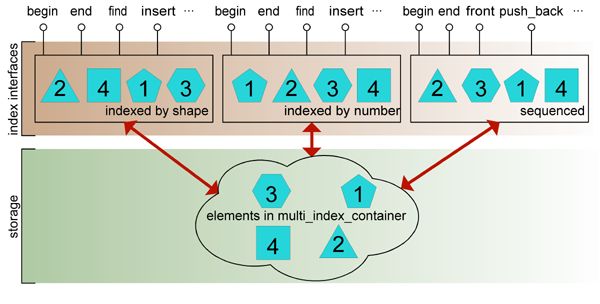
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <list>
#include <string>
#include <boost/multi_index_container.hpp>
#include <boost/multi_index/ordered_index.hpp>
#include <boost/multi_index/identity.hpp>
#include <boost/multi_index/member.hpp>
#include <boost/lambda/lambda.hpp>
/*
标题:boost.Multi_Index库的使用
功能:类似std::map的容器,但是可以用多个关键词索引数据
描述:boost::multi_index::multi_index_container为容器内的数据建立多个视图
不同的索引字段(Key)对应不同的视图
boost::multi_index::multi_index_container经常可以采用不同的表达方式实现
同样的功能。
这里只列举一种能满足我们添加、删除、修改、检索记录的需求示例代码,有兴趣的话
可以通过参考资料中的官网地址得到如何使用其它方式达到这里功能需求的知识。
环境:Windows 8.1 64bit(英文版)
Visual Studio 2013 Professional with SP1
boost 1.55
注意:编写和template相关的代码一旦出错不会给出正确的错误位置
所以建议每完成一个函数,就写一个测试这个函数的函数。
最后更新日期:2014-5-10
应用范围:定制自己的内存数据库
参考资料:http://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_55_0/libs/multi_index/doc/index.html
*/
#pragma region 定义 employee
//使用名字空间是为了防止数据类型名称冲突
namespace kagula
{
namespace datatype
{
//为了后面的代码能通过id和name名字取视图,定义了这两个结构
struct id{};
struct name{};
//employee是我们示例代码中表的结构
struct employee
{
int id;
std::wstring name;
employee(int id, const std::wstring& name) :id(id), name(name){}
//重载<运算符函数让后面名为id的视图按照id字段的升序排列
bool operator<(const employee& e)const{ return id<e.id; }
//重载<=运算符函数是为了得到指定id字段值范围的记录
bool operator<=(const employee& e)const{ return id<=e.id; }
//重载<<运算符函数是为了我们方便打印记录的内容
friend std::wostream& operator<<(std::wostream& os, const employee& dt);
};
std::wostream& operator<<(std::wostream& os, const employee& dt)
{
os << L"[" << dt.id << L',' << dt.name.c_str() << L"]";
return os;
}
//后面的代码,更新指定记录name字段的值要用到change_name类
//通过这个示例你可以知道如何修改符合搜索条件的,指定记录的任意字段值
struct change_name
{
change_name(const std::wstring& new_name) :new_name(new_name){}
void operator()(employee& e)
{
e.name = new_name;
}
private:
std::wstring new_name;
};
// 定义基于id和name关键词的多值索引集合类型
// 这个容器有id和name两个视图
typedef boost::multi_index::multi_index_container<
employee,
boost::multi_index::indexed_by<
//第一个视图,使用employee实例作为key,所以采用了employee::operator<运算符函数排序,因此基于id字段
//boost::multi_index::ordered_unique中的unique指定key只能唯一,这样就无法插入id字段值相同的记录了
//boost::multi_index::ordered_unique中的ordered指定第一个视图,按照key的升序排列,哪怕你插入的数据顺序是乱的
//在这里你可以定义多个boost::multi_index::ordered_unique类型的视图
//boost::multi_index::identity把对象作为索引的key
//boost::multi_index::tag<id>是为了以后能通过id名取第一个视图
//你可以去掉boost::multi_index::tag<id>,如果你不需要根据名字id来取视图的话
boost::multi_index::ordered_unique<boost::multi_index::tag<id>, boost::multi_index::identity<employee> >,
//第二个视图,它的key是employee对象的name字段,所以它的key类型是std::wstring
//所以使用了std::wstring::operator<运算符函数排序
//boost::multi_index::ordered_non_unique中的non_unique指定这个key允许有重复.
//boost::multi_index::ordered_non_unique中的ordered指定第二视图,以这个key升序排列 .
