poj 3608(旋转卡壳求解两凸包之间的最短距离)
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |||
| Total Submissions: 9768 | Accepted: 2866 | Special Judge | ||
Description
Thousands of thousands years ago there was a small kingdom located in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. The territory of the kingdom consists two separated islands. Due to the impact of the ocean current, the shapes of both the islands became convex polygons. The king of the kingdom wanted to establish a bridge to connect the two islands. To minimize the cost, the king asked you, the bishop, to find the minimal distance between the boundaries of the two islands.
Input
The input consists of several test cases.
Each test case begins with two integers N, M. (3 ≤ N, M ≤ 10000)
Each of the next N lines contains a pair of coordinates, which describes the position of a vertex in one convex polygon.
Each of the next M lines contains a pair of coordinates, which describes the position of a vertex in the other convex polygon.
A line with N = M = 0 indicates the end of input.
The coordinates are within the range [-10000, 10000].
Output
For each test case output the minimal distance. An error within 0.001 is acceptable.
Sample Input
4 4 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 1.00000 1.00000 1.00000 1.00000 0.00000 2.00000 0.00000 2.00000 1.00000 3.00000 1.00000 3.00000 0.00000 0 0
Sample Output
1.00000
引自:http://blog.csdn.net/acmaker/article/details/3178696
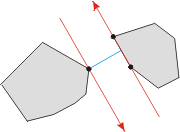
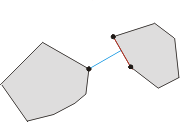
两个凸多边形 P 和 Q 之间的最小距离由多边形间的对踵点对确立。 存在凸多边形间的三种多边形间的对踵点对, 因此就有三种可能存在的最小距离模式:
- “顶点-顶点”的情况
- “顶点-边”的情况
- “边-边”的情况
换句话说, 确定最小距离的点对不一定必须是顶点。 下面的三个图例表明了以上结论:
给定结果, 一个基于旋转卡壳的算法自然而然的产生了:
考虑如下的算法, 算法的输入是两个分别有 m 和 n 个顺时针给定顶点的凸多边形 P 和 Q。
- 计算 P 上 y 坐标值最小的顶点(称为 yminP ) 和 Q 上 y 坐标值最大的顶点(称为 ymaxQ)。
- 为多边形在 yminP 和 ymaxQ 处构造两条切线 LP 和 LQ 使得他们对应的多边形位于他们的右侧。 此时 LP 和 LQ 拥有不同的方向, 并且 yminP 和ymaxQ 成为了多边形间的一个对踵点对。
- 计算距离(yminP,ymaxQ) 并且将其维护为当前最小值。
- 顺时针同时旋转平行线直到其中一个与其所在的多边形的边重合。
- 如果只有一条线与边重合, 那么只需要计算“顶点-边”对踵点对和“顶点-顶点”对踵点对距离。 都将他们与当前最小值比较, 如果小于当前最小值则进行替换更新。 如果两条切线都与边重合, 那么情况就更加复杂了。 如果边“交叠”, 也就是可以构造一条与两条边都相交的公垂线(但不是在顶点处相交), 那么就计算“边-边”距离。 否则计算三个新的“顶点-顶点”对踵点对距离。 所有的这些距离都与当前最小值进行比较, 若小于当前最小值则更新替换。
- 重复执行步骤4和步骤5, 直到新的点对为(yminP,ymaxQ)。
- 输出最小距离。
模板如下:
/* 叉积的一个非常重要的性质是可以通过它的符号来判断两矢量相互之间的顺逆时针关系: 若 P * Q > 0,则 P 在 Q 的顺时针方向; 若 P * Q < 0, 则 P 在 Q 的逆时针方向; 若 P * Q = 0,则 P 与 Q 共线,但不确定 P, Q 的方向是否相同; */ #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <math.h> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const double esp = 1e-10; const int N = 10005; struct Point { double x,y; } p[N],q[N]; int n,m; ///叉积 double mult_cross(Point a,Point b,Point c) { return (a.x-c.x)*(b.y-c.y)-(b.x-c.x)*(a.y-c.y); } ///点积 double mult_point(Point a,Point b,Point c){ return (a.x-c.x)*(b.x-c.x)+(a.y-c.y)*(b.y-c.y); } ///距离 double dis(Point a,Point b) { return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); } ///将点集按照顺时钟排序 void clockwise_sort(Point p[],int n){ for(int i=0;i<n-2;i++){ double tmp = mult_cross(p[i+1],p[i+2],p[i]); if(tmp>0) return; else if(tmp<0){ reverse(p,p+n); return; } } } ///点c到直线ab的最短距离 double GetDist(Point a,Point b,Point c){ if(dis(a,b)<esp) return dis(b,c); ///a,b是同一个点 if(mult_point(b,c,a)<-esp) return dis(a,c); ///投影 if(mult_point(a,c,b)<-esp) return dis(b,c); return fabs(mult_cross(b,c,a)/dis(a,b)); } ///求一条线段ab的两端点到另外一条线段bc的距离,反过来一样,共4种情况 double MinDist(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d){ return min(min(GetDist(a,b,c),GetDist(a,b,d)),min(GetDist(c,d,a),GetDist(c,d,b))); } double min_PQ(Point p[],Point q[],int n,int m){ int yminP = 0,ymaxQ=0; for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ ///找到点集p组成的凸包的左下角 if(p[i].y<p[yminP].y||(p[i].y==p[yminP].y)&&(p[i].x<p[yminP].x)) yminP = i; } for(int i=1;i<m;i++){ ///找到点集q组成的凸包的右上角 if(q[i].y>q[ymaxQ].y||(q[i].y==q[ymaxQ].y)&&(q[i].x>q[ymaxQ].x)) ymaxQ = i; } double ans = dis(p[yminP],q[ymaxQ]); ///距离(yminP,ymaxQ)维护为当前最小值。 p[n]=p[0],q[m]=q[0]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ double tmp; while(tmp=(mult_cross(q[ymaxQ+1],p[yminP],p[yminP+1])-mult_cross(q[ymaxQ],p[yminP],p[yminP+1]))>esp) ymaxQ = (ymaxQ+1)%m; if(tmp<-esp) ans = min(ans,GetDist(p[yminP],p[yminP+1],q[ymaxQ])); else ans=min(ans,MinDist(p[yminP],p[yminP+1],q[ymaxQ],q[ymaxQ+1])); yminP = (yminP+1)%n; } return ans; } int main() { while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF,n+m) { for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); } for(int i=0; i<m; i++) { scanf("%lf%lf",&q[i].x,&q[i].y); } clockwise_sort(p,n); clockwise_sort(q,m); double ans = min(min_PQ(p,q,n,m),min_PQ(q,p,m,n)); printf("%.5lf\n",ans); } return 0; }