opencv 数字图像处理-图像缩放 自己写cvResize()函数
以下有灰度图像的最近邻插值法、双线性插值法和彩色图像的最近邻插值法、双线性插值法
########################################################################3#
void cvResize( const CvArr* src, CvArr* dst, int interpolation = CV_INTER_LINEAR );
最后一个参数指定插值方法,默认为线性插值法。可用的插值方法如下表所示:
| 插值方法 |
含义 |
| CV_INTER_NN |
最近邻插值 |
| CV_INTER_LINEAR |
线性插值 |
| CV_INTER_AREA |
区域插值 |
| CV_INTER_CUBIC |
三次样条插值 |
############################################################################
0阶和1阶灰度插值法
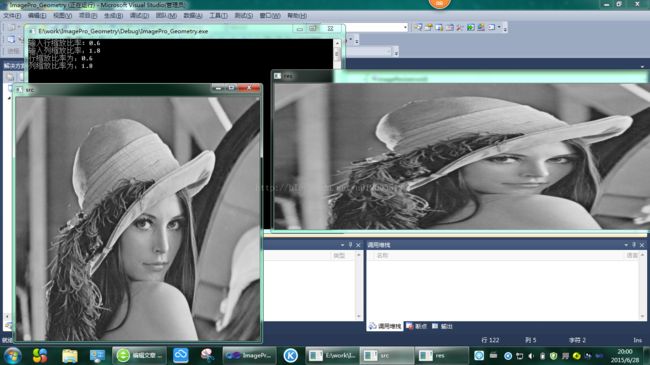
最近邻插值法
2倍放大
//最近邻插值法 将原图像中每行像素重复取值一遍,每列像素重复取值一遍 优点:较为简单 缺点:放大倍数太大时,容易出现马赛克效应
for (i=0; i<pImg->height; i++)
for (j=0; j<pImg->width; j++)
{
pImg1->imageData[i*2*pImg1->widthStep + j*2] = pImg->imageData[i*pImg->widthStep + j];
pImg1->imageData[i*2*pImg1->widthStep + j*2+1] = pImg->imageData[i*pImg->widthStep + j];
pImg1->imageData[(i+1)*2*pImg1->widthStep + j*2] = pImg->imageData[i*pImg->widthStep + j];
pImg1->imageData[(i+1)*2*pImg1->widthStep + j*2+1] = pImg->imageData[i*pImg->widthStep + j];
}
cout<<pImg1->origin<<endl;
cout<<pImg1->width<<endl;
cout<<pImg1->height<<endl;
cout<<pImg1->widthStep<<endl;
cout<<pImg->origin<<endl;
cout<<pImg->width<<endl;
cout<<pImg->height<<endl;
cout<<pImg1->widthStep<<endl;
缩放均可
void nearestNeighbor(IplImage *src, IplImage *res, float ratio_x, float ratio_y)//最近邻插值法
{//将结果图像上的像素点的值设定为原始图像上最接近的像素点的值 ratio_x为行权重值 ratio_y为列权重值
int res_wid = 0;
int res_hei = 0;
res_wid = res->width;
res_hei = res->height;
unsigned char *src_data = (unsigned char *)src->imageData;
unsigned char *res_data = (unsigned char *)res->imageData;
int res_x, res_y, src_x, src_y;
for (int i=0; i<res_wid; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<res_hei; j++)
{
res_x = j;//结果图像第x行
res_y = i;//结果图像第y列
src_x = (int)(((float)j+0.5)/ratio_x);//原始图像第x行
src_y = (int)(((float)i+0.5)/ratio_y);//原始图像第y列
res_data[res_x*res->widthStep+res_y] = src_data[src_x*src->widthStep+src_y];
}
}
cvNamedWindow("src");
cvNamedWindow("res");
cvShowImage("src", src);
cvShowImage("res", res);
cvWaitKey(0);
cvReleaseImage(&src);
cvReleaseImage(&res);
cvDestroyAllWindows();
}
行压缩率:1.3
列压缩率:0.5
自己想了好久还是没有头绪,在网上找了一下,发现了一篇很不错的博文,贴一下链接:
http://blog.csdn.net/tangshuai8888/article/details/43405277
下面这个是自己写得
void bilinear(IplImage *src, IplImage *res, float ratio_x, float ratio_y)
{//取原图像中相临近的四个像素点,按距离大小远近取不同权重值,加权得出结果图像相应的像素点的值
//设带插值像素点为(x,y),四个临近像素点分别为(x0, y0)、(x0+1, y0)、(x0, y0+1)、(x0+1, y0+1)
//则(x,y)点的值为 g(x, y)=(1-b)*[(1-a)*g(x0,y0)+a*g(x0+1, y0)]+b*[(1-a)*g(x0, y0+1)+a*g(x0+1, y0+1)]
//a, b分别为列行权重值
int res_wid = 0;
int res_hei = 0;
res_wid = res->width;
res_hei = res->height;
unsigned char *src_data = (unsigned char *)src->imageData;
unsigned char *res_data = (unsigned char *)res->imageData;
int v00, v01, v10, v11;
float weightx, weighty;
int res_x, res_y, src_x0, src_y0;
for (int i=0; i<res_wid; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<res_hei; j++)
{
res_x = j;//结果图像第x行
res_y = i;//结果图像第y列
src_x0 = (int)((float)j/ratio_x);//原始图像第x行
src_y0 = (int)((float)i/ratio_y);//原始图像第y列
weightx = ((float)j)/ratio_x - src_x0;//行权重值
weighty = ((float)i)/ratio_y - src_y0;//列权重值
v00 = (int)src_data[src_x0*src->widthStep+src_y0];
v01 = (int)src_data[src_x0*src->widthStep+src_y0+1];
v10 = (int)src_data[(1+src_x0)*src->widthStep+src_y0];
