leveldb学习:Memtable和Varint
Memtable:
Memtable是leveldb数据在内存中的存储形式,写操作的数据都会先写到memtable中,memtable的size有限制最大值(write_buffer_size)。memtable的底层数据结构是skiplist,class memtable完成的只是key-value的打包和调用底层跳表的接口。
首先看看Memtable的成员变量:
//实例化跳表模板
typedef SkipList<const char*, KeyComparator> Table;
//字符大小比较器
KeyComparator comparator_;
//memtable的引用计数
int refs_;
//内存池
Arena arena_;
//底层跳表
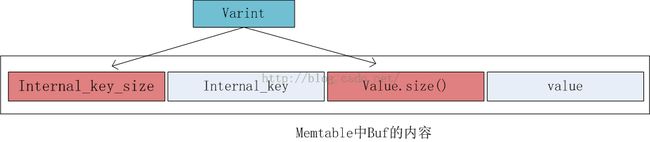
Table table_;由于memtable只是一个配接器,entry的插入操作交由底层的skiplist接口完成,关于leveldb的skiplist实现请看我写的另一篇博客。memtable真正完成的任务是打包key_value数据。memtable中存储的数据格式如下图:
- 首先把key、SequenceNumber、valueType打包成InternalKey。注:SequenceNumber是leveldb的不同版本,每次更新(put/delete)操作都会产生新的版本;valueType是区分entry是真实的KV数据还是删除操作,valueType是delete型的数据表示是要删除的数据,leveldb先记录,在后台的compact线程中完成真实的删除工作。存储时,SequenceNumber占56bits,valueType占8bits,两者共同占64bits(uint_64t)。
- 打包除了有key(InternalKey)和value,还加入了key、value的长度信息,而两者均是自定义的Varint(变长整型)数据,需要完成把int型转化为Varint型。
参见MemTable::Add函数:
void MemTable::Add(SequenceNumber s, ValueType type,
const Slice& key,
const Slice& value) {
// Format of an entry is concatenation of:
// key_size : varint32 of internal_key.size()
// key bytes : char[internal_key.size()]
// value_size : varint32 of value.size()
// value bytes : char[value.size()]
size_t key_size = key.size();
size_t val_size = value.size();
//sequencenumber和valuetype另占8字节
size_t internal_key_size = key_size + 8;
//插入的entry打包后的长度
//VarintLength(int)计算int转化为varint所要字节
const size_t encoded_len =
VarintLength(internal_key_size) + internal_key_size +
VarintLength(val_size) + val_size;
//分配内存
char* buf = arena_.Allocate(encoded_len);
//EncodeVarint32()完成varint型转化工作
char* p = EncodeVarint32(buf, internal_key_size);
//写入内存
memcpy(p, key.data(), key_size);
p += key_size;
//把sequencenumber和valuetype写入内存
EncodeFixed64(p, (s << 8) | type);
p += 8;
//把valuesize和value写入内存
p = EncodeVarint32(p, val_size);
memcpy(p, value.data(), val_size);
assert((p + val_size) - buf == encoded_len);
//把char指针插入跳表
table_.Insert(buf);
}在bool MemTable::Get( )就是查找操作
bool MemTable::Get(const LookupKey& key, std::string* value, Status* s) {
//LookupKey是leveldb为了在memtable/sstable查找方便,为key包装的类型
//调用成员函数memtable_key可以返回在memtable中的key格式
Slice memkey = key.memtable_key();
//利用skiplist的专属迭代器查找key
Table::Iterator iter(&table_);
iter.Seek(memkey.data());
if (iter.Valid()) {
// entry format is:
// klength varint32
// userkey char[klength]
// tag uint64
// vlength varint32
// value char[vlength]
// Check that it belongs to same user key. We do not check the
// sequence number since the Seek() call above should have skipped
// all entries with overly large sequence numbers.
