Struts2中Result类型介绍
1.在Struts2中,Result类型有12种,分别为dispatcher,redirect,chain,redirectAction,freemarker,httpheader,stream,velocity,xslt,plainText,titles,postback。下面对这12种Result类型分别进行介绍,其中最常用的有dispatcher,redirect,chain,redirectAction,如果不指定result的type属性,默认为dispatcher分发跳转方式。
2.其中在struts.xml配置文件中,里面的包继承的包为struts_default,而包所继承的这个struts_default为一个xml文件,放在struts2的核心代码库里面,即下图的红色箭头指向处:
打开下图的红色箭头的struts-default.xml文件:
打开后我们可以看到如下图所示:
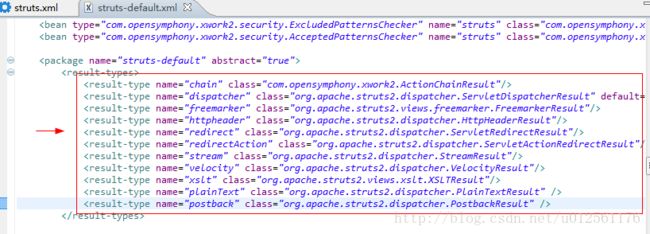
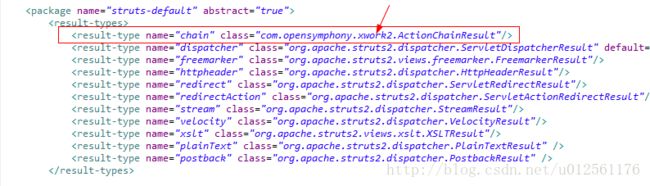
其中我们可以看到result的type类型有11种,相应的名字和对应的类,所以我们在学习的时候可以看相应的class类,即看源代码学习,下面将对这11种result类型进行介绍。
3.上面的要我们看我们查看源代码学习,所以我们应该学习如何才能看到我们的源代码,没导入jar包和路径的话,都是字节码,不能看到我们熟悉的Java代码,其中我们导入的路径位于我们下载的struts2所需的文档,jar包等等,所以下面介绍如何导入相应的路径来看我们的源代码:
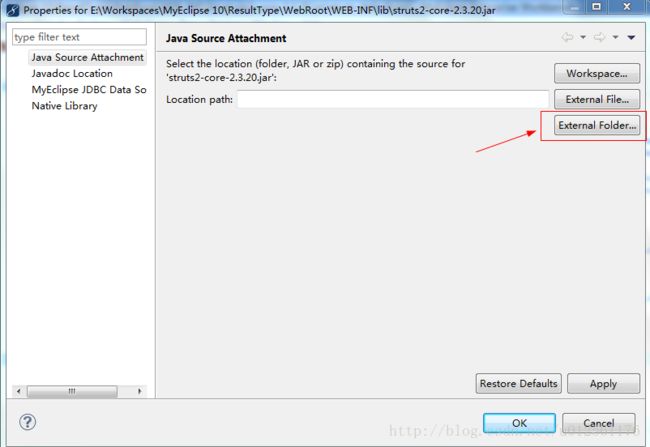
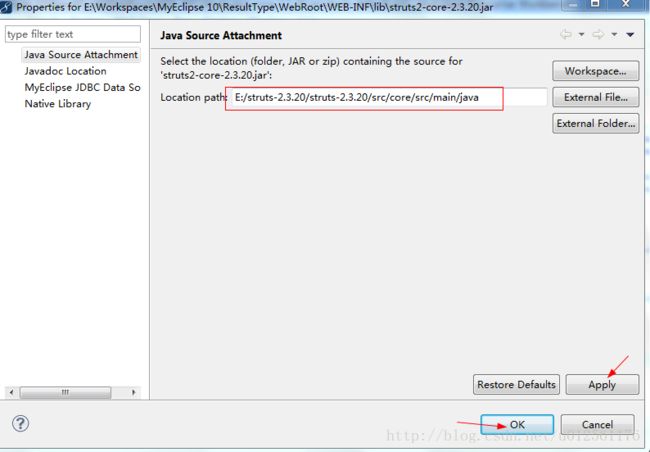
(1).首先,我们选择struts2-core-2.3.20.jar包,然后鼠标右键选择Properties,即属性这个选项,出现下图,点击下图的红色箭头指向处的按钮:
(2).其中我在网上下载的struts-2.3.20-all.zip的压缩包,我们要导入源代码的话,我的是这个路径:E:\struts-2.3.20\struts-2.3.20\src\core\src\main\java,大家看后面几个文件夹便可以找到了,如下图所示:
这样我们就可以查看相应的类文件代码了。
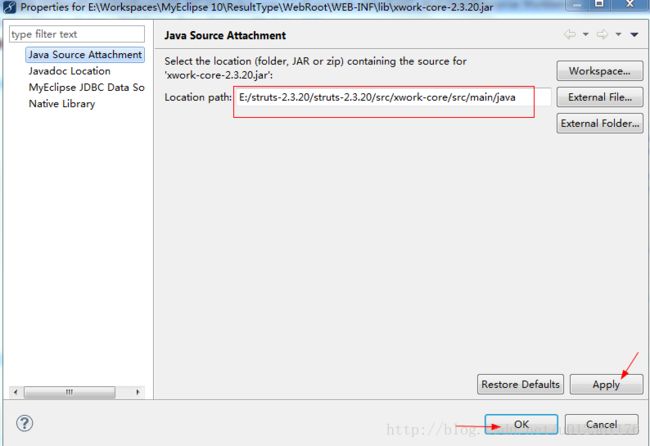
对于result的type属性中有一个是放在xwork-core-2.3.20.jar包下的,所以也需要导入源代码,我的路径为:E:\struts-2.3.20\struts-2.3.20\src\xwork-core\src\main\java,然后像上面一步一样打开属性,然后就可以了,如下图所示:
这样便可以查看底层的代码了。
3.前面说了那么多,还没说到重点,即result的type类型,上面也是为了学习result的type而做的部分工作,接下来便开始介绍result的type了:
(1).dispatcher:运用服务器跳转到jsp页面(视图),不可以跳转到Action,只可以跳转到视图,在struts.xml配置文件中,如果没有为result设置type属性的话,默认就是通过这种方式跳转的。
(2).redirect:客户端跳转(重定向),其中url(地址栏的地址)会发生变化,不可以跳转到Action,只可以跳转到视图。
(3).chain:用来处理Action链,跳转到Action,可以动用到Action,在访问Action时,Action前面不要加 "/" 。
(4).redirectAction:客户端跳转到Action,其中url(地址栏的地址)会发生变化。
(5).freemarker:处理FreeMarker模板。
(6).httpheader:用来控制特殊的Http行为,发送一个Http头。
(7).stream:意思是流,向浏览器发送InputSream对象,通常用来处理文件下载。
(8).velocity:处理Velocity模板。
(9).xslt:处理XML/XLST模板。
(10).plainText:返回页面的源码。
(11).titles:把页面分成几块,每个页面可以动态的指定。
(12).postback:回传,即页面在首次加载后向服务器提交数据,然后服务器把处理好的数据传递到客户端并显示出来。
4.下面新建一个struts2项目,项目名为ResultType,这个项目只对常用的几个result类型进行介绍:
(1).首先,打开index.jsp页面,修改编码方式为utf-8,具体代码如下:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<ol>