v11 = (int)src_data[(1+src_x0)*src->widthStep+src_y0+1];
res_data[res_x*res->widthStep+res_y] = (1-weightx)*(1-weighty)*v00+(1-weightx)*weighty*v01+weightx*(1-weighty)*v10+weightx*weighty*v11;
}
}
cvNamedWindow("src");
cvNamedWindow("res");
cvShowImage("src", src);
cvShowImage("res", res);
cvWaitKey(0);
cvReleaseImage(&src);
cvReleaseImage(&res);
cvDestroyAllWindows();
}
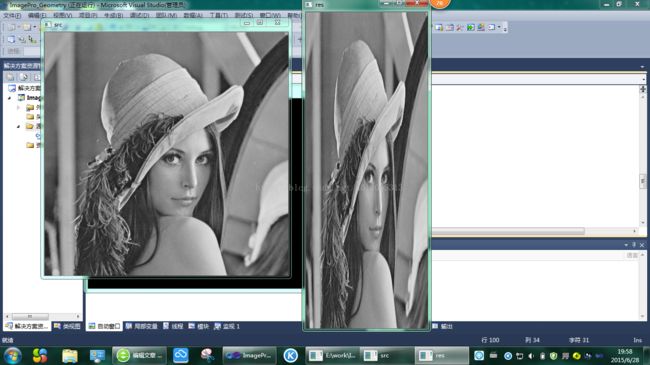
行压缩率:0.6
列压缩率:1.8
############################################################################
彩色图像的最近邻插值法、双线性插值法
最近邻插值法
void nearestNeighbor(IplImage *src, IplImage *res, float ratio_x, float ratio_y)//最近邻插值法
{//将结果图像上的像素点的值设定为原始图像上最接近的像素点的值
int res_wid = 0;
int res_hei = 0;
res_wid = res->width;
res_hei = res->height;
unsigned char *src_data = (unsigned char *)src->imageData;
unsigned char *res_data = (unsigned char *)res->imageData;
int res_x, res_y, src_x, src_y;
for (int i=0; i<res_wid; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<res_hei; j++)
{
res_x = j;//结果图像第x行
res_y = i;//结果图像第y列
src_x = (int)(((float)j+0.5)/ratio_x);//原始图像第x行
src_y = (int)(((float)i+0.5)/ratio_y);//原始图像第y列
//res_data[res_x*res->widthStep+res_y] = src_data[src_x*src->widthStep+src_y];
res_data[res_x*res->widthStep+res_y*3] = src_data[src_x*src->widthStep+src_y*3];
res_data[res_x*res->widthStep+res_y*3+1] = src_data[src_x*src->widthStep+src_y*3+1];
res_data[res_x*res->widthStep+res_y*3+2] = src_data[src_x*src->widthStep+src_y*3+2];
}
}
cvNamedWindow("src");
cvNamedWindow("res");
cvShowImage("src", src);
cvShowImage("res", res);
cvWaitKey(0);
cvReleaseImage(&src);
cvReleaseImage(&res);
cvDestroyAllWindows();
}
行压缩比率:0.8
列压缩比率:1.3
双线性插值法
void bilinear(IplImage *src, IplImage *res, float ratio_x, float ratio_y)
{//取原图像中相临近的四个像素点,按距离大小远近取不同权重值,加权得出结果图像相应的像素点的值
//设带插值像素点为(x,y),四个临近像素点分别为(x0, y0)、(x0+1, y0)、(x0, y0+1)、(x0+1, y0+1)
//则(x,y)点的值为 g(x, y)=(1-b)*[(1-a)*g(x0,y0)+a*g(x0+1, y0)]+b*[(1-a)*g(x0, y0+1)+a*g(x0+1, y0+1)]
//a, b分别为列行权重值
int res_wid = 0;
int res_hei = 0;
res_wid = res->width;
res_hei = res->height;
unsigned char *src_data = (unsigned char *)src->imageData;
unsigned char *res_data = (unsigned char *)res->imageData;
int v00, v01, v10, v11;
float weightx, weighty;
int res_x, res_y, src_x0, src_y0;
for (int i=0; i<res_wid; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<res_hei; j++)
{
res_x = j;//结果图像第x行
res_y = i;//结果图像第y列
src_x0 = (int)((float)j/ratio_x);//原始图像第x行
src_y0 = (int)((float)i/ratio_y);//原始图像第y列
weightx = ((float)j)/ratio_x - src_x0;//行权重值
weighty = ((float)i)/ratio_y - src_y0;//列权重值
for (int k=0; k<3; k++)//3通道
{
v00 = (int)src_data[src_x0*src->widthStep+src_y0*3+k];
v01 = (int)src_data[src_x0*src->widthStep+(src_y0+1)*3+k];
v10 = (int)src_data[(1+src_x0)*src->widthStep+src_y0*3+k];
v11 = (int)src_data[(1+src_x0)*src->widthStep+(src_y0+1)*3+k];
res_data[res_x*res->widthStep+res_y*3+k] = (1-weightx)*(1-weighty)*v00+(1-weightx)*weighty*v01+weightx*(1-weighty)*v10+weightx*weighty*v11;
}
}
}
cvNamedWindow("src");
cvNamedWindow("res");
cvShowImage("src", src);
cvShowImage("res", res);
cvWaitKey(0);
cvReleaseImage(&src);
cvReleaseImage(&res);
cvDestroyAllWindows();
}
行压缩率:1.4
列压缩率:1.4
#########################################
可以将上述灰度图像和彩色图像的最近邻插值法和双线性插值法函数结合起来,在函数开始时先检测图像是灰度图像还是彩色图像,然后分别进行相应的计算