//如果你不需要视图按照key的顺序排列,可以用hashed代替ordered,例如
//boost::multi_index::ordered_non_unique 被代替为 boost::multi_index::hashed_non_unique
//就可以避免对插入的数据排序,需要包含<boost/multi_index/hashed_index.hpp>头文件
//boost::multi_index::member把对象的成员作为索引的key
//boost::multi_index::tag<name>是为了以后的代码能通过name名取第二个视图,当视图很多的时候,这个功能将会非常有用
boost::multi_index::ordered_non_unique<boost::multi_index::tag<name>, boost::multi_index::member<employee, std::wstring, &employee::name> >
//这里视图的定义采用了下面的语法形式
//(ordered_unique | ordered_non_unique) <[(key extractor)[, (comparison predicate)]]>
//作为key的对象类型必须实现<运算符函数,除非你指定了comparison predicate.
>
> employee_set;
}
}
#pragma endregion
using namespace kagula::datatype;
void print_out_by_id(const employee_set& es)
{
//得到id视图(它是基于id字段的)
const employee_set::index<id>::type& id_index = es.get<id>();
//下面注释掉的代码,是基于序号索引视图,0代表第一个视图,1代表第二个视图,依次类推
//const employee_set::nth_index<0>::type& id_index = es.get<0>();
//采用同std::set容器一样的方式打印元素
std::copy(
id_index.begin(), id_index.end(),
std::ostream_iterator<employee, wchar_t>(std::wcout));
std::wcout << std::endl << std::endl;
}
void print_out_by_name(const employee_set& es)
{
//得到name视图(它是基于name字段的)
const employee_set::index<name>::type& name_index = es.get<name>();
//下面注释掉的代码,是基于序号索引视图,代表第二个视图,依次类推
//const employee_set::nth_index<1>::type& name_index = es.get<1>();
//采用同std::set容器一样的方式打印元素
std::copy(
name_index.begin(), name_index.end(),
std::ostream_iterator<employee,wchar_t>(std::wcout));
std::wcout << std::endl << std::endl;
}
//建立测试数据
void CreateSample(employee_set& table)
{
table.insert(employee(0, L"Z"));
table.insert(employee(1, L"Z"));
table.insert(employee(2, L"X"));
//Error:下面这条记录无法成功插入,因为在建立第一张视图时指定了id必须唯一
// 所以执行插入编号为2的记录会没有效果, 即table中id为2的记录它还是原来的值
// 但是代码也不会抛出Excetion。
//table.insert(employee(2, L"新插入的id为2的记录"));
//插入name字段的值为"Z"成功
//虽然name字段的值已经存在,但建立第二视图的时候指定了name字段的值可以有重复
//所以下面的添加记录功能可以正常运行
table.insert(employee(3, L"Z"));
table.insert(employee(100, L"Judy Smith"));
table.insert(employee(101, L"Judy Smith"));
table.insert(employee(200, L"Anna Jones"));
table.insert(employee(201, L"Anna Jones"));
}
void select_stat(employee_set& table)
{
std::wcout << L"第一个视图按照id字段的升序排列" << std::endl;
print_out_by_id(table);
{
std::wcout << L"第一个视图按照id字段的降序打印" << std::endl;
const employee_set::index<id>::type& viewId = table.get<id>();
std::copy(viewId.rbegin(), viewId.rend(),
std::ostream_iterator<employee, wchar_t>(std::wcout));
std::wcout << std::endl << std::endl;
}
std::wcout << L"第二个视图按照name字段的升序排列" << std::endl;
print_out_by_name(table);
{
std::wcout << L"检索出id==2的记录" << std::endl;
employee cond(2, L"");
employee_set::index<id>::type::iterator iter = table.find(cond);
std::wcout << *iter << std::endl << std::endl;
}
{
std::wcout << L"通过boost::lambda检索出指定id范围的记录集合" << std::endl;;
std::pair<employee_set::iterator, employee_set::iterator> p;
p = table.range(employee(100, L"") <= boost::lambda::_1, boost::lambda::_1 <= employee(200, L"")); // 100<= x <=200
//下面被注释掉的代码,演示了如何取指定范围的记录
//p = table.range(employee(100, L"")<boost::lambda::_1, boost::lambda::_1<employee(200, L"")); // 100< x < 200
//p = table.range(employee(100, L"") <= boost::lambda::_1, boost::lambda::_1<employee(200, L"")); // 100<= x < 200
//p = table.range(employee(100, L"") <= boost::lambda::_1, boost::multi_index::unbounded); // 100 <= x
//p = table.range(boost::multi_index::unbounded, boost::lambda::_1<employee(200, L"")); // x < 200
//p = table.range(boost::multi_index::unbounded, boost::multi_index::unbounded); // equiv. to std::make_pair(s.begin(),s.end())