const char* entry = iter.key();
uint32_t key_length;
//找到了再把memtable中记录的userkey和查找对象做一次检查,要求相等
const char* key_ptr = GetVarint32Ptr(entry, entry+5, &key_length);
if (comparator_.comparator.user_comparator()->Compare(
Slice(key_ptr, key_length - 8),
key.user_key()) == 0) {
// Correct user key
//从memtable中的entry提取valuetype
//valuetype = kTypeValue,是真实的数据,查找成功
//valuetype = kTypeDeletion,是要删除的数据,并非不代表数据真实存在
const uint64_t tag = DecodeFixed64(key_ptr + key_length - 8);
switch (static_cast<ValueType>(tag & 0xff)) {
case kTypeValue: {
Slice v = GetLengthPrefixedSlice(key_ptr + key_length);
value->assign(v.data(), v.size());
return true;
}
case kTypeDeletion:
*s = Status::NotFound(Slice());
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}GetVarint32Ptr函数就是varint型编码的逆过程,解码。
关于Varint(变长整型)
Varint是一种紧凑的表示数字的方法。Varint中的每个byte的最高位bit有特殊的含义,如果该位为 1,表示后续的byte也是该数字的一部分,如果该位为0,则结束。其他的7个bit都用来表示数字。因此小于128的int都可以用一个byte表示。大于 128的数字,比如300,会用两个字节来表示:1010 1100 0000 0010,而4字节的int型最多需要5字节用varint表示。
有关varint的编码和解码部分实现都在coding.cc中。
int VarintLength(uint64_t v) {
int len = 1;
while (v >= 128) {
v >>= 7;
len++;
}
return len;
}编码:
char* EncodeVarint32(char* dst, uint32_t v) {
// Operate on characters as unsigneds
unsigned char* ptr = reinterpret_cast<unsigned char*>(dst);
static const int B = 128;
if (v < (1<<7)) {
*(ptr++) = v;
} else if (v < (1<<14)) {
*(ptr++) = v | B;
*(ptr++) = v>>7;
} else if (v < (1<<21)) {
*(ptr++) = v | B;
*(ptr++) = (v>>7) | B;
*(ptr++) = v>>14;
} else if (v < (1<<28)) {
*(ptr++) = v | B;
*(ptr++) = (v>>7) | B;
*(ptr++) = (v>>14) | B;
*(ptr++) = v>>21;
} else {
*(ptr++) = v | B;
*(ptr++) = (v>>7) | B;
*(ptr++) = (v>>14) | B;
*(ptr++) = (v>>21) | B;
*(ptr++) = v>>28;
}
return reinterpret_cast<char*>(ptr);
}解码:
inline const char* GetVarint32Ptr(const char* p,
const char* limit,
uint32_t* value) {
if (p < limit) {
uint32_t result = *(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char*>(p));
if ((result & 128) == 0) {
*value = result;
return p + 1;
}
}
return GetVarint32PtrFallback(p, limit, value);
}
const char* GetVarint32PtrFallback(const char* p,
const char* limit,
uint32_t* value) {
uint32_t result = 0;
for (uint32_t shift = 0; shift <= 28 && p < limit; shift += 7) {
uint32_t byte = *(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char*>(p));
p++;
if (byte & 128) {
// More bytes are present
result |= ((byte & 127) << shift);
} else {
result |= (byte << shift);
*value = result;
return reinterpret_cast<const char*>(p);
}
}
return NULL;
}没什么可说的,用心体会里面的移位操作。
看完32位int转varint,来看看进阶版64位int的编码和解码,里面采用了循环结构
char* EncodeVarint64(char* dst, uint64_t v) {
static const int B = 128;
unsigned char* ptr = reinterpret_cast<unsigned char*>(dst);
while (v >= B) {
*(ptr++) = (v & (B-1)) | B;
v >>= 7;
}
*(ptr++) = static_cast<unsigned char>(v);
return reinterpret_cast<char*>(ptr);
}const char* GetVarint64Ptr(const char* p, const char* limit, uint64_t* value) {
uint64_t result = 0;
for (uint32_t shift = 0; shift <= 63 && p < limit; shift += 7) {
uint64_t byte = *(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char*>(p));
p++;
if (byte & 128) {
// More bytes are present
result |= ((byte & 127) << shift);
} else {
result |= (byte << shift);
*value = result;
return reinterpret_cast<const char*>(p);
}
}
return NULL;
}