<li><a href="r/r1">dispatcher</a></li>
<li><a href="r/r2">redirect</a></li>
<li><a href="r/r3">chain</a></li>
<li><a href="r/r4">redirectAction</a></li>
<li><a href="r/r5">plainText</a></li>
</ol>
</body>
</html>
(2).接着新建两个jsp页面,分别为r1.jsp和r2.jsp,其中内容自定:
r1.jsp页面代码如下:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
dispacther成功
</body>
</html>
r2.jsp页面代码如下:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
redirect成功
</body>
</html>
(3).下面对常用的几个result类型进行配置:
dispatcher,相应的struts.xml配置如下:
<action name="r1"> <result type="dispatcher">/r1.jsp</result> </action>
跳转到r1.jsp页面。
redirect,相应的struts.xml配置如下:
<action name="r2"> <result type="redirect">/r2.jsp</result> </action>
重定向到r2.jsp页面,其中地址栏的地址发生变化。
chain,相应的struts.xml配置如下:
<action name="r3"> <result type="chain">r1</result> </action>
r1这个action,跳转到r1.jsp页面
redirectAction,相应的struts.xml配置如下:
<action name="r4"> <result type="redirectAction">r2</result> </action>
访问r2这个action,其中url发生改变,重定向到r2.jsp页面。
注:当访问不同的namespace下的Action时,则使用如下方式:
<action name="r5"> <result type="chain"> <param name="actionName">r1</param><!-- action名称 --> <param name="namespace">/r</param><!-- namespace值 --> </result> </action>
其中为什么要定义actionname,namespace这两个参数呢,因为在底层代码中所有,所以必须把这两个参数传进去,才可以跳转页面,其中chain这个类型放在 哪里呢,我们可以打开前面我们所说的struts-default.xml文件,打开之后,如下图:
我们可以打开这个com.opensymphony.xwork2包下的ActionChainResult类,代码如下:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2006,2009 The Apache Software Foundation.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.opensymphony.xwork2;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.inject.Inject;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.TextParseUtil;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.logging.Logger;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.logging.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.*;
/**
* <!-- START SNIPPET: description -->
*
* This result invokes an entire other action, complete with it's own interceptor stack and result.
*
* <!-- END SNIPPET: description -->
*
* <b>This result type takes the following parameters:</b>
