ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--InflationLayer

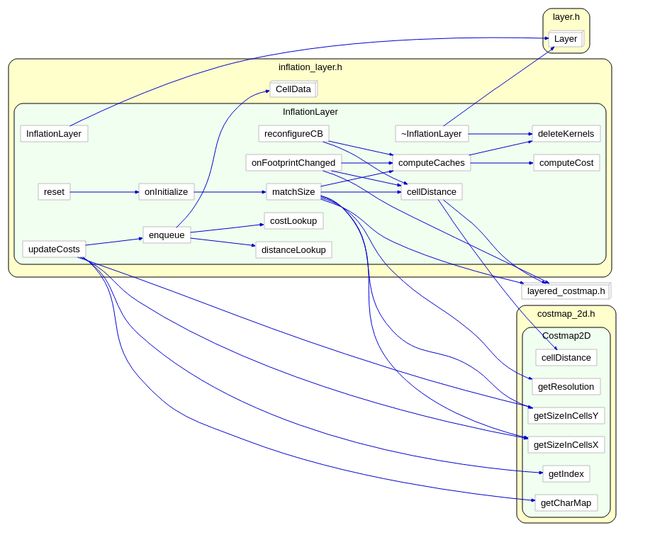
这是costmap_2d的最后一个重要的类了。InflationLayer 本身不存储map数据,所以所谓的地图层的概念,仅仅指的是一种对地图的操作,并不是数据层面的地图。
首先来看一个数据结构,知道有这个东西就行了:
class CellData
{
public:
CellData(double d, double i, unsigned int x, unsigned int y, unsigned int sx, unsigned int sy) :
distance_(d), index_(i), x_(x), y_(y), src_x_(sx), src_y_(sy)
{
}
double distance_;//
unsigned int index_;//this cell在map的一维索引
unsigned int x_, y_;//this cell在map的x,y二维索引
unsigned int src_x_, src_y_;//this cell距离最近的障碍物点,这个障碍物cell的x,y二维索引
};
//对应的class CellData的比较操作,用于priority queue操作
inline bool operator<(const CellData &a, const CellData &b)
{
return a.distance_ > b.distance_;
}函数onInitialize 配置了动态参数服务的回调函数,然后在最后一行调用了matchSize:
void InflationLayer::matchSize()
{
boost::unique_lock < boost::recursive_mutex > lock(*inflation_access_);
costmap_2d::Costmap2D* costmap = layered_costmap_->getCostmap();
resolution_ = costmap->getResolution();
cell_inflation_radius_ = cellDistance(inflation_radius_);
computeCaches();//这个函数通过cell_inflation_radius_计算了两个buffer,这两个二维buffer直接存储了[i,j]的distance 和cost
unsigned int size_x = costmap->getSizeInCellsX(), size_y = costmap->getSizeInCellsY();
if (seen_)
delete[] seen_; seen_size_ = size_x * size_y; seen_ = new bool[seen_size_]; }函数void InflationLayer::updateBounds 内部基本什么都没做,因此
( double* min_x, double* min_y, double* max_x, double* max_y) 会维持上一层地图调用updateBounds的值。
函数void InflationLayer::onFootprintChanged() 也会去调用computeCaches(); 更新两个两个维度为[cell_inflation_radius_+2][cell_inflation_radius_+2] 的二维buffer:cached_costs_,cached_distances_ 。
接下来的函数,需要重点注意,因为这是关乎inflation 具体是如何操作完成的膨胀的工作:
void InflationLayer::updateCosts(costmap_2d::Costmap2D& master_grid, int min_i, int min_j, int max_i,
int max_j)
{
boost::unique_lock < boost::recursive_mutex > lock(*inflation_access_);
if (!enabled_)
return;
// make sure the inflation queue is empty at the beginning of the cycle (should always be true)
ROS_ASSERT_MSG(inflation_queue_.empty(), "The inflation queue must be empty at the beginning of inflation");
unsigned char* master_array = master_grid.getCharMap();
unsigned int size_x = master_grid.getSizeInCellsX(), size_y = master_grid.getSizeInCellsY();
if (seen_ == NULL) {
ROS_WARN("InflationLayer::updateCosts(): seen_ array is NULL");
seen_size_ = size_x * size_y;
//这里分配了一个size 和master map 尺寸一样的bool 数组
seen_ = new bool[seen_size_];
}
else if (seen_size_ != size_x * size_y)
{
ROS_WARN("InflationLayer::updateCosts(): seen_ array size is wrong");
delete[] seen_;
seen_size_ = size_x * size_y;
seen_ = new bool[seen_size_];
}
memset(seen_, false, size_x * size_y * sizeof(bool));
// We need to include in the inflation cells outside the bounding
// box min_i...max_j, by the amount cell_inflation_radius_. Cells
// up to that distance outside the box can still influence the costs
// stored in cells inside the box.
