃了自己以前使用Handler更新UI的做法 */
public class CountDownActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private MyCountDownTimer mc;
private Button countBtn;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_count_down);
countBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.show);
// 共计30S,1S调用一次onTick
mc = new MyCountDownTimer(30000, 1000);
mc.start();
}
public void oncancel(View view) {
mc.cancel();
}
public void restart(View view) {
mc.start();
}
/** * 自定义倒计时类 */
class MyCountDownTimer extends CountDownTimer {
/** * @param millisInFuture 表示以毫秒为单位 倒计时的总数 * <p/> * 例如 millisInFuture=1000 表示1秒 * @param countDownInterval 表示 间隔 多少微秒 调用一次 onTick 方法 * <p/> * 例如: countDownInterval =1000 ; * 表示每1000毫秒调用一次onTick() */
public MyCountDownTimer(long millisInFuture, long countDownInterval) {
super(millisInFuture, countDownInterval);
}
@Override
public void onTick(long millisUntilFinished) {
countBtn.setText("倒计时(" + millisUntilFinished / 1000 + ")...");
}
@Override
public void onFinish() {
countBtn.setText("done");
}
}
}
运行图
CountDownTimer源码
/* * Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */
package android.os;
/** * Schedule a countdown until a time in the future, with * regular notifications on intervals along the way. * * Example of showing a 30 second countdown in a text field: * * <pre class="prettyprint"> * new CountDownTimer(30000, 1000) { * * public void onTick(long millisUntilFinished) { * mTextField.setText("seconds remaining: " + millisUntilFinished / 1000); * } * * public void onFinish() { * mTextField.setText("done!"); * } * }.start(); * </pre> * * The calls to {@link #onTick(long)} are synchronized to this object so that * one call to {@link #onTick(long)} won't ever occur before the previous * callback is complete. This is only relevant when the implementation of * {@link #onTick(long)} takes an amount of time to execute that is significant * compared to the countdown interval. */
public abstract class CountDownTimer {
/** * Millis since epoch when alarm should stop. */
private final long mMillisInFuture;
/** * The interval in millis that the user receives callbacks */
private final long mCountdownInterval;
private long mStopTimeInFuture;
/** * boolean representing if the timer was cancelled */
private boolean mCancelled = false;
/** * @param millisInFuture The number of millis in the future from the call * to {@link #start()} until the countdown is done and {@link #onFinish()} * is called. * @param countDownInterval The interval along the way to receive * {@link #onTick(long)} callbacks. */
public CountDownTimer(long millisInFuture, long countDownInterval) {
mMillisInFuture = millisInFuture;
mCountdownInterval = countDownInterval;
}
/** * Cancel the countdown. */
public synchronized final void cancel() {
mCancelled = true;
mHandler.removeMessages(MSG);
}
/** * Start the countdown. */
public synchronized final CountDownTimer start() {
mCancelled = false;
if (mMillisInFuture <= 0) {
onFinish();
return this;
}
mStopTimeInFuture = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() + mMillisInFuture;
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG));
return this;
}
/** * Callback fired on regular interval. * @param millisUntilFinished The amount of time until finished. */
public abstract void onTick(long millisUntilFinished);
/** * Callback fired when the time is up. */
public abstract void onFinish();
private static final int MSG = 1;
// handles counting down
private Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
synchronized (CountDownTimer.this) {
if (mCancelled) {
return;
}
final long millisLeft = mStopTimeInFuture - SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
if (millisLeft <= 0) {
onFinish();
} else if (millisLeft < mCountdownInterval) {
// no tick, just delay until done
sendMessageDelayed(obtainMessage(MSG), millisLeft);
} else {
long lastTickStart = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
onTick(millisLeft);
// take into account user's onTick taking time to execute
long delay = lastTickStart + mCountdownInterval - SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
// special case: user's onTick took more than interval to
// complete, skip to next interval
while (delay < 0) delay += mCountdownInterval;
sendMessageDelayed(obtainMessage(MSG), delay);
}
}
}
};
}