*
* <!-- START SNIPPET: params -->
*
* <ul>
*
* <li><b>actionName (default)</b> - the name of the action that will be chained to</li>
*
* <li><b>namespace</b> - used to determine which namespace the Action is in that we're chaining. If namespace is null,
* this defaults to the current namespace</li>
*
* <li><b>method</b> - used to specify another method on target action to be invoked.
* If null, this defaults to execute method</li>
*
* <li><b>skipActions</b> - (optional) the list of comma separated action names for the
* actions that could be chained to</li>
*
* </ul>
*
* <!-- END SNIPPET: params -->
*
* <b>Example:</b>
*
* <pre><!-- START SNIPPET: example -->
* <package name="public" extends="struts-default">
* <!-- Chain creatAccount to login, using the default parameter -->
* <action name="createAccount" class="...">
* <result type="chain">login</result>
* </action>
*
* <action name="login" class="...">
* <!-- Chain to another namespace -->
* <result type="chain">
* <param name="actionName">dashboard</param>
* <param name="namespace">/secure</param>
* </result>
* </action>
* </package>
*
* <package name="secure" extends="struts-default" namespace="/secure">
* <action name="dashboard" class="...">
* <result>dashboard.jsp</result>
* </action>
* </package>
* <!-- END SNIPPET: example --></pre>
*
* @author <a href='mailto:the_mindstorm[at]evolva[dot]ro'>Alexandru Popescu</a>
*/
public class ActionChainResult implements Result {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ActionChainResult.class);
/**
* The result parameter name to set the name of the action to chain to.
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_PARAM = "actionName";
/**
* The action context key to save the chain history.
*/
private static final String CHAIN_HISTORY = "CHAIN_HISTORY";
/**
* The result parameter name to set the name of the action to chain to.
*/
public static final String SKIP_ACTIONS_PARAM = "skipActions";
private ActionProxy proxy;
private String actionName;
private String namespace;
private String methodName;
/**
* The list of actions to skip.