//由于(min_i,min_j,max_i,max_j)是由上一层的地图已经在updateBounds中更新过,而InflationLayer层并未去改变它。因此这里的操作是将传入的boudns,按照机器人的膨胀尺寸,扩张这个bounds
min_i -= cell_inflation_radius_;
min_j -= cell_inflation_radius_;
max_i += cell_inflation_radius_;
max_j += cell_inflation_radius_;
min_i = std::max(0, min_i);
min_j = std::max(0, min_j);
max_i = std::min(int(size_x), max_i);
max_j = std::min(int(size_y), max_j);
//下面的两重循环完成将master map中的LETHAL_OBSTACLE cell的下标index,i,j传给函数inline void InflationLayer::enqueue(unsigned char* grid, unsigned int index, unsigned int mx, unsigned int my,unsigned int src_x, unsigned int src_y),注意这个函数的参数,因此这里传给enqueue的信息为:将master map中,目标cell索引为(index,mx,my),最近的障碍物索引为(src_x,src_y)的。
for (int j = min_j; j < max_j; j++)
{
for (int i = min_i; i < max_i; i++)
{
int index = master_grid.getIndex(i, j);
unsigned char cost = master_array[index];
if (cost == LETHAL_OBSTACLE)
{
//enqueue函数首先检查当前cell(i, j)到障碍物cell(i, j)的distance,通过查表即可distanceLookup(mx, my, src_x, src_y);如果距离小于cell_inflation_radius_,则检查cost,通过查表即可costLookup(mx, my, src_x, src_y),然后用cost更新master map 中当前cell的值。最后将当前的cell 打包成CellData类型,并塞到inflation_queue_
enqueue(master_array, index, i, j, i, j);
}
}
}
//通过上面的操作,现在inflation_queue_里面全部都是obstacle cell,这些cell被打包成CellData类型,包含了这些cell本身的索引,最近障碍物的索引(即它们本身),距离(0)
while (!inflation_queue_.empty())
{
// get the highest priority cell and pop it off the priority queue
const CellData& current_cell = inflation_queue_.top();
unsigned int index = current_cell.index_;
unsigned int mx = current_cell.x_;
unsigned int my = current_cell.y_;
unsigned int sx = current_cell.src_x_;
unsigned int sy = current_cell.src_y_;
// pop once we have our cell info
inflation_queue_.pop();
//上面首先从priority queue中弹出最大distance的cell,再将这个cell的前后左右四个cell都塞进inflation_queue_。由于下面关于enqueue的调用,最后两个参数(sx, sy)没有改变,所以保证了这个索引一定是obstacle cell。由于在 enqueue入口会检查 if (!seen_[index]),这保证了这些cell不会被重复的塞进去。由于这是一个priority queue,因此障碍物的周边点,每次都是离障碍物最远的点被弹出,并被检查,这样保证了这种扩张是朝着离障碍物远的方向进行。
// attempt to put the neighbors of the current cell onto the queue
if (mx > 0)
enqueue(master_array, index - 1, mx - 1, my, sx, sy);
if (my > 0)
enqueue(master_array, index - size_x, mx, my - 1, sx, sy);
if (mx < size_x - 1)
enqueue(master_array, index + 1, mx + 1, my, sx, sy);
if (my < size_y - 1)
enqueue(master_array, index + size_x, mx, my + 1, sx, sy);
}
}inline void InflationLayer::enqueue(unsigned char* grid, unsigned int index, unsigned int mx, unsigned int my,
unsigned int src_x, unsigned int src_y)
{
// set the cost of the cell being inserted
if (!seen_[index])//避免cell被重复的塞进来
{
// we compute our distance table one cell further than the inflation radius dictates so we can make the check below
double distance = distanceLookup(mx, my, src_x, src_y);
// we only want to put the cell in the queue if it is within the inflation radius of the obstacle point
if (distance > cell_inflation_radius_)//保证了只处理在cell_inflation_radius_范围内的cell
return;
// assign the cost associated with the distance from an obstacle to the cell
unsigned char cost = costLookup(mx, my, src_x, src_y);
unsigned char old_cost = grid[index];
if (old_cost == NO_INFORMATION && cost >= INSCRIBED_INFLATED_OBSTACLE)
grid[index] = cost;
else
grid[index] = std::max(old_cost, cost);
// push the cell data onto the queue and mark
seen_[index] = true;
CellData data(distance, index, mx, my, src_x, src_y);
inflation_queue_.push(data);
}
}理解了上述过程,也就明白了,究竟是怎么实现的膨胀操作。
另外distance 计算costmap,是一个指数衰减关系:
inline unsigned char computeCost(double distance) const
{
unsigned char cost = 0;
if (distance == 0)
cost = LETHAL_OBSTACLE;
else if (distance * resolution_ <= inscribed_radius_)
cost = INSCRIBED_INFLATED_OBSTACLE;
else
{
// make sure cost falls off by Euclidean distance
double euclidean_distance = distance * resolution_;
double factor = exp(-1.0 * weight_ * (euclidean_distance - inscribed_radius_));
cost = (unsigned char)((INSCRIBED_INFLATED_OBSTACLE - 1) * factor);
}
return cost;
}