for (employee_set::iterator it = p.first; it != p.second; it++)
{
std::wcout << *it << L" , ";
}
std::wcout << std::endl << std::endl;
}
{
std::wcout << L"检索出name==Judy Smith的第一条记录" << std::endl;
const employee_set::index<name>::type& viewName = table.get<name>();
employee_set::index<name>::type::iterator it = viewName.find(L"Judy Smith");
std::wcout << *it << std::endl << std::endl;
std::wcout << L"统计name==Judy Smith的记录有多少" << std::endl;
unsigned int count = viewName.count(L"Judy Smith");
std::wcout << count << std::endl << std::endl;
}
{
std::wcout << L"检索出name==z的记录集合" << std::endl;;
const employee_set::index<name>::type& viewName = table.get<name>();
std::pair<employee_set::index<name>::type::iterator, employee_set::index<name>::type::iterator> p;
p = viewName.equal_range(L"Z");
for (employee_set::index<name>::type::iterator it = p.first; it != p.second; it++)
{
std::wcout << *it << L" , ";
}
std::wcout << std::endl << std::endl;
}
}
void delete_stat(employee_set& table)
{
//从表中删除id值为2的的记录,name字段可以为任意值
{
std::wcout << L"删除id==2的记录" << std::endl;
employee cond(2, L"");
int nCount = table.erase(cond);
//nCount为1,因为我们的id值是唯一的。
//如果id字段不是唯一的,我们可以通过判断nCount,删除所有符合条件的记录
std::wcout << L"有" << nCount << L"条记录被删除。" << std::endl << std::endl;
}
//从表中删除name字段值为Z的全部记录
{
std::wcout << L"删除name==Z的所有记录" << std::endl;
employee_set::index<name>::type& viewName = table.get<name>();
while ( table.erase(*viewName.find(L"Z")) > 0 );
print_out_by_id(table);
}
//重新建立样本
table.clear();
CreateSample(table);
//删除id在指定范围的记录
std::wcout << L"删除100<= id <=200的所有记录" << std::endl;
std::pair<employee_set::iterator, employee_set::iterator> p;
p = table.range(employee(100, L"") <= boost::lambda::_1, boost::lambda::_1 <= employee(200, L"")); // 100<= x <=200
table.erase(p.first, p.second);
print_out_by_id(table);
}
void update_stat(employee_set& table)
{
std::wcout << L"替换名为Anna Jones的记录为Anna Smith,但是只修改符合条件的第一条记录!" << std::endl;
typedef employee_set::index<name>::type employee_set_by_name;
//因为要修改iter所指向的数据所以下面的语句不能使用const修饰
employee_set_by_name& name_index = table.get<name>();
employee_set_by_name::iterator it = name_index.find(L"Anna Jones");
//修改key的值,key必须可以读写
name_index.modify_key(it, boost::lambda::_1 = L"Anna Smith");
print_out_by_id(table);
std::wcout << L"把名为Anna Smith的第一条记录修改为Anna Jones" << std::endl;
//下面这种方法可以修改对象某个属性的值,但是需要定义change_name类
it = name_index.find(L"Anna Smith");
name_index.modify(it, change_name(L"Anna Jones"));
print_out_by_id(table);
{
std::wcout << L"修改所有name==Z的记录为kagula" << std::endl;
employee_set_by_name& viewName = table.get<name>();
employee_set_by_name::iterator it;
while ( (it = viewName.find(L"Z")) != viewName.end() )
{
viewName.modify(it, change_name(L"kagula"));
}
print_out_by_id(table);
//Warnning:
//不要在生产环境中,使用下面的代码来修改所有符合条件的记录
//因为如果没有上边的代码段,下面的代码只会修改第一条符合条件的记录
//后,提早退出循环。
std::wcout << L"修改所有name==kagula的记录为Z" << std::endl;
viewName = table.get<name>();
std::pair<employee_set_by_name::iterator, employee_set_by_name::iterator> p;
p = viewName.equal_range(L"kagula");
for (employee_set_by_name::iterator it = p.first; it != p.second; it++)
{
viewName.modify(it, change_name(L"Z"));
}
print_out_by_id(table);
}
//因为修改记录的值是通过it对象,所以可以使用select_stat介绍的知识修改指定范围的记录
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//使std::wcout能够打印中文
std::wcout.imbue(std::locale(std::locale("chs")));
//建立样本
//等价SQL,Add语句的相关功能
employee_set table;
CreateSample(table);
//这里测试等价SQL,Select语句的相关功能
select_stat(table);
//这里测试等价SQL,Update语句的相关功能
update_stat(table);
//这里测试等价SQL,Delete语句的相关功能
delete_stat(table);
//暂停,输入任意键继续
system("pause");
return 0;
}