*/
private String skipActions;
private ActionProxyFactory actionProxyFactory;
public ActionChainResult() {
super();
}
public ActionChainResult(String namespace, String actionName, String methodName) {
this.namespace = namespace;
this.actionName = actionName;
this.methodName = methodName;
}
public ActionChainResult(String namespace, String actionName, String methodName, String skipActions) {
this.namespace = namespace;
this.actionName = actionName;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.skipActions = skipActions;
}
/**
* @param actionProxyFactory the actionProxyFactory to set
*/
@Inject
public void setActionProxyFactory(ActionProxyFactory actionProxyFactory) {
this.actionProxyFactory = actionProxyFactory;
}
/**
* Set the action name.
*
* @param actionName The action name.
*/
public void setActionName(String actionName) {
this.actionName = actionName;
}
/**
* sets the namespace of the Action that we're chaining to. if namespace
* is null, this defaults to the current namespace.
*
* @param namespace the name of the namespace we're chaining to
*/
public void setNamespace(String namespace) {
this.namespace = namespace;
}
/**
* Set the list of actions to skip.
* To test if an action should not throe an infinite recursion,
* only the action name is used, not the namespace.
*
* @param actions The list of action name separated by a white space.
*/
public void setSkipActions(String actions) {
this.skipActions = actions;
}
public void setMethod(String method) {
this.methodName = method;
}
public ActionProxy getProxy() {
return proxy;
}
/**
* Get the XWork chain history.
* The stack is a list of <code>namespace/action!method</code> keys.
*/
public static LinkedList<String> getChainHistory() {
LinkedList<String> chainHistory = (LinkedList<String>) ActionContext.getContext().get(CHAIN_HISTORY);
// Add if not exists
if (chainHistory == null) {
chainHistory = new LinkedList<String>();
ActionContext.getContext().put(CHAIN_HISTORY, chainHistory);
}
return chainHistory;
}
/**
* @param invocation the DefaultActionInvocation calling the action call stack
*/
public void execute(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
// if the finalNamespace wasn't explicitly defined, assume the current one
if (this.namespace == null) {
this.namespace = invocation.getProxy().getNamespace();
}
ValueStack stack = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
String finalNamespace = TextParseUtil.translateVariables(namespace, stack);
String finalActionName = TextParseUtil.translateVariables(actionName, stack);
String finalMethodName = this.methodName != null
? TextParseUtil.translateVariables(this.methodName, stack)
: null;
if (isInChainHistory(finalNamespace, finalActionName, finalMethodName)) {
addToHistory(finalNamespace, finalActionName, finalMethodName);
throw new XWorkException("Infinite recursion detected: "
+ ActionChainResult.getChainHistory().toString());
}
if (ActionChainResult.getChainHistory().isEmpty() && invocation != null && invocation.getProxy() != null) {
addToHistory(finalNamespace, invocation.getProxy().getActionName(), invocation.getProxy().getMethod());
}
addToHistory(finalNamespace, finalActionName, finalMethodName);
HashMap<String, Object> extraContext = new HashMap<String, Object>();
extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK, ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack());
extraContext.put(ActionContext.PARAMETERS, ActionContext.getContext().getParameters());
extraContext.put(CHAIN_HISTORY, ActionChainResult.getChainHistory());
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Chaining to action " + finalActionName);
}
proxy = actionProxyFactory.createActionProxy(finalNamespace, finalActionName, finalMethodName, extraContext);
proxy.execute();
}
@Override public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
final ActionChainResult that = (ActionChainResult) o;
if (actionName != null ? !actionName.equals(that.actionName) : that.actionName != null) return false;
if (methodName != null ? !methodName.equals(that.methodName) : that.methodName != null) return false;
if (namespace != null ? !namespace.equals(that.namespace) : that.namespace != null) return false;
return true;
}
@Override public int hashCode() {
int result;
result = (actionName != null ? actionName.hashCode() : 0);
result = 31 * result + (namespace != null ? namespace.hashCode() : 0);
result = 31 * result + (methodName != null ? methodName.hashCode() : 0);
return result;
}
private boolean isInChainHistory(String namespace, String actionName, String methodName) {
LinkedList<? extends String> chainHistory = ActionChainResult.getChainHistory();
if (chainHistory == null) {
return false;
} else {
// Actions to skip
Set<String> skipActionsList = new HashSet<String>();
if (skipActions != null && skipActions.length() > 0) {
ValueStack stack = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
String finalSkipActions = TextParseUtil.translateVariables(this.skipActions, stack);
skipActionsList.addAll(TextParseUtil.commaDelimitedStringToSet(finalSkipActions));
}
if (!skipActionsList.contains(actionName)) {
// Get if key is in the chain history
return chainHistory.contains(makeKey(namespace, actionName, methodName));
}
return false;
}
}
private void addToHistory(String namespace, String actionName, String methodName) {
List<String> chainHistory = ActionChainResult.getChainHistory();
chainHistory.add(makeKey(namespace, actionName, methodName));
}
private String makeKey(String namespace, String actionName, String methodName) {
if (null == methodName) {
return namespace + "/" + actionName;
}
return namespace + "/" + actionName + "!" + methodName;
}
}
该类里面有actionName,namespace属性,还有一些属性,如methodName等。
plainText,相应的struts.xml配置如下:
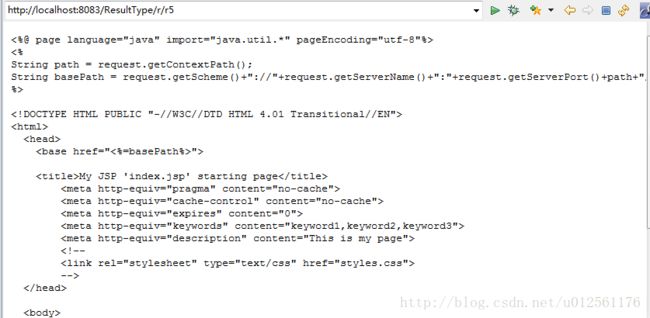
<action name="r5"> <result type="plainText"> <param name="location">/index.jsp</param><!-- 跳转的页面位置 --> <param name="charSet">utf-8</param><!-- 指定文件的编码 --> </result> </action>这个会 返回index.jsp页面的源码,其中两个参数,可以看struts-default.xml文件,看plainText放在哪个类中,看源码可看出也是需要两个参数的,这里就不多说了,大家可以自己琢磨!
(4).完整的struts.xml配置文件代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd">
<struts>
<constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="true"></constant>
<package name="rt" namespace="/r" extends="struts-default">
<action name="r1">
<result type="dispatcher">/r1.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="r2">
<result type="redirect">/r2.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="r3">
<result type="chain">r1</result>
</action>
<action name="r4">
<result type="redirectAction">r2</result>
</action>
<action name="r5">
<result type="plainText">
<param name="location">/index.jsp</param>
<param name="charSet">utf-8</param><!-- 指定文件的编码 -->
</result>
</action>
</package>
<package name="user" namespace="/g" extends="struts-default">
<action name="r5">
<result type="chain">
<param name="actionName">r1</param><!-- action名称 -->
<param name="namespace">/r</param><!-- namespace值 -->
</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
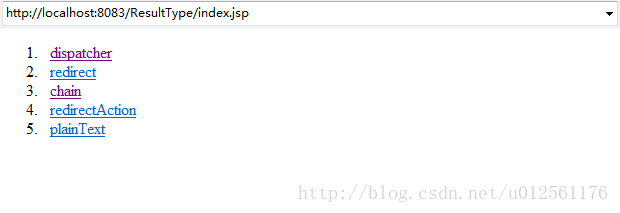
接着部署该项目到Tomcat服务器上,开启Tomcat服务器,访问index.jsp页面,如下:
依次点击超链接,如下所示:
然后我们访问不同包下的action,如下所示:
5.以上内容仅供大家学习参考,写得不好,请见谅,如有错误,请指出,谢谢!